Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (203.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
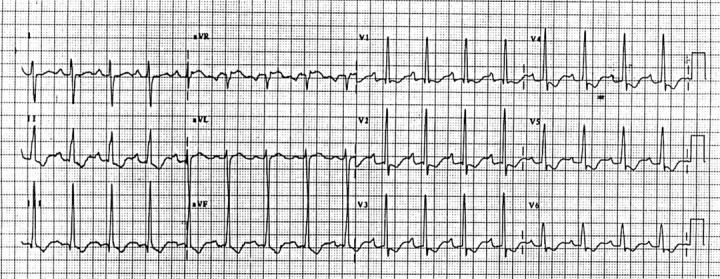
Typical ECG of chronic pulmonary hypertension showing right ventricular hypertrophy.
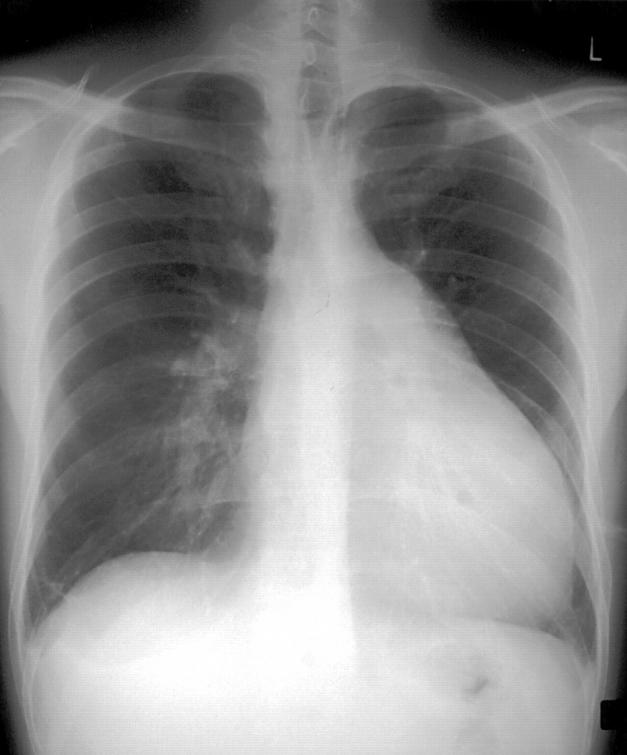
Figure 2 .
Chest radiograph of a patient with primary pulmonary hypertension. Note the enlarged proximal pulmonary arteries.
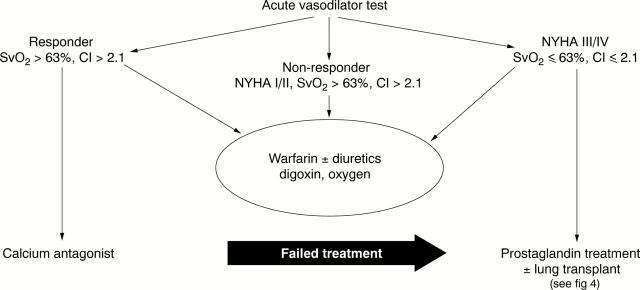
Figure 3 .
Management of pulmonary arterial hypertension. CI, cardiac index; SvO2, pulmonary arterial oxygen saturation; NYHA, New York Heart Association.
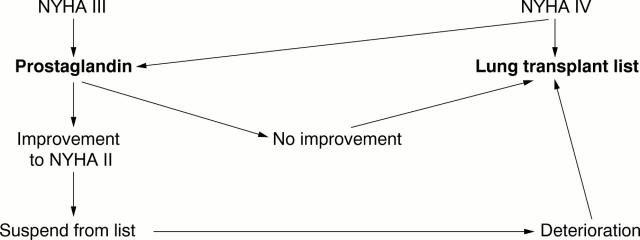
Figure 4 .
