Abstract
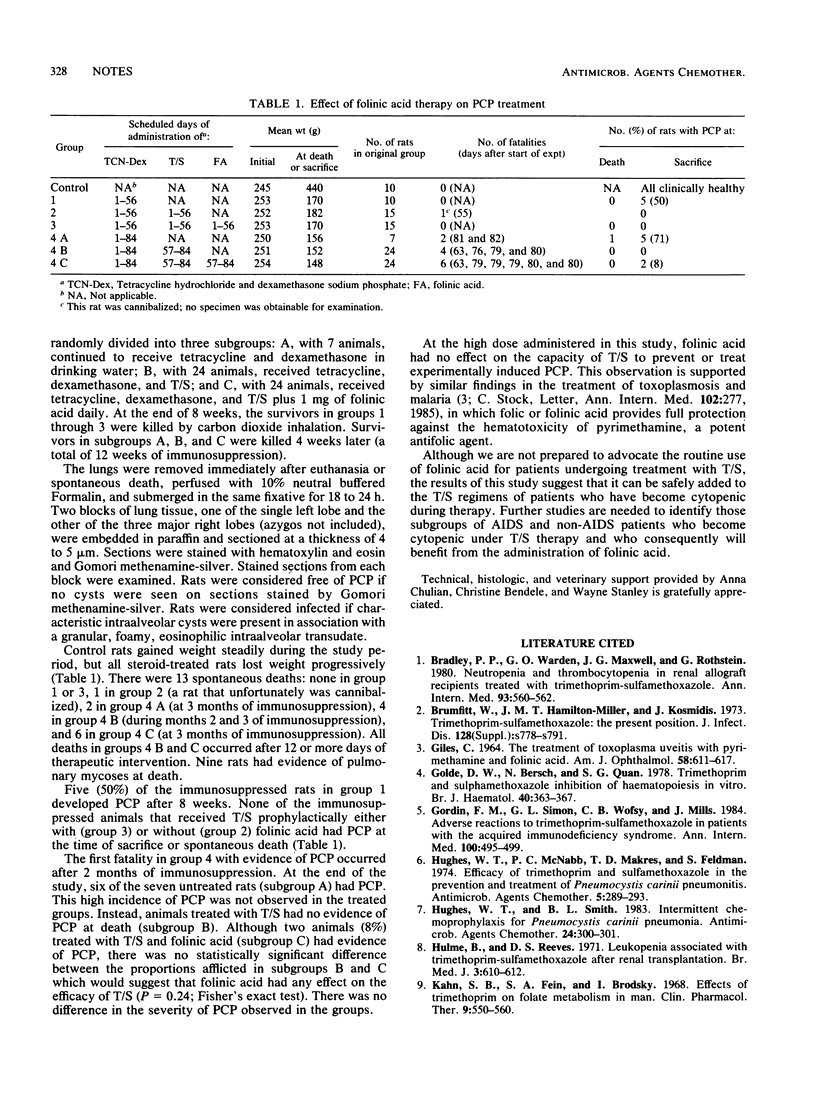
Daily administration of 1 mg of folinic acid to immunosuppressed rats with incipient or established Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia did not impair the capacity of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole to either prevent or treat this disease. These observations constitute the first experimental support for the use of folinic acid to prevent or control cytopenias that occur in patients with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia who are under trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole treatment.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley P. P., Warden G. D., Maxwell J. G., Rothstein G. Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia in renal allograft recipients treated with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Oct;93(4):560–562. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-4-560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES C. L. THE TREATMENT OF TOXOPLASMA UVEITIS. Am J Ophthalmol. 1964 Oct;58:611–616. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(64)91378-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde D. W., Bersch N., Quan S. G. Trimethoprim and sulphamethoxazole inhibition of haematopoiesis in vitro. Br J Haematol. 1978 Nov;40(3):363–367. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb05807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordin F. M., Simon G. L., Wofsy C. B., Mills J. Adverse reactions to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):495–499. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., McNabb P. C., Makres T. D., Feldman S. Efficacy of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole in the prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Mar;5(3):289–293. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.3.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. T., Smith B. L. Intermittent chemoprophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):300–301. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulme B., Reeves D. S. Leucopenia associated with trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole after renal transplantation. Br Med J. 1971 Sep 11;3(5775):610–612. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5775.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn S. B., Fein S. A., Brodsky I. Effects of trimethoprim on folate metabolism in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1968 Sep-Oct;9(5):550–560. doi: 10.1002/cpt196895550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobrinsky N. L., Ramsay N. K. Acute megaloblastic anemia induced by high-dose trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):780–781. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn P. P., Allistone J. C. Resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Implication of folinic acid. Chest. 1984 Jul;86(1):149–150. doi: 10.1378/chest.86.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. E., Campbell C. L., Rabinovitch P. S., Hillman R. S. The effect of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole on Friend erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):501–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Lau W. K., Gale R. P., Young L. S. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Jun;92(6):762–769. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-6-762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



