Abstract
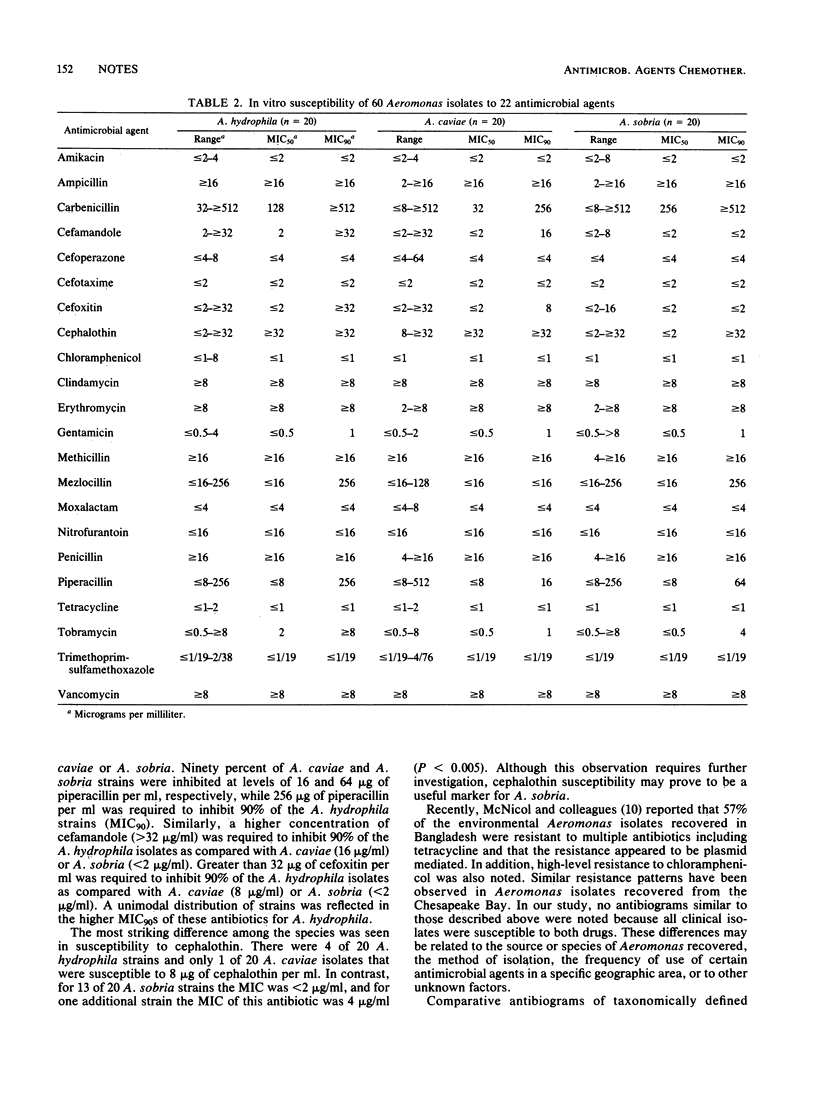
MICs of 22 antimicrobial agents for 60 strains of three Aeromonas species were determined by a microdilution method. The newer cephalosporins such as moxalactam, cefotaxime, and cefoperazone, the aminoglycosides, and chloramphenicol, tetracycline, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole inhibited most of the strains studied. Within the genus, A. hydrophila was more resistant than either A. caviae or A. sobria to the antibiotics tested.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke V., Robinson J., Beaman J., Gracey M., Lesmana M., Rockhill R., Echeverria P., Janda J. M. Correlation of enterotoxicity with biotype in Aeromonas spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1196–1200. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1196-1200.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champsaur H., Adremont A., Mathieu D., Rottman E., Auzepy P. Cholera-like illness due to Aeromonas sobria. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):248–254. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daily O. P., Joseph S. W., Coolbaugh J. C., Walker R. I., Merrell B. R., Rollins D. M., Seidler R. J., Colwell R. R., Lissner C. R. Association of Aeromonas sobria with human infection. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):769–777. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.769-777.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. A., 2nd, Kane J. G., Garagusi V. F. Human aeromonas infections: a review of the literature and a case report of endocarditis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 May;57(3):267–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainstein V., Weaver S., Bodey G. P. In vitro susceptibilities of Aeromonas hydrophila against new antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Sep;22(3):513–514. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fass R. J., Barnishan J. In vitro susceptibilities of Aeromonas hydrophila to 32 antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):357–358. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Bottone E. J., Reitano M. Aeromonas species in clinical microbiology: significance, epidemiology, and speciation. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;1(3):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(83)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Reitano M., Bottone E. J. Biotyping of Aeromonas isolates as a correlate to delineating a species-associated disease spectrum. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jan;19(1):44–47. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.1.44-47.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNicol L. A., Aziz K. M., Huq I., Kaper J. B., Lockman H. A., Remmers E. F., Spira W. M., Voll M. J., Colwell R. R. Isolation of drug-resistant Aeromonas hydrophila from aquatic environments. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Mar;17(3):477–483. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.3.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overman T. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Aeromonas hydrophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Apr;17(4):612–614. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.4.612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popoff M., Véron M. A taxonomic study of the Aeromonas hydrophila-Aeromonas punctata group. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):11–22. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Lee J. V., Miliotis M. D., Van de Walle S., Koornhof H. J., Jeffery L., Bryant T. N. Enterotoxin production in relation to taxonomic grouping and source of isolation of Aeromonas species. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.175-180.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