Management of prostaglandin therapy and lung transplantation.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abenhaim L., Moride Y., Brenot F., Rich S., Benichou J., Kurz X., Higenbottam T., Oakley C., Wouters E., Aubier M. Appetite-suppressant drugs and the risk of primary pulmonary hypertension. International Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996 Aug 29;335(9):609–616. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199608293350901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R., Scazziota A., Rouvier J., Gurfinkel E., Favaloro R., Perrone S., Fareed J. Coagulation and fibrinolytic parameters in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Clin Cardiol. 1996 Jul;19(7):549–554. doi: 10.1002/clc.4960190706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badesch D. B., Tapson V. F., McGoon M. D., Brundage B. H., Rubin L. J., Wigley F. M., Rich S., Barst R. J., Barrett P. S., Kral K. M. Continuous intravenous epoprostenol for pulmonary hypertension due to the scleroderma spectrum of disease. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2000 Mar 21;132(6):425–434. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-132-6-200003210-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bando K., Keenan R. J., Paradis I. L., Konishi H., Komatsu K., Hardesty R. L., Griffith B. P. Impact of pulmonary hypertension on outcome after single-lung transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994 Nov;58(5):1336–1342. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(94)91908-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst R. J., Maislin G., Fishman A. P. Vasodilator therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension in children. Circulation. 1999 Mar 9;99(9):1197–1208. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.9.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst R. J., Rubin L. J., Long W. A., McGoon M. D., Rich S., Badesch D. B., Groves B. M., Tapson V. F., Bourge R. C., Brundage B. H. A comparison of continuous intravenous epoprostenol (prostacyclin) with conventional therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1996 Feb 1;334(5):296–301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199602013340504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barst R. J., Rubin L. J., McGoon M. D., Caldwell E. J., Long W. A., Levy P. S. Survival in primary pulmonary hypertension with long-term continuous intravenous prostacyclin. Ann Intern Med. 1994 Sep 15;121(6):409–415. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-121-6-199409150-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergin C. J., Sirlin C. B., Hauschildt J. P., Huynh T. V., Auger W. R., Fedullo P. F., Kapelanski D. P. Chronic thromboembolism: diagnosis with helical CT and MR imaging with angiographic and surgical correlation. Radiology. 1997 Sep;204(3):695–702. doi: 10.1148/radiology.204.3.9280245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer J. J., Busst C. M., Denison D. M., Shinebourne E. A. Effect of long term oxygen treatment at home in children with pulmonary vascular disease. Br Heart J. 1986 Apr;55(4):385–390. doi: 10.1136/hrt.55.4.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugiardini R., Galvani M., Ferrini D., Gridelli C., Mari L., Puddu P., Lenzi S. Effects of iloprost, a stable prostacyclin analog, on exercise capacity and platelet aggregation in stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Sep 1;58(6):453–459. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clabby M. L., Canter C. E., Moller J. H., Bridges N. D. Hemodynamic data and survival in children with pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997 Aug;30(2):554–560. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conte J. V., Gaine S. P., Orens J. B., Harris T., Rubin L. J. The influence of continuous intravenous prostacyclin therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension on the timing and outcome of transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1998 Jul;17(7):679–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alonzo G. E., Barst R. J., Ayres S. M., Bergofsky E. H., Brundage B. H., Detre K. M., Fishman A. P., Goldring R. M., Groves B. M., Kernis J. T. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Sep 1;115(5):343–349. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-5-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daliento L., Somerville J., Presbitero P., Menti L., Brach-Prever S., Rizzoli G., Stone S. Eisenmenger syndrome. Factors relating to deterioration and death. Eur Heart J. 1998 Dec;19(12):1845–1855. doi: 10.1053/euhj.1998.1046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. L., deBoisblanc B. P., Glynn C. E., Ramirez C., Summer W. R. Effect of prostacyclin on microvascular pressures in a patient with pulmonary veno-occlusive disease. Chest. 