Abstract
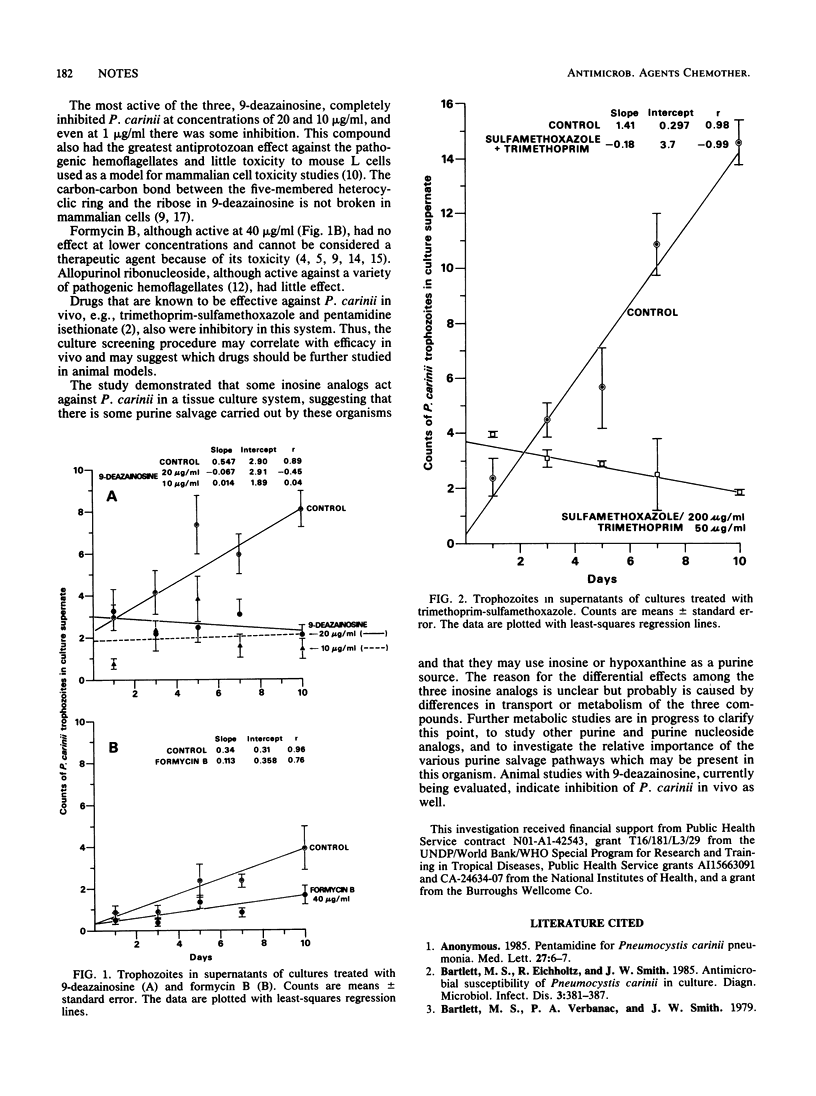
Three analogs of inosine, formycin B, allopurinol ribonucleoside, and 9-deazainosine, were tested for their ability to suppress proliferation of Pneumocystis carinii in culture with WI-38 cells. The organism was inhibited by 9-deazainosine at 10 micrograms/ml, and there was some inhibition at 1 microgram/ml. Formycin B was effective only at 40 micrograms/ml. Allopurinol ribonucleoside had little effect.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett M. S., Eichholtz R., Smith J. W. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Pneumocystis carinii in culture. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;3(5):381–387. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(85)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett M. S., Verbanac P. A., Smith J. W. Cultivation of Pneumocystis carinii with WI-38 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Dec;10(6):796–799. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.6.796-799.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman J. D., Rainey P., Santi D. V. Metabolism of formycin B by Leishmania amastigotes in vitro. Comparative metabolism in infected and uninfected human macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):252–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer R. I., Lloyd L. S. Effects of 8-azaadenosine and formycin on cell lethality and the synthesis and methylation of nucleic acids in human colon carcinoma cells in culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Oct 15;31(20):3207–3214. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90551-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordin F. M., Simon G. L., Wofsy C. B., Mills J. Adverse reactions to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Apr;100(4):495–499. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORI M., TAKITA T., KOYAMA G., TADEUCHI T., UMEZAWA H. A NEW ANTIBIOTIC, FORMYCIN. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1964 May;17:96–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond D. J., Gutteridge W. E. Purine and pyrimidine metabolism in the Trypanosomatidae. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Nov;13(3):243–261. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchings G. H. The purine metabolism of protozoa. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1982;20:375–386. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(82)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFon S. W., Nelson D. J., Berens R. L., Marr J. J. Inosine analogs. Their metabolism in mouse L cells and in Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9660–9665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr J. J., Berens R. L., Cohn N. K., Nelson D. J., Klein R. S. Biological action of inosine analogs in Leishmania and Trypanosoma spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):292–295. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marr J. J., Berens R. L. Pyrazolopyrimidine metabolism in the pathogenic trypanosomatidae. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Apr;7(4):339–356. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Rohde H. J., Steffen R., Maidhof A., Lachmann M., Zahn R. K., Umezawa H. Influence of formycin B on polyadenosine diphosphoribose synthesis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1975 Dec;35(12):3673–3681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Sawa T., Fukagawa Y., Homma I., Ishizuka M. Studies on formycin and formycin B in cells of Ehrlich carcinoma and E. coli. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Nov;20(6):308–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. C., Fuller W., Reich E. Stereochemical analysis of the specificity of pancreatic RNAse with polyformycin as substrate: differentiation of the transphosphorylation and hydrolysis reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):581–588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


