Abstract
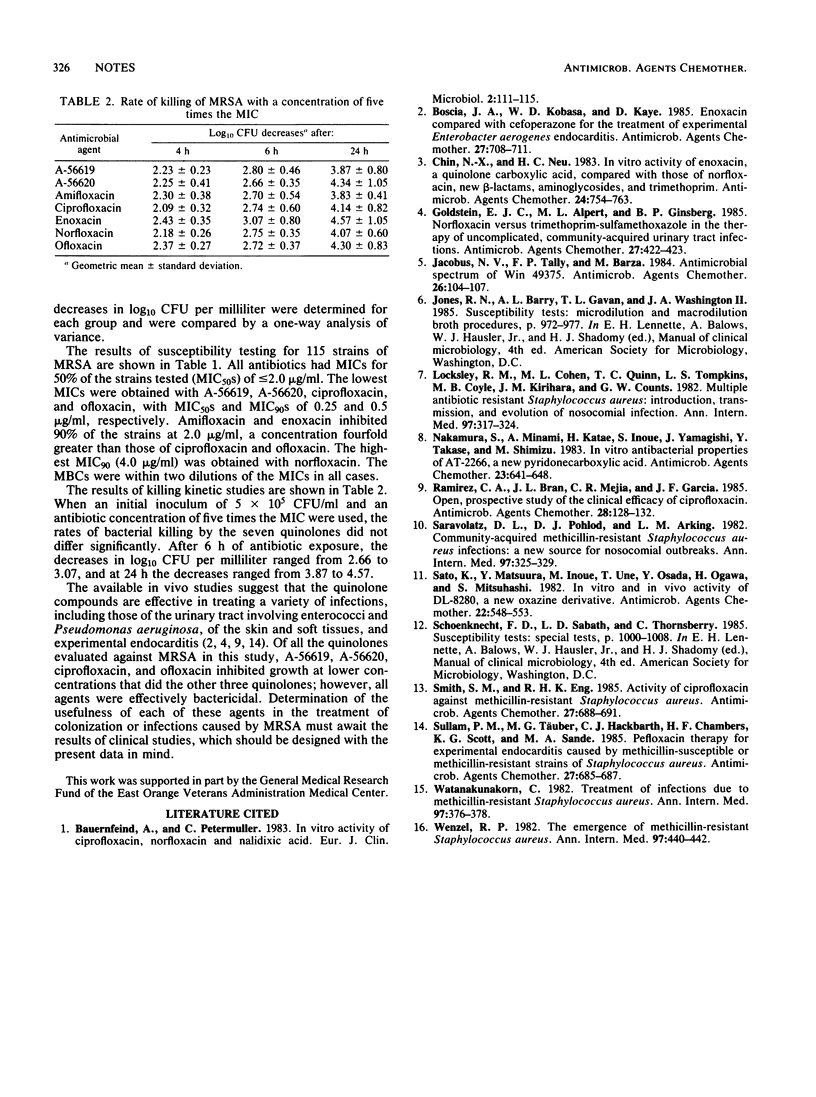
Seven quinolone antibiotics were tested against 115 isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. The MICs for 90% of the strains tested were 0.5 microgram/ml for A-56619, A-56620, ciprofloxacin, and ofloxacin; 2.0 micrograms/ml for amifloxacin and enoxacin; and 4.0 micrograms/ml for norfloxacin. Killing kinetic studies showed a similar killing rate for all seven antibiotics.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boscia J. A., Kobasa W. D., Kaye D. Enoxacin compared with cefoperazone for the treatment of experimental Enterobacter aerogenes endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):708–711. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of enoxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid, compared with those of norfloxacin, new beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, and trimethoprim. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):754–763. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein E. J., Alpert M. L., Ginsberg B. P. Norfloxacin versus trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the therapy of uncomplicated, community-acquired urinary tract infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Mar;27(3):422–423. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.3.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobus N. V., Tally F. P., Barza M. Antimicrobial spectrum of Win 49375. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):104–107. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locksley R. M., Cohen M. L., Quinn T. C., Tompkins L. S., Coyle M. B., Kirihara J. M., Counts G. W. Multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: introduction, transmission, and evolution of nosocomial infection. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):317–324. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura S., Minami A., Katae H., Inoue S., Yamagishi J., Takase Y., Shimizu M. In vitro antibacterial properties of AT-2266, a new pyridonecarboxylic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):641–648. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez C. A., Bran J. L., Mejia C. R., Garcia J. F. Open, prospective study of the clinical efficacy of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saravolatz L. D., Pohlod D. J., Arking L. M. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: a new source for nosocomial outbreaks. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):325–329. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Matsuura Y., Inoue M., Une T., Osada Y., Ogawa H., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of DL-8280, a new oxazine derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):548–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Eng R. H. Activity of ciprofloxacin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):688–691. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullam P. M., Täuber M. G., Hackbarth C. J., Chambers H. F., Scott K. G., Sande M. A. Pefloxacin therapy for experimental endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible or methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):685–687. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanakunakorn C. Treatment of infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):376–378. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel R. P. The emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):440–442. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