1995 Dec;108(6):1754–1756. doi: 10.1378/chest.108.6.1754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng Z., Morse J. H., Slager S. L., Cuervo N., Moore K. J., Venetos G., Kalachikov S., Cayanis E., Fischer S. G., Barst R. J. Familial primary pulmonary hypertension (gene PPH1) is caused by mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein receptor-II gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2000 Jul 20;67(3):737–744. doi: 10.1086/303059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinh Xuan A. T., Higenbottam T. W., Scott J. P., Wallwork J. Primary pulmonary hypertension: diagnosis, medical and surgical treatment. Respir Med. 1990 May;84(3):189–197. doi: 10.1016/s0954-6111(08)80033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig J. C., Corris P. A., Hilton C. J., Dark J. H., Bexton R. S. Effect of single lung transplantation on pulmonary hypertension in patients with end stage fibrosing lung disease. Br Heart J. 1991 Dec;66(6):431–434. doi: 10.1136/hrt.66.6.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufour B., Maître S., Humbert M., Capron F., Simonneau G., Musset D. High-resolution CT of the chest in four patients with pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis or pulmonary venoocclusive disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998 Nov;171(5):1321–1324. doi: 10.2214/ajr.171.5.9798872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkayam U., Amin J., Mehra A., Vasquez J., Weber L., Rahimtoola S. H. A prospective, randomized, double-blind, crossover study to compare the efficacy and safety of chronic nifedipine therapy with that of isosorbide dinitrate and their combination in the treatment of chronic congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1990 Dec;82(6):1954–1961. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.6.1954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltorky M. A., Headley A. S., Winer-Muram H., Garrett H. E., Jr, Griffin J. P. Pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis: a clinicopathologic review. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994 Mar;57(3):772–776. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(94)90595-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eysmann S. B., Palevsky H. I., Reichek N., Hackney K., Douglas P. S. Two-dimensional and Doppler-echocardiographic and cardiac catheterization correlates of survival in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1989 Aug;80(2):353–360. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R., Mears J. G., Barst R. J. Continuous infusion of prostacyclin normalizes plasma markers of endothelial cell injury and platelet aggregation in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1997 Nov 4;96(9):2782–2784. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.9.2782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuster V., Steele P. M., Edwards W. D., Gersh B. J., McGoon M. D., Frye R. L. Primary pulmonary hypertension: natural history and the importance of thrombosis. Circulation. 1984 Oct;70(4):580–587. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.4.580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein R. E., Boccuzzi S. J., Cruess D., Nattel S. Diltiazem increases late-onset congestive heart failure in postinfarction patients with early reduction in ejection fraction. The Adverse Experience Committee; and the Multicenter Diltiazem Postinfarction Research Group. Circulation. 1991 Jan;83(1):52–60. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf H. Endothelial control of cell migration and proliferation. Eur Heart J. 1993 Nov;14 (Suppl 1):183–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves B. M., Rubin L. J., Frosolono M. F., Cato A. E., Reeves J. T. A comparison of the acute hemodynamic effects of prostacyclin and hydralazine in primary pulmonary hypertension. Am Heart J. 1985 Dec;110(6):1200–1204. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(85)90013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurtner H. P. Aminorex and pulmonary hypertension. A review. Cor Vasa. 1985;27(2-3):160–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam R. J., McClenaghan M. D. Measurement of circulating prostacyclin. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):364–366. doi: 10.1038/292364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden A. M. Balloon atrial septostomy increases cardiac index and may reduce mortality among pulmonary hypertension patients awaiting lung transplantation. J Transpl Coord. 1997 Sep;7(3):131–133. doi: 10.7182/prtr.1.7.3.b5v5j80353hx0716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann L. A., Assmann A., DoMinh T., Garbe E. Oral progestogen-only contraceptives and cardiovascular risk: results from the Transnational Study on Oral Contraceptives and the Health of Young Women. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 1999 Jun;4(2):67–73. doi: 10.3109/13625189909064007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higenbottam T. W., Butt A. Y., Dinh-Xaun A. T., Takao M., Cremona G., Akamine S. Treatment of pulmonary hypertension with the continuous infusion of a prostacyclin analogue, iloprost. Heart. 1998 Feb;79(2):175–179. doi: 10.1136/hrt.79.