Abstract
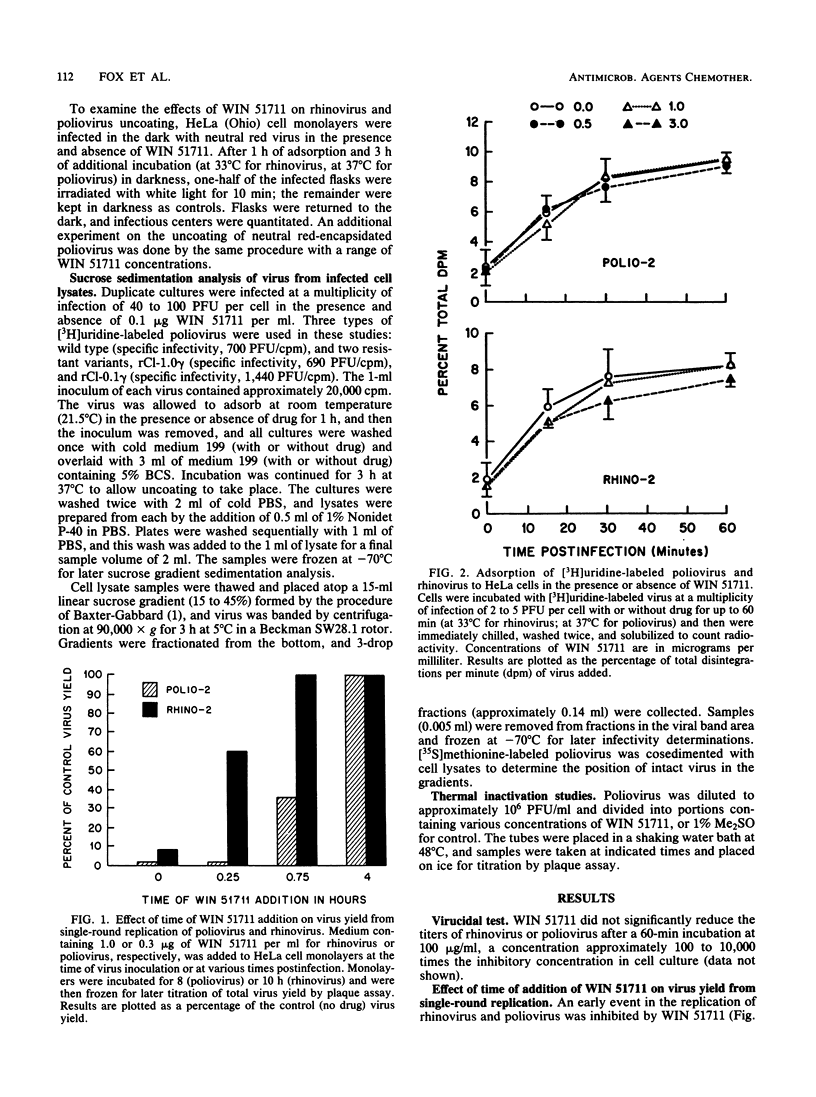
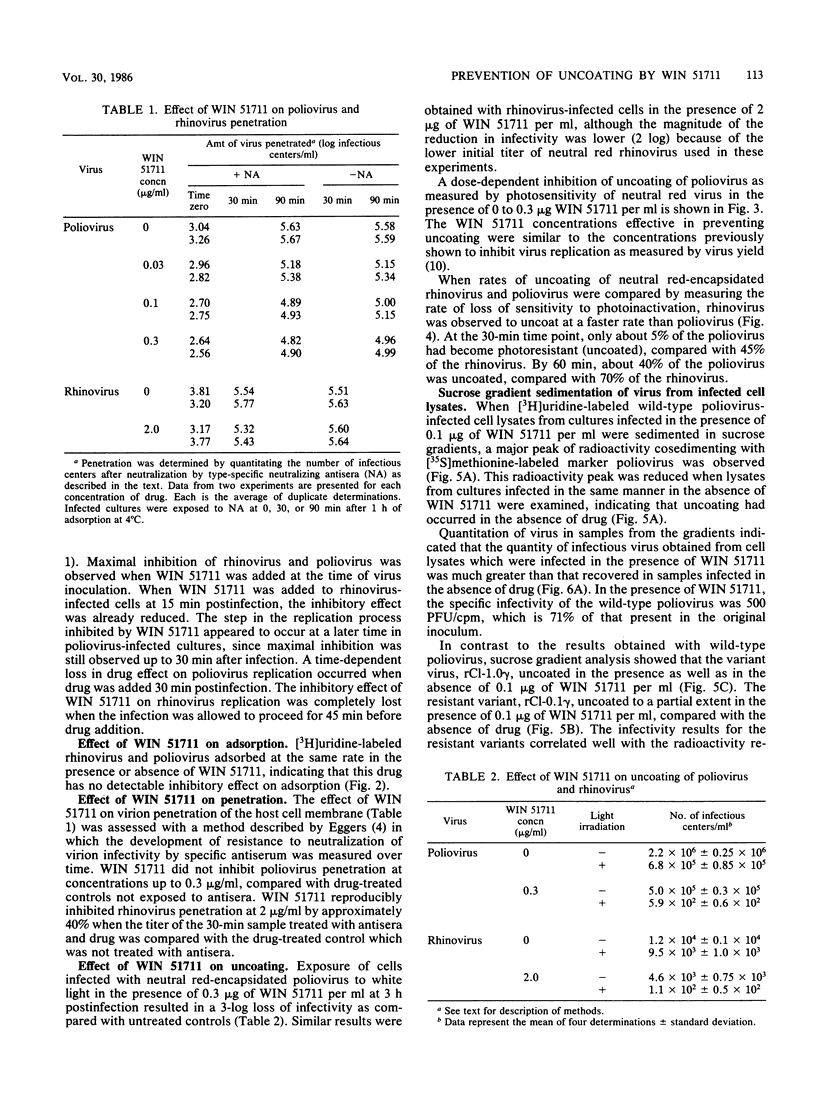
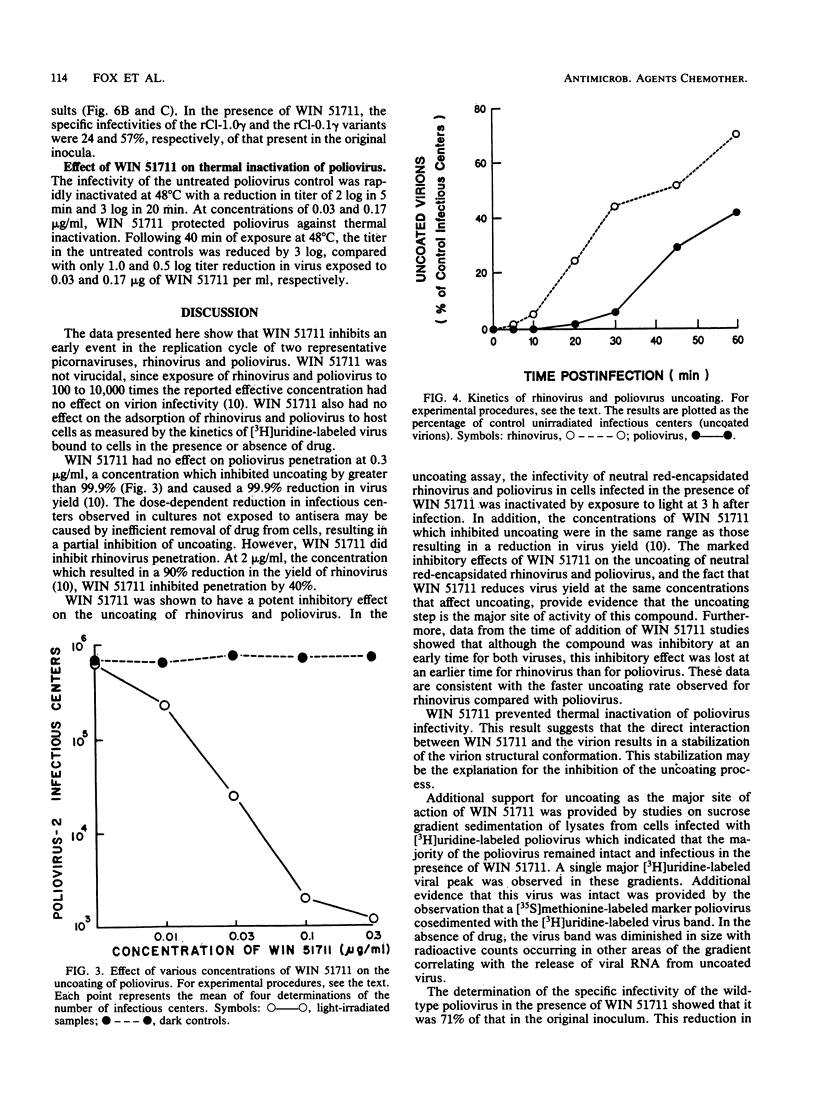
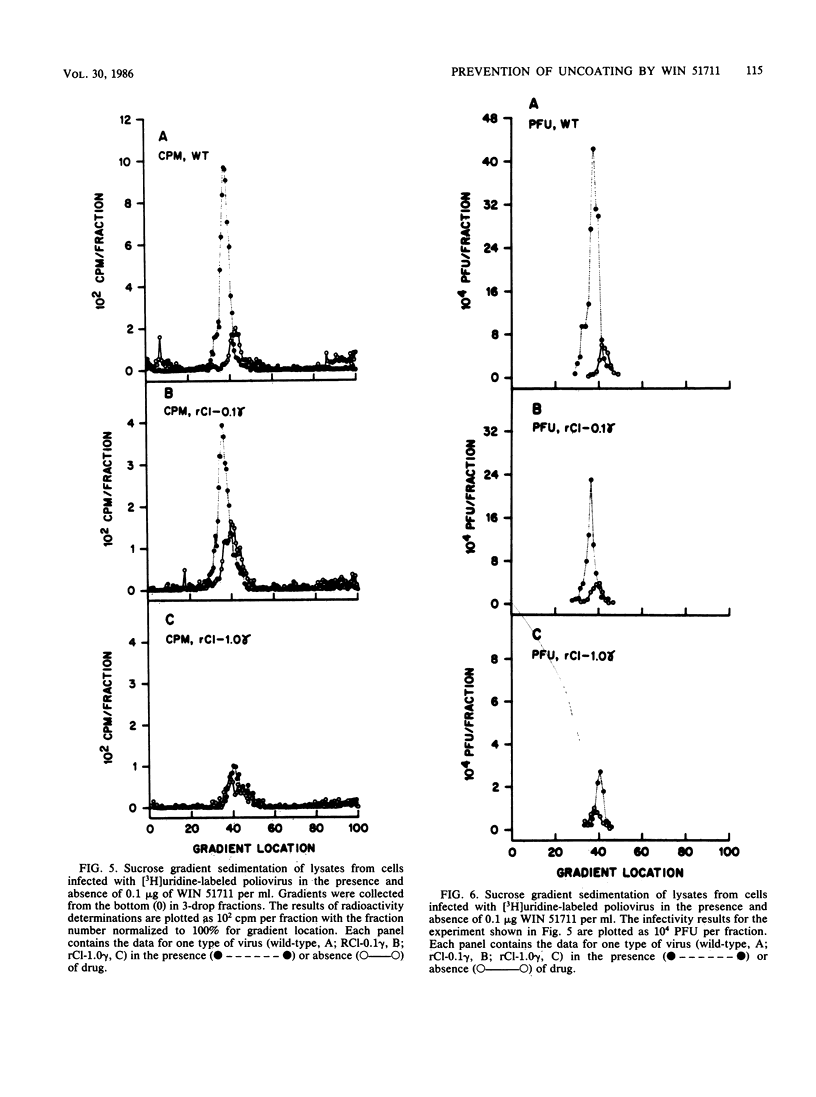
WIN 51711, a potent new antipicornavirus drug, has been shown to inhibit an early event in the replication cycle of human poliovirus type 2 and human rhinovirus type 2. WIN 51711 was not virucidal and had no measurable effect on the adsorption of [3H]uridine-labeled virions to cells. When virion penetration of the plasma membrane was determined through loss of sensitivity to neutralizing antisera, WIN 51711 had no effect on poliovirus penetration, but inhibited rhinovirus penetration by 40%. In the presence of WIN 51711, exposure of neutral red-encapsidated virus-infected cells to light at 3 h postinfection resulted in a 3-log reduction in the number of infectious centers, indicating that WIN 51711 maintained the viral RNA in the encapsidated state after penetrating the cell membrane. The inhibition of uncoating by WIN 51711 in the neutral red assay was found to be concentration dependent, with a concentration of 0.03 micrograms/ml resulting in a 90% inhibition of uncoating. Sucrose gradient sedimentation of lysates from whole cells infected with [3H]uridine-labeled poliovirus showed that poliovirions remained intact in the presence of WIN 51711, but were uncoated in the absence of drug. WIN 51711 also prevented