Abstract
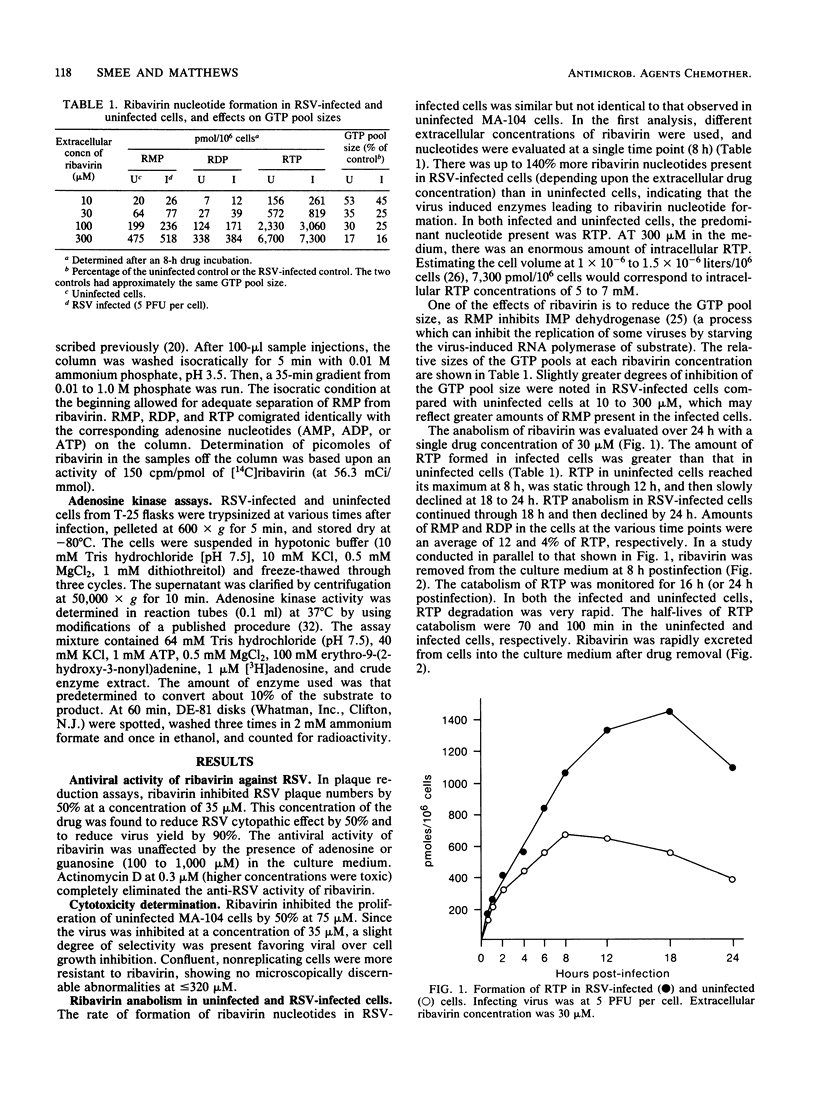
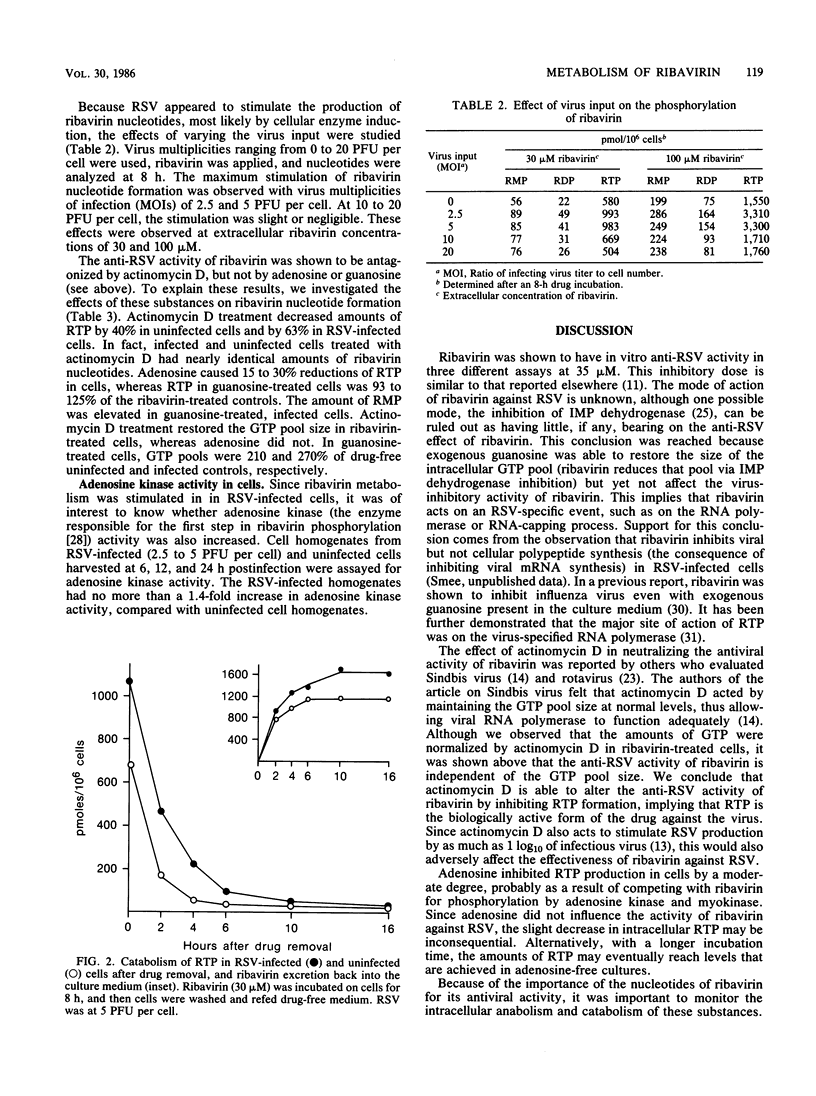
The metabolism of ribavirin to its mono-, di-, and triphosphate derivatives was examined in uninfected and respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells. The degree of phosphorylation was dose dependent upon extracellular ribavirin concentration. The major species formed was the triphosphate, with mono- and diphosphates being approximately 12 and 4% of the triphosphate, respectively. Amounts of triphosphate formed in infected cells were up to 2.6-fold greater than those in uninfected cells. Upon drug removal, ribavirin triphosphate degradation was very rapid, with decay half-lives of 70 to 100 min. Actinomycin D inhibited triphosphate production and also neutralized the antiviral effect of ribavirin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biron K. K., Stanat S. C., Sorrell J. B., Fyfe J. A., Keller P. M., Lambe C. U., Nelson D. J. Metabolic activation of the nucleoside analog 9-[( 2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)ethoxy]methyl)guanine in human diploid fibroblasts infected with human cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2473–2477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson B., Helgstrand E., Johansson N. G., Larsson A., Misiorny A., Norén J. O., Philipson L., Stenberg K., Stening G., Stridh S. Inhibition of influenza virus ribonucleic acid polymerase by ribavirin triphosphate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):946–951. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freitas V. R., Smee D. F., Chernow M., Boehme R., Matthews T. R. Activity of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine compared with that of acyclovir against human, monkey, and rodent cytomegaloviruses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):240–245. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., de Miranda P., St Clair M. H., Elion G. B. Metabolism of acyclovir in virus-infected and uninfected cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):518–524. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goswami B. B., Borek E., Sharma O. K., Fujitaki J., Smith R. A. The broad spectrum antiviral agent ribavirin inhibits capping of mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):830–836. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91853-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell C. L., Miller M. J. Effect of sucrose phosphate and sorbitol on infectivity of enveloped viruses during storage. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):658–662. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.658-662.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska J. F., Bernstein J. M., Douglas R. G., Jr, Hall C. B. Effects of ribavirin on respiratory syncytial virus in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 May;17(5):770–775. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.5.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruska J. F., Morrow P. E., Suffin S. C., Douglas R. G., Jr In vivo inhibition of respiratory syncytial virus by ribavirin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):125–130. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinoski F., Stollar V. Inhibition of Sindbis virus replication in Aedes albopictus cells by virazole (ribavirin) and its reversal by actinomycin: a correction. Virology. 1980 Apr 30;102(2):473–476. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. P., Kigwana L. J., Streeter D. G., Robins R. K., Simon L. N., Roboz J. The relationship between the metabolism of ribavirin and its proposed mechanism of action. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Mar 4;284:211–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb21953.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons M. W., Lambert A. L., Lambert D. M., Rochovansky O. M. Improvement of respiratory syncytial virus replication in actively growing HEp-2 cells. J Virol Methods. 