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higenbottam T. W., Spiegelhalter D., Scott J. P., Fuster V., Dinh-Xuan A. T., Caine N., Wallwork J. Prostacyclin (epoprostenol) and heart-lung transplantation as treatments for severe pulmonary hypertension. Br Heart J. 1993 Oct;70(4):366–370. doi: 10.1136/hrt.70.4.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinderliter A. L., Willis P. W., 4th, Barst R. J., Rich S., Rubin L. J., Badesch D. B., Groves B. M., McGoon M. D., Tapson V. F., Bourge R. C. Effects of long-term infusion of prostacyclin (epoprostenol) on echocardiographic measures of right ventricular structure and function in primary pulmonary hypertension. Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group. Circulation. 1997 Mar 18;95(6):1479–1486. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.6.1479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeper M. M., Schwarze M., Ehlerding S., Adler-Schuermeyer A., Spiekerkoetter E., Niedermeyer J., Hamm M., Fabel H. Long-term treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension with aerosolized iloprost, a prostacyclin analogue. N Engl J Med. 2000 Jun 22;342(25):1866–1870. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200006223422503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins W. E., Ochoa L. L., Richardson G. W., Trulock E. P. Comparison of the hemodynamics and survival of adults with severe primary pulmonary hypertension or Eisenmenger syndrome. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1996 Jan;15(1 Pt 1):100–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert M., Maître S., Capron F., Rain B., Musset D., Simonneau G. Pulmonary edema complicating continuous intravenous prostacyclin in pulmonary capillary hemangiomatosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 May;157(5 Pt 1):1681–1685. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.157.5.9708065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert M., Sanchez O., Fartoukh M., Jagot J. L., Le Gall C., Sitbon O., Parent F., Simonneau G. Short-term and long-term epoprostenol (prostacyclin) therapy in pulmonary hypertension secondary to connective tissue diseases: results of a pilot study. Eur Respir J. 1999 Jun;13(6):1351–1356. doi: 10.1183/09031936.99.13613579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman W. H., Vessey M. P., Westerholm B., Engelund A. Thromboembolic disease and the steroidal content of oral contraceptives. A report to the Committee on Safety of Drugs. Br Med J. 1970 Apr 25;2(5703):203–209. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5703.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson S. W. Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy. Heart. 1998 Feb;79(2):118–120. doi: 10.1136/hrt.79.2.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolliet P., Bulpa P., Thorens J. B., Ritz M., Chevrolet J. C. Nitric oxide and prostacyclin as test agents of vasoreactivity in severe precapillary pulmonary hypertension: predictive ability and consequences on haemodynamics and gas exchange. Thorax. 1997 Apr;52(4):369–372. doi: 10.1136/thx.52.4.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadikar A., Maurer J., Kesten S. The six-minute walk test: a guide to assessment for lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 1997 Mar;16(3):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanemoto N. Natural history of pulmonary hemodynamics in primary pulmonary hypertension. Am Heart J. 1987 Aug;114(2):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck B. M., Bennett L. E., Fiol B. S., Daily O. P., Novick R. J., Hosenpud J. D. Worldwide thoracic organ transplantation: a report from the UNOS/ISHLT International Registry for Thoracic Organ Transplantation. Clin Transpl. 1998:39–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerstein D., Levy P. S., Hsu D. T., Hordof A. J., Gersony W. M., Barst R. J. Blade balloon atrial septostomy in patients with severe primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1995 Apr 1;91(7):2028–2035. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.7.2028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo P. C., Johnson L. B., Plotkin J. S., Howell C. D., Bartlett S. T., Rubin L. J. Continuous intravenous infusion of epoprostenol for the treatment of portopulmonary hypertension. Transplantation. 1997 Feb 27;63(4):604–606. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199702270-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langleben D. Familial primary pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 1994 Feb;105(2 Suppl):13S–16S. doi: 10.1378/chest.105.2_supplement.13s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyd J. E., Butler M. G., Foroud T. M., Conneally P. M., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Newman J. H. Genetic anticipation and abnormal gender ratio at birth in familial primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Jul;152(1):93–97. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.152.1.7599869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyd J. E., Primm R. K., Newman J. H. Familial primary pulmonary hypertension: clinical patterns. