Abstract
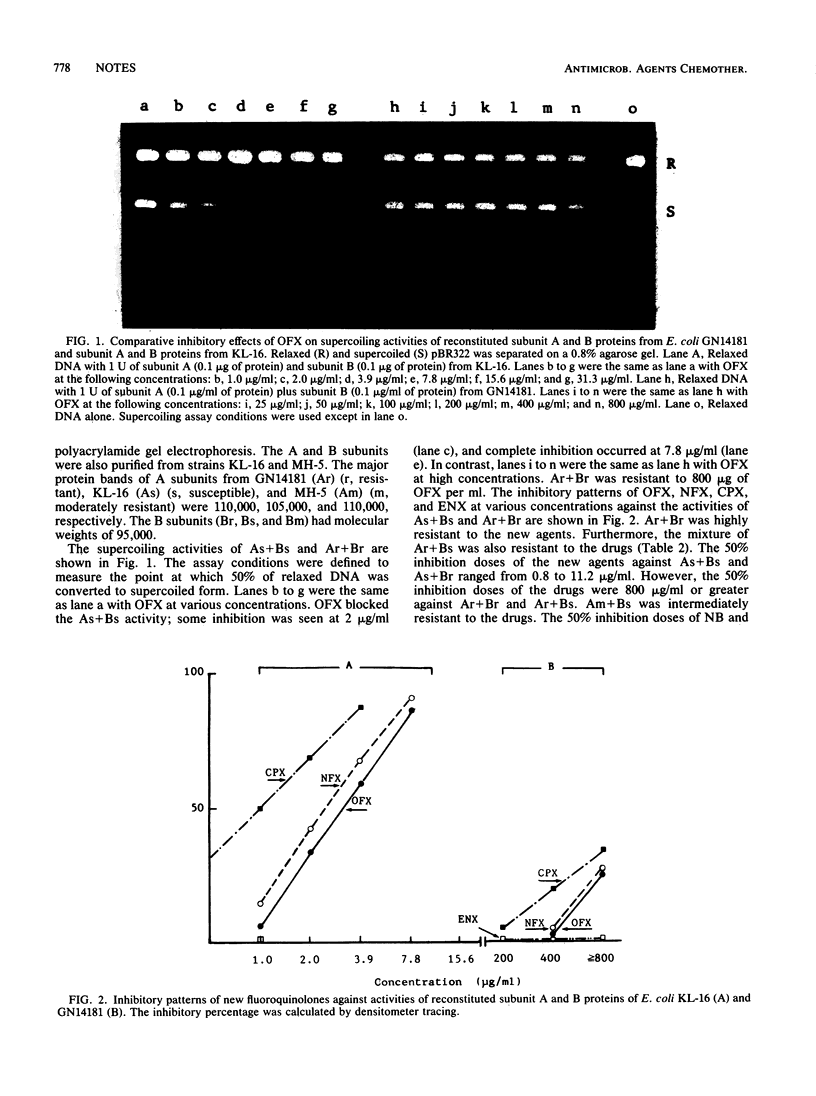
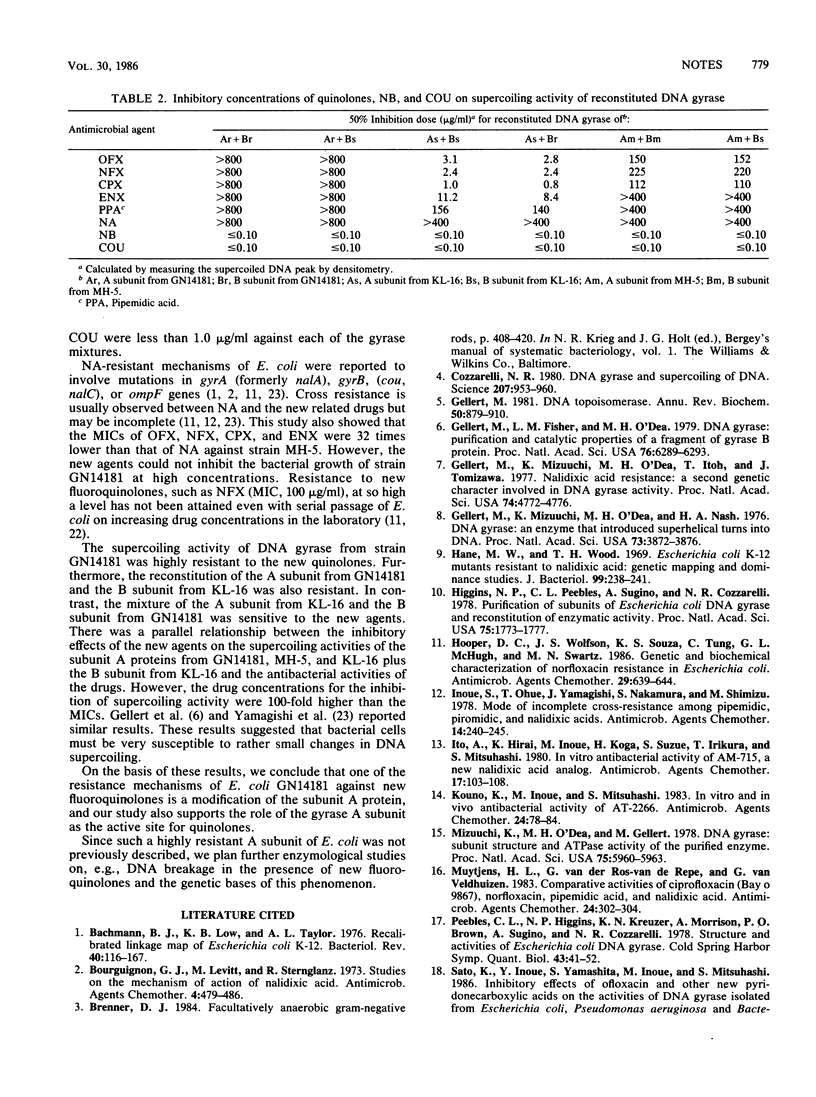
Subunit A and B proteins of DNA gyrase were separately purified from fluoroquinolone-resistant Escherichia coli GN14181 (MIC of ofloxacin, 100 micrograms/ml) and susceptible strain KL-16. The supercoiling activities of reconstituted Ar+Br (r, resistant) and Ar+Bs (s, susceptible) were 250-fold more resistant to new fluoroquinolones than those of As+Bs and As+Br.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B., Taylor A. L. Recalibrated linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):116–167. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.116-167.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon G. J., Levitt M., Sternglanz R. Studies on the mechanism of action of nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Oct;4(4):479–486. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.4.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Fisher L. M., O'Dea M. H. DNA gyrase: purification and catalytic properties of a fragment of gyrase B protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6289–6293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Peebles C. L., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Purification of subunits of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and reconstitution of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1773–1777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Tung C., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):639–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Ohue T., Yamagishi J., Nakamura S., Shimizu M. Mode of incomplete cross-resistance among pipemidic, piromidic, and nalidixic acids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):240–245. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito A., Hirai K., Inoue M., Koga H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro antibacterial activity of AM-715, a new nalidixic acid analog. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Feb;17(2):103–108. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouno K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of AT-2266. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. DNA gyrase: subunit structure and ATPase activity of the purified enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5960–5963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muytjens H. L., van der Ros-van de Repe J., van Veldhuizen G. Comparative activities of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867), norfloxacin, pipemidic acid, and nalidixic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):302–304. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Higgins N. P., Kreuzer K. N., Morrison A., Brown P. O., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Structure and activities of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):41–52. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Matsuura Y., Inoue M., Une T., Osada Y., Ogawa H., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of DL-8280, a new oxazine derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Oct;22(4):548–553. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.4.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Drlica K. DNA gyrase on the bacterial chromosome: DNA cleavage induced by oxolinic acid. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):287–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L., Orr E. DNA gyrase: affinity chromatography on novobiocin-Sepharose and catalytic properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3589–3603. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenney J. H., Maack R. W., Chippendale G. R. Rapid selection of organisms with increasing resistance on subinhibitory concentrations of norfloxacin in agar. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):188–189. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi J., Furutani Y., Inoue S., Ohue T., Nakamura S., Shimizu M. New nalidixic acid resistance mutations related to deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):450–458. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.450-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




