Abstract
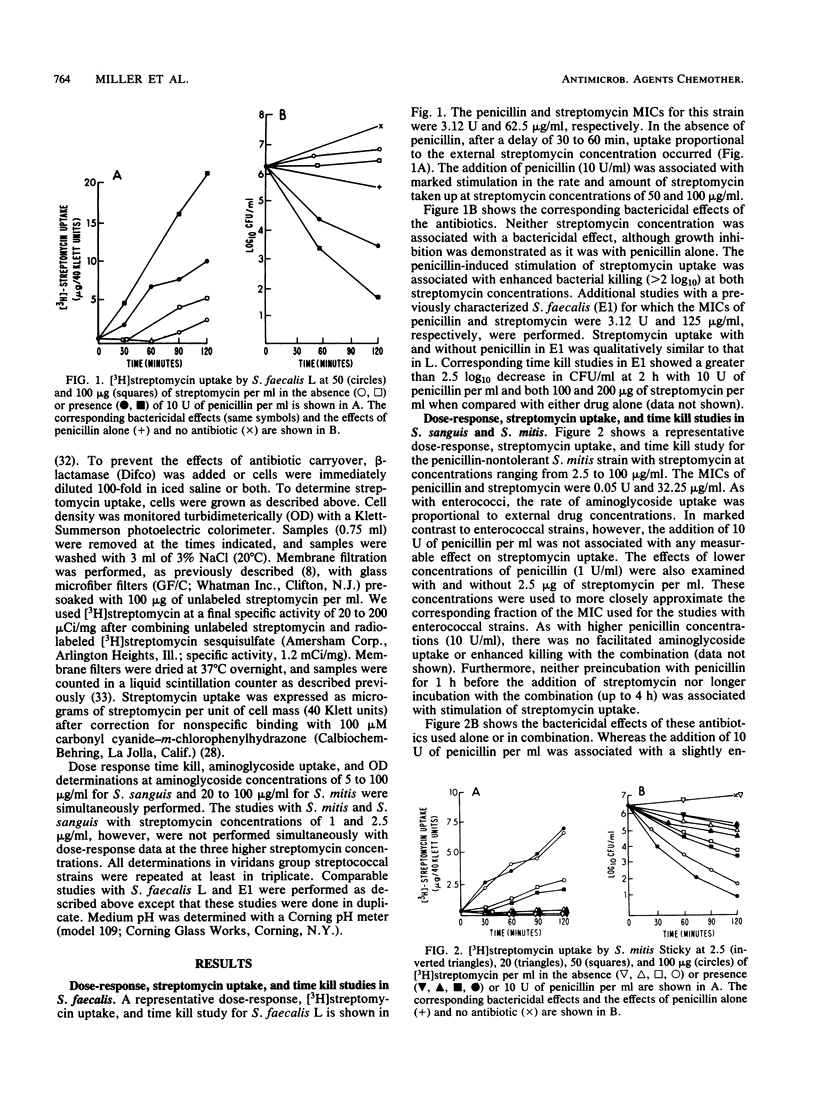
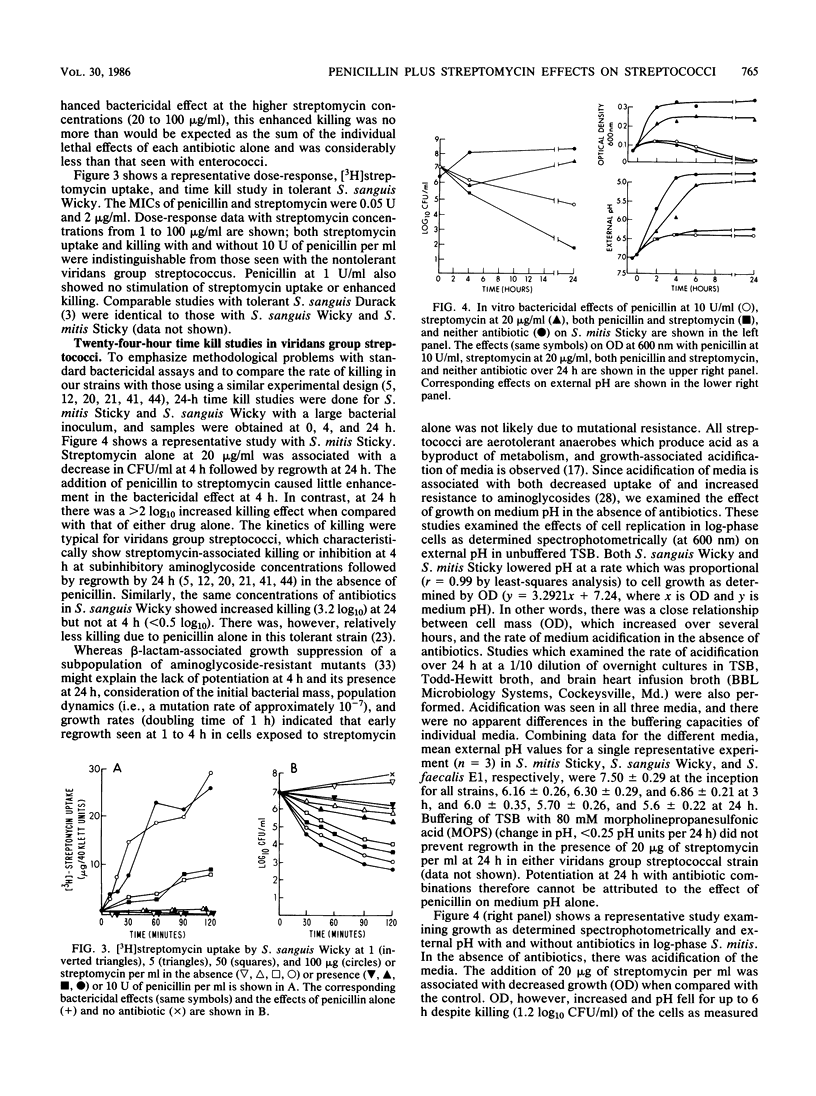
In vitro studies with penicillin and [3H]streptomycin in four strains of streptococci (S. faecalis, S. sanguis, and S. mitis) were performed by simultaneously measuring the rates of bacterial killing and uptake of streptomycin. In S. faecalis, penicillin stimulated streptomycin uptake, as has been shown by Moellering and Weinberg (R. C. Moellering, Jr., and A. N. Weinberg, J. Clin. Invest. 50:2580-2584, 1971). Moreover, the antibiotic combination was associated with an enhanced bactericidal rate which temporally correlated with beta-lactam-induced aminoglycoside uptake. In contrast, in viridans group streptococci (S. sanguis and S. mitis) penicillin had no effect on streptomycin uptake and a minimal effect on bactericidal rate when compared with either drug alone. These data suggested that the stimulation of streptomycin uptake in streptococci by penicillin is strain or species specific and that important differences exist between enterococci and viridans group streptococci regarding the mechanisms of beta-lactam-aminoglycoside potentiation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOUNT J. G. BACTERIAL ENDOCARDITIS. Am J Med. 1965 Jun;38:909–922. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgault A. M., Wilson W. R., Washington J. A., 2nd Antimicrobial susceptibilities of species of viridans streptococci. J Infect Dis. 1979 Sep;140(3):316–321. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.3.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan R. O., Durack D. T. Therapeutic significance of penicillin tolerance in experimental streptococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):273–277. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. B., Brause B. D., Roberts R. B. Antimicrobial therapy of vitamin B6-dependent streptococcal endocarditis. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Aug;87(2):150–154. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-2-150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman W. G., Jr, Leive L. Two mutations which affect the barrier function of the Escherichia coli K-12 outer membrane. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):899–910. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.899-910.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Quantitative association between electrical potential across the cytoplasmic membrane and early gentamicin uptake and killing in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):863–867. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.863-867.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Pavuk R. A. Early synergistic interaction between semisynthetic penicillins and aminoglycosidic aminocyclitols against Enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):902–906. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J., Dankert J., Durack D. Significance of penicillin tolerance in vivo: prevention of experimental Streptococcus sanguis endocarditis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jun;11(6):555–564. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.6.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hook E. W., 3rd, Roberts R. B., Sande M. A. Antimicrobial therapy of experimental enterococcal endocarditis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Nov;8(5):564–570. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.5.