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Jan;129(1):194–197. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.1.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer E., Dahm M., Hake U., Schmid F. X., Pitton M., Kupferwasser I., Iversen S., Oelert H. Mid-term results of pulmonary thromboendarterectomy for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Ann Thorac Surg. 1996 Jun;61(6):1788–1792. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(96)00169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin V. V., Genthner D. E., Panella M. M., Hess D. M., Rich S. Compassionate use of continuous prostacyclin in the management of secondary pulmonary hypertension: a case series. Ann Intern Med. 1999 May 4;130(9):740–743. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-130-9-199905040-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin V. V., Genthner D. E., Panella M. M., Rich S. Reduction in pulmonary vascular resistance with long-term epoprostenol (prostacyclin) therapy in primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1998 Jan 29;338(5):273–277. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199801293380501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers B. F., Lynch J., Trulock E. P., Guthrie T. J., Cooper J. D., Patterson G. A. Lung transplantation: a decade of experience. Ann Surg. 1999 Sep;230(3):362–371. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199909000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikhail G., Gibbs J., Richardson M., Wright G., Khaghani A., Banner N., Yacoub M. An evaluation of nebulized prostacyclin in patients with primary and secondary pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J. 1997 Sep;18(9):1499–1504. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a015478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Nagaya N., Satoh T., Kyotani S., Sakamaki F., Fujita M., Nakanishi N., Miyatake K. Clinical correlates and prognostic significance of six-minute walk test in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Comparison with cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Feb;161(2 Pt 1):487–492. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.161.2.9906015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Gryglewski R., Bunting S., Vane J. R. An enzyme isolated from arteries transforms prostaglandin endoperoxides to an unstable substance that inhibits platelet aggregation. Nature. 1976 Oct 21;263(5579):663–665. doi: 10.1038/263663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. M., McCormack D. G., Griffiths M. J., Morgan C. J., Barnes P. J., Evans T. W. Adenosine as a vasodilator in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1991 Sep;84(3):1145–1149. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.3.1145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser K. M., Auger W. R., Fedullo P. F., Jamieson S. W. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: clinical picture and surgical treatment. Eur Respir J. 1992 Mar;5(3):334–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. C., Koller D. L., Slovis B., Foroud T., Terry V. H., Arnold N. D., Siemieniak D. R., Wheeler L., Phillips J. A., 3rd, Newman J. H. Localization of the gene for familial primary pulmonary hypertension to chromosome 2q31-32. Nat Genet. 1997 Mar;15(3):277–280. doi: 10.1038/ng0397-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicod P., Moser K. M. Primary pulmonary hypertension. The risk and benefit of lung biopsy. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1486–1488. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olschewski H., Ghofrani H. A., Schmehl T., Winkler J., Wilkens H., Höper M. M., Behr J., Kleber F. X., Seeger W. Inhaled iloprost to treat severe pulmonary hypertension. An uncontrolled trial. German PPH Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 2000 Mar 21;132(6):435–443. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-132-6-200003210-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olschewski H., Walmrath D., Schermuly R., Ghofrani A., Grimminger F., Seeger W. Aerosolized prostacyclin and iloprost in severe pulmonary hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1996 May 1;124(9):820–824. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-124-9-199605010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer M. Is it ethical to administer vasodilator drugs to patients with primary pulmonary hypertension? Chest. 1989 Jun;95(6):1173–1175. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.6.1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer M., O'Connor C. M., Ghali J. K., Pressler M. L., Carson P. E., Belkin R. N., Miller A. B., Neuberg G. W., Frid D., Wertheimer J. H. Effect of amlodipine on morbidity and mortality in severe chronic heart failure. Prospective Randomized Amlodipine Survival Evaluation Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996 Oct 10;335(15):1107–1114. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199610103351504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer M. Vasodilator therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension. Limitations and hazards. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Aug;103(2):258–270. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-2-258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palevsky H. I., Schloo B. L., Pietra G. G., Weber K. T., Janicki J. S., Rubin E., Fishman A. P. Primary pulmonary hypertension. Vascular structure, morphometry, and responsiveness to vasodilator agents. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1207–1221. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasque M. K., Cooper J. D., Kaiser L. R., Haydock D. A., Triantafillou A., Trulock E. P. Improved technique for bilateral lung transplantation: rationale and initial clinical experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990 May;49(5):785–791. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(90)90023-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasque M. K., Kaiser L. R., Dresler C. M., Trulock E., Triantafillou A. N., Cooper J. D. Single lung transplantation for pulmonary hypertension. Technical aspects and immediate hemodynamic results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1992 Mar;103(3):475–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffy O., Azarian R., Brenot F., Parent F., Sitbon O., Petitpretz P., Hervé P., Duroux P., Dinh-Xuan A. T., Simonneau G. Clinical significance of the pulmonary vasodilator response during short-term infusion of prostacyclin in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1996 Feb 1;93(3):484–488. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.93.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz B. A., Wallwork J. L., Hunt S. A., Pennock J. L., Billingham M. E., Oyer P. E., Stinson E. B., Shumway N. E. Heart-lung transplantation: successful therapy for patients with pulmonary vascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Mar 11;306(10):557–564. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198203113061001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Brundage B. H. High-dose calcium channel-blocking therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension: evidence for long-term reduction in pulmonary arterial pressure and regression of right ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation. 1987 Jul;76(1):135–141. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.76.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Dantzker D. R., Ayres S. M., Bergofsky E. H., Brundage B. H., Detre K. M., Fishman A. P., Goldring R. M., Groves B. M., Koerner S. K. Primary pulmonary hypertension. A national prospective study. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Aug;107(2):216–223. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Dodin E., McLaughlin V. V. Usefulness of atrial septostomy as a treatment for primary pulmonary hypertension and guidelines for its application. Am J Cardiol. 1997 Aug 1;80(3):369–371. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(97)00370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Kaufmann E., Levy P. S. The effect of high doses of calcium-channel blockers on survival in primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 9;327(2):76–81. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207093270203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., McLaughlin V. V. The effects of chronic prostacyclin therapy on cardiac output and symptoms in primary pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999 Oct;34(4):1184–1187. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(99)00320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich S., Seidlitz M., Dodin E., Osimani D., Judd D., Genthner D., McLaughlin V., Francis G. The short-term effects of digoxin in patients with right ventricular dysfunction from pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 1998 Sep;114(3):787–792. doi: 10.1378/chest.114.3.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel M., Stanek V., Widimsky J., Prerovsky I. Longterm follow-up of patients with pulmonary thromboembolism. Late prognosis and evolution of hemodynamic and respiratory data. Chest. 1982 Feb;81(2):151–158. doi: 10.1378/chest.81.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenzweig E. B., Kerstein D., Barst R. J. Long-term prostacyclin for pulmonary hypertension with associated congenital heart defects. Circulation. 1999 Apr 13;99(14):1858–1865. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.99.14.1858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. J., Groves B. M., Reeves J. T., Frosolono M., Handel F., Cato A. E. Prostacyclin-induced acute pulmonary vasodilation in primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 1982 Aug;66(2):334–338. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.2.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. J., Mendoza J., Hood M., McGoon M., Barst R., Williams W. B., Diehl J. H., Crow J., Long W. Treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension with continuous intravenous prostacyclin (epoprostenol). Results of a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Apr 1;112(7):485–491. