Abstract
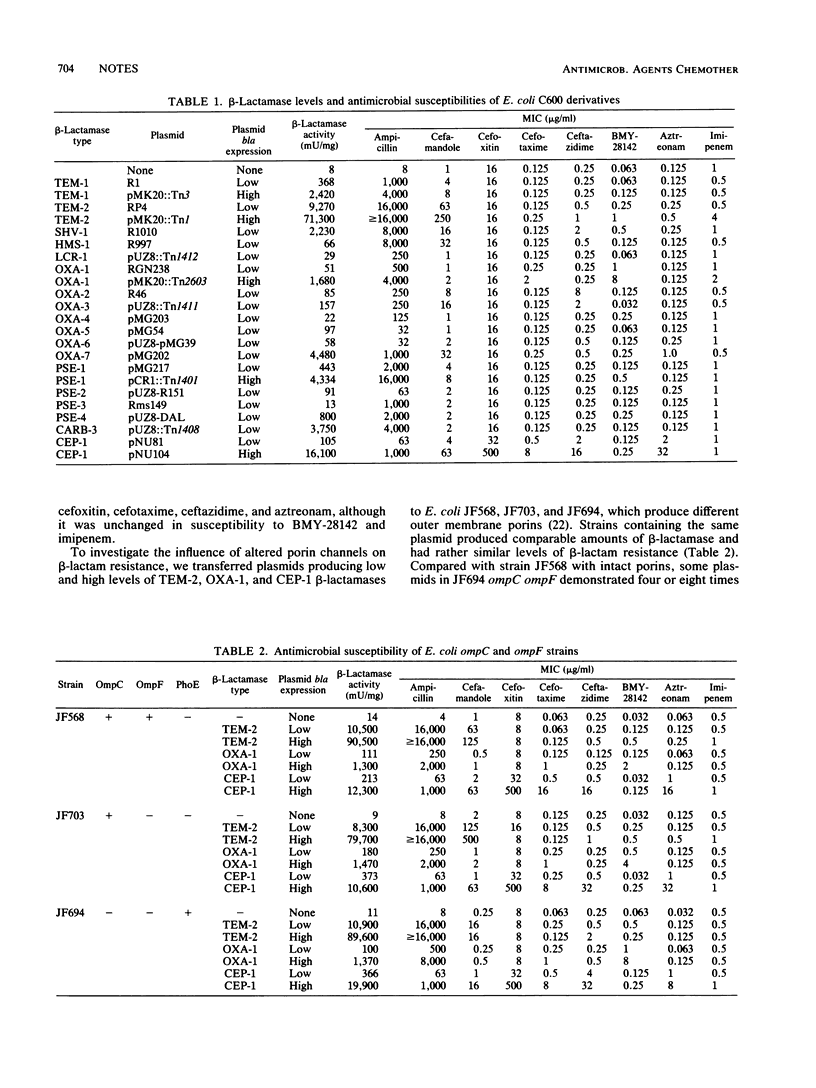
Escherichia coli strains determining 17 different plasmid-determined beta-lactamases were tested for resistance to new broad-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotics. Several beta-lactamases demonstrated enhanced resistance to cefamandole but only low-level resistance to other agents. High production of cloned E. coli chromosomal beta-lactamase, however, provided resistance to cefamandole, cefoxitin, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, and aztreonam but not to BMY-28142 or imipenem.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergström S., Olsson O., Normark S. Common evolutionary origin of chromosomal beta-lactamase genes in enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):528–534. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.528-534.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush K., Tanaka S. K., Bonner D. P., Sykes R. B. Resistance caused by decreased penetration of beta-lactam antibiotics into Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):555–560. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder K. J., Nikaido H., Matsuhashi M. Mutants of Escherichia coli that are resistant to certain beta-lactam compounds lack the ompF porin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacoby G. A. Compatibility and molecular properties of plasmid Rms 149 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Matthew M. Acquisition by Escherichia coli of plasmid-borne beta-lactamases normally confined to Pseudomonas spp. Plasmid. 1979 Apr;2(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Jacob A. E., Hedges R. W. Recombination between plasmids of incompatibility groups P-1 and P-2. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1278–1285. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1278-1285.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Sutton L. Activity of beta-lactam antibiotics against Pseudomonas aeruginosa carrying R plasmids determining different beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Aug;16(2):243–245. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffé A., Chabbert Y. A., Derlot E. Selection and characterization of beta-lactam-resistant Escherichia coli K-12 mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):622–625. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurin B., Grundström T., Normark S. Sequence elements determining ampC promoter strength in E. coli. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):875–881. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn M., Kolter R., Thomas C., Figurski D., Meyer R., Remaut E., Helinski D. R. Plasmid cloning vehicles derived from plasmids ColE1, F, R6K, and RK2. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:268–280. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsu K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Transposition of the carbenicillin-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase gene. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):483–489. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.483-489.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Guionie M., Barthélémy M. Properties of three carbenicillin-hydrolysing beta-lactamases (CARB) from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: identification of a new enzyme. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque R., Roy P. H. Mapping of the plasmid (pLQ3) from Achromobacter and cloning of its cephalosporinase gene in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew M., Hedges R. W., Smith J. T. Types of beta-lactamase determined by plasmids in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jun;138(3):657–662. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.3.657-662.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A. Beta-lactamases. Br Med Bull. 1984 Jan;40(1):18–27. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., Cohenford M., Jacoby G. A. Five novel plasmid-determined beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):715–719. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros A. A., Hedges R. W., Jacoby G. A. Spread of a "Pseudomonas-specific" beta-lactamase to plasmids of enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):700–707. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.700-707.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y., Foulds J. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with beta-lactams in intact cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):232–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.232-240.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance during therapy with the newer beta-lactam antibiotics: role of inducible beta-lactamases and implications for the future. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):639–648. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L., Angehrn P. Trapping of nonhydrolyzable cephalosporins by cephalosporinases in Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a possible resistance mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):711–717. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu H., Nikaido H. Role of beta-lactam hydrolysis in the mechanism of resistance of a beta-lactamase-constitutive Enterobacter cloacae strain to expanded-spectrum beta-lactams. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):393–398. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yamagata S., Horii K., Yamagishi S. Comparison of transcription of beta-lactamase genes specified by various ampicillin transposons. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):269–276. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.269-276.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



