Abstract
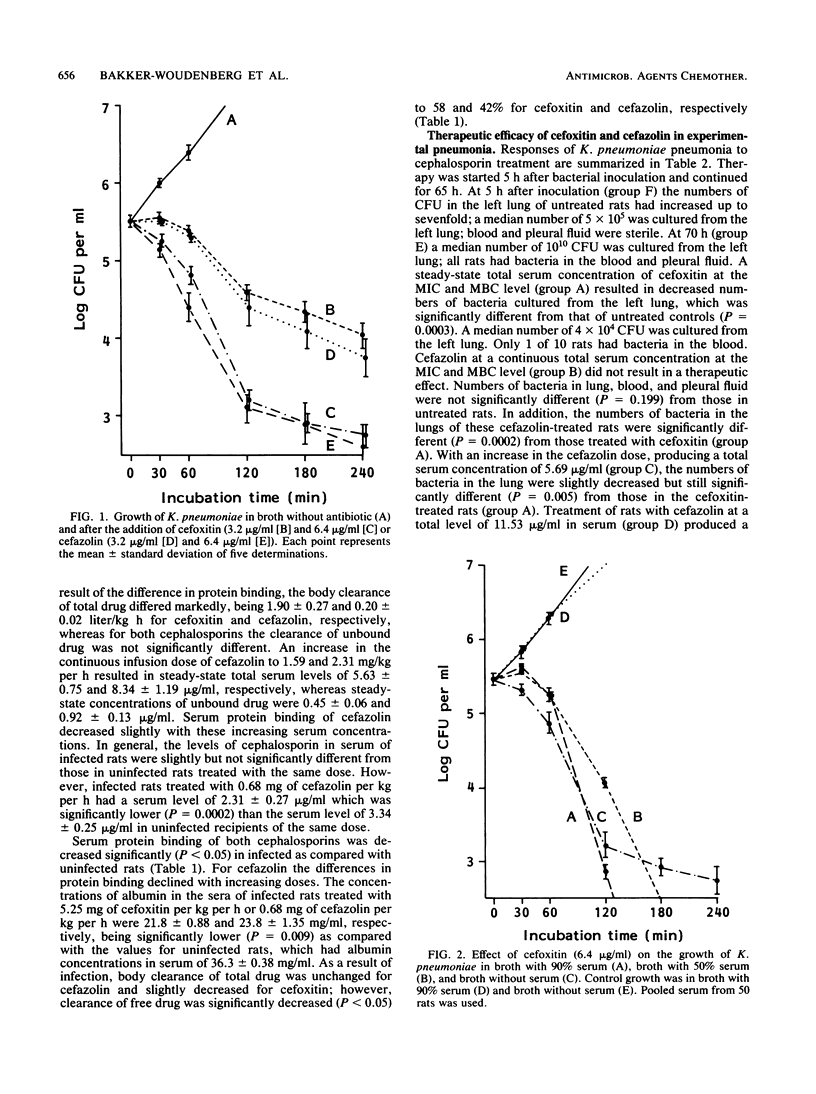
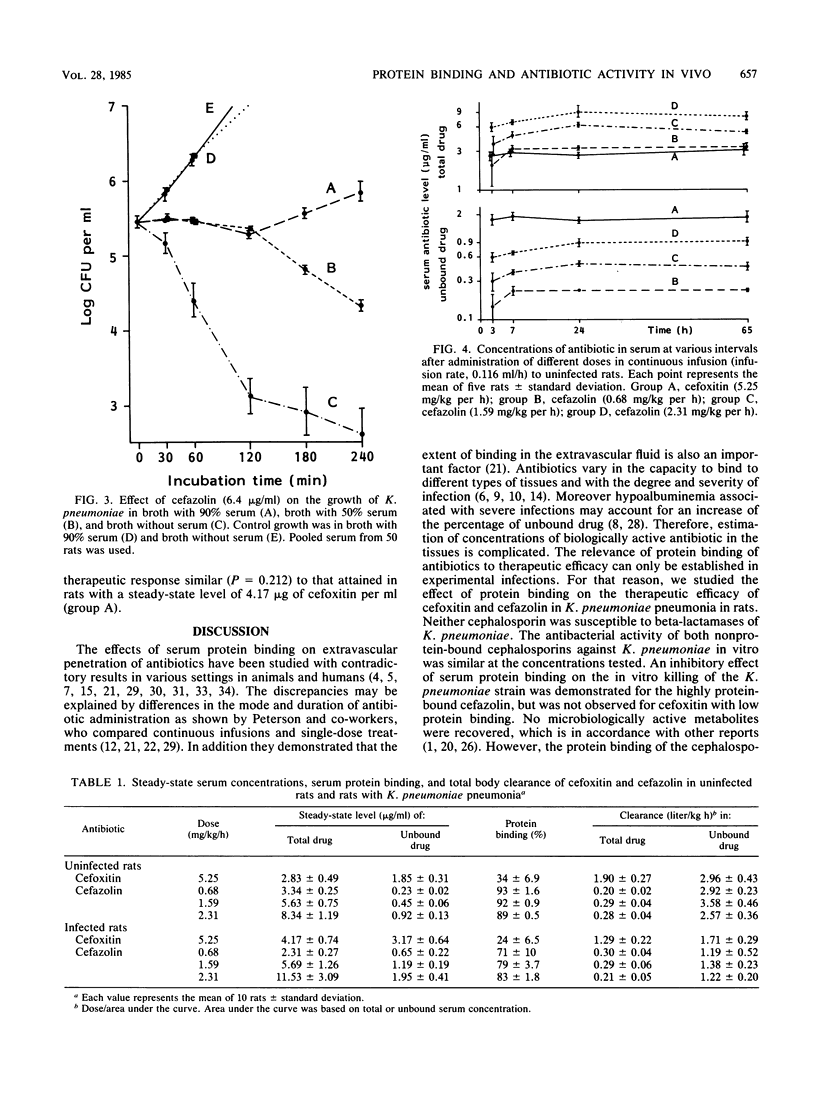
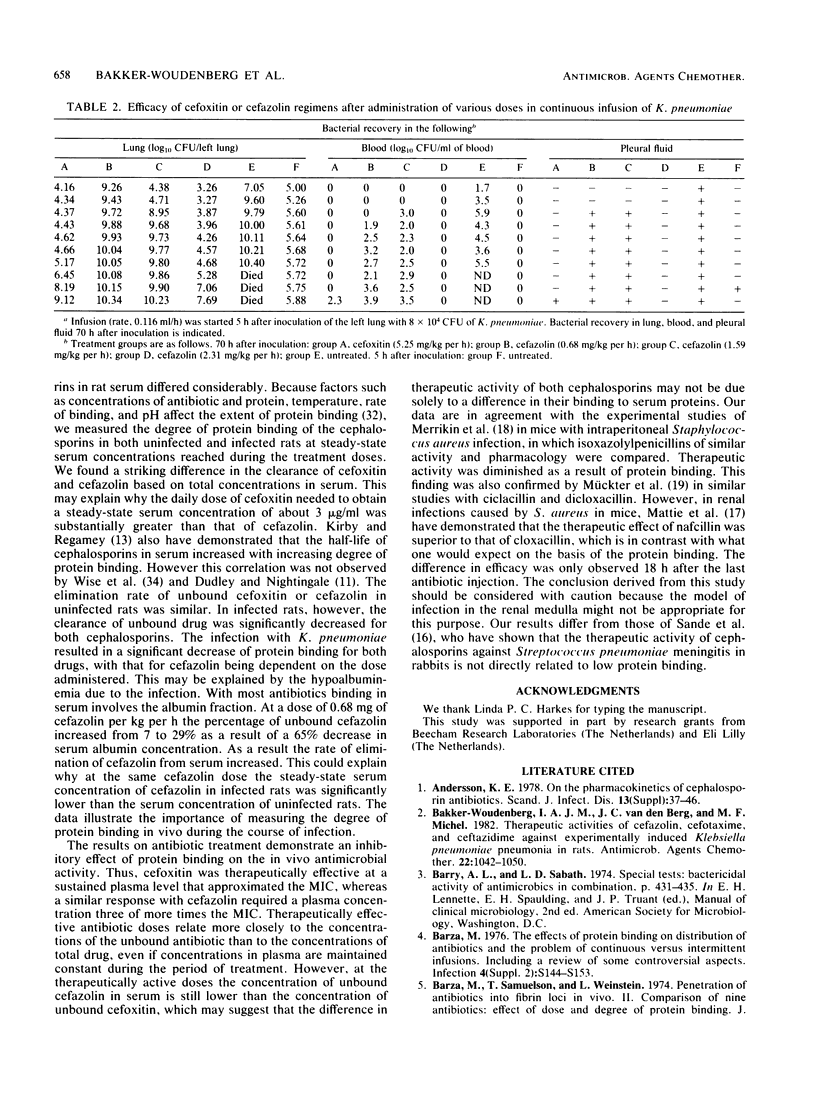
An experimental Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in rats was used to study the effect of protein binding of cefoxitin and cefazolin on their therapeutic activity. Both cephalosporins were similar with respect to their antimicrobial activity against the K. pneumoniae in vitro, but they differed in their degree of protein binding, being 34% for cefoxitin and 89 to 93% for cefazolin in uninfected rats and 24 and 71 to 83%, respectively, in infected rats. Various doses of these agents were administered by continuous infusion, which started 5 h after bacterial inoculation and continued for 65 h. Antimicrobial response was evaluated with respect to the numbers of bacteria recovered from lung and blood at the end of treatment. An inhibitory effect of protein binding on the in vivo antimicrobial activity was demonstrated. Cefoxitin was therapeutically effective at a constant plasma level that reached the MIC. To obtain a similar effect with cefazolin the plasma level of that drug had to be increased to a concentration more than three times the MIC.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson K. E. On the pharmacokinetics of cephalosporin antibiotics. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(13):37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker-Woudenberg I. A., van den Berg J. C., Michel M. F. Therapeutic activities of cefazolin, cefotaxime, and ceftazidime against experimentally induced Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia in rats. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1042–1050. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barza M., Samuelson T., Weinstein L. Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. II. Comparison of nine antibiotics: effect of dose and degree of protein binding. J Infect Dis. 1974 Jan;129(1):66–72. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant R. E., Hammond D. Interaction of purulent material with antibiotics used to treat Pseudomonas infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Dec;6(6):702–707. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.6.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon C., Contrepois A., Brion N., Lamotte-Barrillon S. Penetration of cefazolin, cephaloridine, and cefamandole into interstitial fluid in rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Apr;11(4):594–598. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.4.