thermal inactivation of poliovirus infectivity, indicating a direct stabilizing effect of this compound on virion capsid conformation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter-Gabbard K. L. A simple method for the large-scale preparation of sucrose gradients. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jan 15;20(1):117–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80031-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M. The structure of heated poliovirus particles. J Gen Virol. 1971 Jun;11(3):147–156. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-11-3-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., McSharry J. J., Lawrence G. W. Effect of arildone on modifications of poliovirus in vitro. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diana G. D., McKinlay M. A., Otto M. J., Akullian V., Oglesby C. [[(4,5-Dihydro-2-oxazolyl)phenoxy]alkyl]isoxazoles. Inhibitors of picornavirus uncoating. J Med Chem. 1985 Dec;28(12):1906–1910. doi: 10.1021/jm00150a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggers H. J. Selective inhibiton of uncoating of echovirus 12 by rhodanine. A study on early virus-cell interactions. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Korant B. D. Early interaction of rhinoviruses with host cells. J Virol. 1972 Jan;9(1):29–40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.1.29-40.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. Neutralization of poliovirus: a hypothesis to explain the mechanism and the one-hit character of the neutralization reaction. Virology. 1976 Feb;69(2):500–510. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel B. The relationship between penetration and uncoating of poliovirus in HeLa cells. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):702–712. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinlay M. A., Steinberg B. A. Oral efficacy of WIN 51711 in mice infected with human poliovirus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):30–32. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSharry J. J., Caliguiri L. A., Eggers H. J. Inhibition of uncoating of poliovirus by arildone, a new antiviral drug. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto M. J., Fox M. P., Fancher M. J., Kuhrt M. F., Diana G. D., McKinlay M. A. In vitro activity of WIN 51711, a new broad-spectrum antipicornavirus drug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jun;27(6):883–886. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.6.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwirth B., Eggers H. J. Early processes of echovirus 12-infection: elution, penetration, and uncoating under the influence of rhodanine. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):241–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