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Lethal effect of a heterologous murein hydrolase on penicillin-treated Streptococcus sanguis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):235–246. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. Tolerant response of Streptococcus sanguis to beta-lactams and other cell wall inhibitors. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 May;11(5):888–896. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.5.888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Tomasz A. pH-dependent penicillin tolerance of group B streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):128–135. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Proton motive force in growing Streptococcus lactis and Staphylococcus aureus cells under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):369–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.369-376.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K., Bayer A. S. In vitro bactericidal synergy of gentamicin combined with penicillin G, vancomycin, or cefotaxime against group G streptococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):260–262. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. F., Hanna B. A., Pollock A. A., Simberkoff M. S., Rahal J. J., Jr Penicillin sensitive nutritionally variant streptococcal endocarditis: relapse after penicillin therapy. Am J Med Sci. 1983 Jul-Aug;286(1):31–36. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198307000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy F. D., Chang D. S., Lash P. R. Synergy of combinations of vancomycin, gentamicin, and rifampin against methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):932–934. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy F. D., Neuhaus E. G., Chang D. S., Steigbigel N. H. Penicillin therapy of experimental endocarditis induced by tolerant Streptococcus sanguis and nontolerant Streptococcus mitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):67–73. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy F. D., Walsh J. A., Mayers M. M., Klein R. S., Steigbigel N. H. Antibiotic activity in vitro against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis and therapy of an experimental infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Sep;16(3):314–321. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.3.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy F. D., Wexler M. A., Steigbigel N. H. Therapy of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis experimental endocarditis. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Jul;100(1):94–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel L. J., Eisenberg E. S., Simkin N. J., Miller M. H. Effect of N, N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and nigericin on Staphylococcus aureus susceptibility to gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Sep;24(3):440–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.3.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell G. L., Kaye D., Levison M. E., Hook E. W. Enterococcal endocarditis. An analysis of 38 patients observed at the New York Hospital-Cornell Medical Center. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Feb;125(2):258–264. doi: 10.1001/archinte.125.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates S. M., Eisenberg E. S., Mandel L. J., Patel L., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Membrane potential and gentamicin uptake in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6693–6697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates S. M., Patel L., Kaback H. R., Miller M. H. Membrane potential in anaerobically growing Staphylococcus aureus and its relationship to gentamicin uptake. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Apr;23(4):526–530. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.4.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawer S. L., Greenwood D. Specific and non-specific resistance to aminoglycosides in Escherichia coli. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Jan;31(1):12–15. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Edberg S. C., Mandel L. J., Behar C. F., Steigbigel N. H. Gentamicin uptake in wild-type and aminoglycoside-resistant small-colony mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):722–729. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. H., Wexler M. A., Steigbigel N. H. Single and combination antibiotic therapy of Staphylococcus aureus experimental endocarditis: emergence of gentamicin-resistant mutants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Sep;14(3):336–343. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Murray B. E., Schoenbaum S. C., Adler J., Wennersten C. B. A novel mechanism of resistance to penicillin-gentamicin synergism in Streptococcus faecalis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):81–86. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Weinberg A. N. Studies on antibiotic syngerism against enterococci. II. Effect of various antibiotics on the uptake of 14 C-labeled streptomycin by enterococci. J Clin Invest. 1971 Dec;50(12):2580–2584. doi: 10.1172/JCI106758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr, Wennersten C., Weinberg A. N. Studies on antibiotic synergism against enterococci. I. Bacteriologic studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 May;77(5):821–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLOTZ P. H., DAVIS B. D. Synergism between streptomycin and penicillin: a proposed mechanism. Science. 1962 Mar 23;135(3508):1067–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3508.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sande M. A., Irvin R. G. Penicillin-aminoglycoside synergy in experimental Streptococcus viridans endocarditis. J Infect Dis. 1974 May;129(5):572–576. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.5.572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. S., Kaplan S., Terhune C. A., Jr, Hamburger M. Successful two-week treatment schedule for penicillin-susceptible streptococcus viridans endocarditis. Lancet. 1971 Dec 18;2(7738):1340–1343. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92360-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauvin C., Eliopoulos G. M., Wennersten C., Moellering R. C., Jr Antagonistic effect of penicillin-amikacin combinations against enterococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jul;28(1):78–83. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Calderwood S. B., Moellering R. C., Jr, Tomasz A. Studies on the mechanism of intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in group D streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):813–822. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J. C., Johnson W. D. Penicillin-sensitive streptococcal endocarditis. In-vitro and clinical observations on penicillin-streptomycin therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Aug;81(2):178–181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-81-2-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