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. A., Suh B. Theory and practical impact of binding of antimicrobials to serum proteins and tissue. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1978;(14):92–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerding D. N., Van Etta L. L., Peterson L. R. Role of serum protein binding and multiple antibiotic doses in the extravascular distribution of ceftizoxime and cefotaxime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):844–847. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby W. M., Regamey C. Pharmacokinetics of cefazolin compared with four other cephalosporins. J Infect Dis. 1973 Oct;128(Suppl):S341–S346. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.supplement_2.s341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunin C. M. Binding of antibiotics to tissue homogenates. J Infect Dis. 1970 Jan;121(1):55–64. doi: 10.1093/infdis/121.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau Z., Rubinstein E., Halkin H. Interstitial fluid concentrations of cefoxitin, cephazolin and cefamandole. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 Sep;6(5):657–663. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattie H., Goslings W. R., Noach E. L. Cloxacillin and nafcillin: serum binding and its relationship to antibacterial effect in mice. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):170–177. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrikin D. J., Briant J., Rolinson G. N. Effect of protein binding on antibiotic activity in vivo. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Mar;11(3):233–238. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.3.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mückter H., Sous H., Poszich G., Arend P. Comparative studies of the activity of ciclacillin and dicloxacillin. Chemotherapy. 1976;22(3-4):183–189. doi: 10.1159/000221925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale C. H., Greene D. S., Quintiliani R. Pharmacokinetics and clinical use of cephalosporin antibiotics. J Pharm Sci. 1975 Dec;64(12):1899–1926. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600641202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Influence of protein binding of antibiotics on serum pharmacokinetics and extravascular penetration: clinically useful concepts. Rev Infect Dis. 1980 May-Jun;2(3):340–348. doi: 10.1093/clinids/2.3.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Gerding D. N. Prediction of cefazolin penetration in high- and low-protein-containing extravascular fluid: new method for performing simultaneous studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Oct;14(4):533–538. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.4.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. R., Schierl E. A., Hall W. H. Effect of protein concentration and binding on antibiotic assays. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):540–542. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolinson G. N. The significance of protein binding of antibiotics in antibacterial chemotherapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1980 May;6(3):311–317. doi: 10.1093/jac/6.3.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Sherertz R. J., Zak O., Strausbaugh L. J. Cephalosporin antibiotics in therapy of experimental Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137 (Suppl):S161–S168. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.supplement.s161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrogie J. J., Rogers J. D., Yeh K. C., Davies R. O., Holmes G. I., Skeggs H., Martin C. M. Pharmacokinetics and comparative pharmacology of cefoxitin and cephalosporins. Rev Infect Dis. 1979 Jan-Feb;1(1):90–98. doi: 10.1093/clinids/1.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etta L. L., Kravitz G. R., Russ T. E., Fasching C. E., Gerding D. N., Peterson L. R. Effect of method of administration on extravascular penetration of four antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):873–880. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman N. G., Raff M. J., Scharfenberger L., Barnwell P. A. Protein binding and concentrations of cephaloridine and cefazolin in serum and interstitial fluid of dogs. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133(6):642–647. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.6.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Gillett A. P., Cadge B., Durham S. R., Baker S. The influence of protein binding upon tissue fluid levels of six beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. Protein binding of beta-lactams: the effects on activity and pharmacology particularly tissue penetration. I. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jul;12(1):1–18. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R. Protein binding of beta-lactams: the effects on activity and pharmacology particularly tissue penetration. II. Studies in man. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Aug;12(2):105–118. doi: 10.1093/jac/12.2.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