1983 Oct;7(4):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(83)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz P. M., Novack J., Shipman C., Jr, Drach J. C. Metabolism of arabinosyladenine in herpes simplex virus-infected and uninfected cells. Correlation with inhibition of DNA synthesis and role in antiviral selectivity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 1;33(15):2431–2438. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90715-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidwell R. W., Huffman J. H., Khare G. P., Allen L. B., Witkowski J. T., Robins R. K. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of Virazole: 1-beta-D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):705–706. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Boehme R., Chernow M., Binko B. P., Matthews T. R. Intracellular metabolism and enzymatic phosphorylation of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine and acyclovir in herpes simplex virus-infected and uninfected cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Apr 1;34(7):1049–1056. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90608-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Martin J. C., Verheyden J. P., Matthews T. R. Anti-herpesvirus activity of the acyclic nucleoside 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):676–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Sidwell R. W., Barnett B. B., Spendlove R. S. Bioassay system for determining ribavirin levels in human serum and urine. Chemotherapy. 1981;27(1):1–11. doi: 10.1159/000237948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Sidwell R. W., Clark S. M., Barnett B. B., Spendlove R. S. Inhibition of rotaviruses by selected antiviral substances: mechanisms of viral inhibition and in vivo activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):66–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter D. G., Witkowski J. T., Khare G. P., Sidwell R. W., Bauer R. J., Robins R. K., Simon L. N. Mechanism of action of 1- -D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide (Virazole), a new broad-spectrum antiviral agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stridh S. Determination of ribonucleoside triphosphate pools in influenza A virus-infected MDCK cells. Arch Virol. 1983;77(2-4):223–229. doi: 10.1007/BF01309269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis R. C., Carson D. A., Seegmiller J. E. Adenosine kinase initiates the major route of ribavirin activation in a cultured human cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3042–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkowski J. T., Robins R. K., Sidwell R. W., Simon L. N. Design, synthesis, and broad spectrum antiviral activity of 1- -D-ribofuranosyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-carboxamide and related nucleosides. J Med Chem. 1972 Nov;15(11):1150–1154. doi: 10.1021/jm00281a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray S. K., Gilbert B. E., Noall M. W., Knight V. Mode of action of ribavirin: effect of nucleotide pool alterations on influenza virus ribonucleoprotein synthesis. Antiviral Res. 1985 Feb;5(1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(85)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Goto H., Ogasawara N. Purification and properties of adenosine kinase from rat brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 4;616(2):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman T. P., Deeprose R. D. Metabolism of 5-amino-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylimidazole-4-carboxamide and related five-membered heterocycles to 5'-triphosphates in human blood and L5178Y cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 1;27(5):709–716. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