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-7-485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. J., Nicod P., Hillis L. D., Firth B. G. Treatment of primary pulmonary hypertension with nifedipine. A hemodynamic and scintigraphic evaluation. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):433–438. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. J. Primary pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1997 Jan 9;336(2):111–117. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199701093360207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval J., Gaspar J., Pulido T., Bautista E., Martínez-Guerra M. L., Zeballos M., Palomar A., Gómez A. Graded balloon dilation atrial septostomy in severe primary pulmonary hypertension. A therapeutic alternative for patients nonresponsive to vasodilator treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Aug;32(2):297–304. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(98)00238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrör K., Darius H., Matzky R., Ohlendorf R. The antiplatelet and cardiovascular actions of a new carbacyclin derivative (ZK 36 374)--equipotent to PGI2 in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;316(3):252–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00505658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. M., Oudiz R. J., Cao T., Romano M. A., Beckmann X. J., Georgiou D., Mandayam S., Ginzton L. E., Brundage B. H. Primary pulmonary hypertension: improved long-term effects and survival with continuous intravenous epoprostenol infusion. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997 Aug;30(2):343–349. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. J., Morgan M. D., Scott S., Walters D., Hardman A. E. Development of a shuttle walking test of disability in patients with chronic airways obstruction. Thorax. 1992 Dec;47(12):1019–1024. doi: 10.1136/thx.47.12.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon O., Humbert M., Jagot J. L., Taravella O., Fartoukh M., Parent F., Herve P., Simonneau G. Inhaled nitric oxide as a screening agent for safely identifying responders to oral calcium-channel blockers in primary pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 1998 Aug;12(2):265–270. doi: 10.1183/09031936.98.12020265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricker H., Domenighetti G., Mombelli G. Prostacyclin for HIV-associated pulmonary hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1997 Dec 1;127(11):1043–1043. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-127-11-199712010-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swensen S. J., Tashjian J. H., Myers J. L., Engeler C. E., Patz E. F., Edwards W. D., Douglas W. W. Pulmonary venoocclusive disease: CT findings in eight patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996 Oct;167(4):937–940. doi: 10.2214/ajr.167.4.8819387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson J. R., Machado R. D., Pauciulo M. W., Morgan N. V., Humbert M., Elliott G. C., Ward K., Yacoub M., Mikhail G., Rogers P. Sporadic primary pulmonary hypertension is associated with germline mutations of the gene encoding BMPR-II, a receptor member of the TGF-beta family. J Med Genet. 2000 Oct;37(10):741–745. doi: 10.1136/jmg.37.10.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne S. A. Management of polycythaemia in adults with cyanotic congenital heart disease. Heart. 1998 Apr;79(4):315–316. doi: 10.1136/hrt.79.4.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turbow R., Waffarn F., Yang L., Sills J., Hallman M. Variable oxygenation response to inhaled nitric oxide in severe persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Acta Paediatr. 1995 Nov;84(11):1305–1308. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1995.tb13554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzenblum E., Sautegeau A., Ehrhart M., Mammosser M., Pelletier A. Long-term oxygen therapy can reverse the progression of pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Apr;131(4):493–498. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh C. H., Hassell K. L., Badesch D. B., Kressin D. C., Marlar R. A. Coagulation and fibrinolytic profiles in patients with severe pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 1996 Sep;110(3):710–717. doi: 10.1378/chest.110.3.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodmansey P. A., O'Toole L., Channer K. S., Morice A. H. Acute pulmonary vasodilatory properties of amlodipine in humans with pulmonary hypertension. Heart. 1996 Feb;75(2):171–173. doi: 10.1136/hrt.75.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yock P. G., Popp R. L. Noninvasive estimation of right ventricular systolic pressure by Doppler ultrasound in patients with tricuspid regurgitation. Circulation. 1984 Oct;70(4):657–662. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.70.4.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]