Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (110.6 KB).
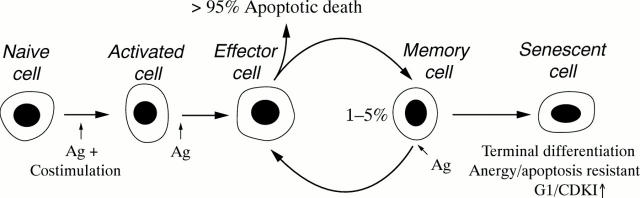
Figure 1 .
Schematic representation of replicative senescence in repeatedly activated autoreactive memory T cells.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbas A. K., Murphy K. M., Sher A. Functional diversity of helper T lymphocytes. Nature. 1996 Oct 31;383(6603):787–793. doi: 10.1038/383787a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe C., Koyama A., Nishimura T. Interleukin-2 induction, response and therapy on murine lupus lesions in the MRL/l strain. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;229:147–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aderka D., Wysenbeek A., Engelmann H., Cope A. P., Brennan F., Molad Y., Hornik V., Levo Y., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Correlation between serum levels of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Aug;36(8):1111–1120. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón-Riquelme M. E., Möller G., Fernández C. Macrophage depletion decreases IgG anti-DNA in cultures from (NZB x NZW)F1 spleen cells by eliminating the main source of IL-6. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Feb;91(2):220–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb05886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alleva D. G., Kaser S. B., Beller D. I. Aberrant cytokine expression and autocrine regulation characterize macrophages from young MRL+/+ and NZB/W F1 lupus-prone mice. J Immunol. 1997 Dec 1;159(11):5610–5619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alleva D. G., Kaser S. B., Beller D. I. Intrinsic defects in macrophage IL-12 production associated with immune dysfunction in the MRL/++ and New Zealand Black/White F1 lupus-prone mice and the Leishmania major-susceptible BALB/c strain. J Immunol. 1998 Dec 15;161(12):6878–6884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Weiner R., Katz D. H., Dixon F. J. Analysis of T cell function in autoimmune murine strains. Defects in production and responsiveness to interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):791–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balomenos D., Rumold R., Theofilopoulos A. N. Interferon-gamma is required for lupus-like disease and lymphoaccumulation in MRL-lpr mice. J Clin Invest. 1998 Jan 15;101(2):364–371. doi: 10.1172/JCI750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balomenos D., Rumold R., Theofilopoulos A. N. The proliferative in vivo activities of lpr double-negative T cells and the primary role of p59fyn in their activation and expansion. J Immunol. 1997 Sep 1;159(5):2265–2273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchieri M. H., Knittweis L., Seaton D. S. Cytokine production by NZB, C58, and NZB X C58 recombinant inbred mice. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell J. M., Yui M. A., Burt D. W., Kelley V. E. Increased tumor necrosis factor and IL-1 beta gene expression in the kidneys of mice with lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):3050–3054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan D. C., Yui M. A., Wuthrich R. P., Kelley V. E. Tumor necrosis factor and IL-1 in New Zealand Black/White mice. Enhanced gene expression and acceleration of renal injury. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3470–3475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carballo E., Lai W. S., Blackshear P. J. Feedback inhibition of macrophage tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by tristetraprolin. Science. 1998 Aug 14;281(5379):1001–1005. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5379.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caver T. E., O'Sullivan F. X., Gold L. I., Gresham H. D. Intracellular demonstration of active TGFbeta1 in B cells and plasma cells of autoimmune mice. IgG-bound TGFbeta1 suppresses neutrophil function and host defense against Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Clin Invest. 1996 Dec 1;98(11):2496–2506. doi: 10.1172/JCI119068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Y., Takeoka Y., Pike-Nobile L., Ansari A. A., Boyd R., Gershwin M. E. Autoantibody production and cytokine profiles of MHC class I (beta2-microglobulin) gene deleted New Zealand black (NZB) mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997 Sep;84(3):318–327. doi: 10.1006/clin.1997.4398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow C. W., Rincón M., Davis R. J. Requirement for transcription factor NFAT in interleukin-2 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Mar;19(3):2300–2307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.3.2300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. L., Cooper S. M., Budd R. C. Abnormal regulation of the IL-2 promoter in lpr CD4-CD8- T lymphocytes results in constitutive expression of a novel nuclear factor of activated T cells-binding factor. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 15;154(12):6372–6381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. L., Wolfe J., Cooper S. M., Budd R. C. Reversal of hyporesponsiveness in lpr CD4-CD8- T cells is achieved by induction of cell cycling and normalization of CD2 and p59fyn expression. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Mar;24(3):558–565. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clynes R., Dumitru C., Ravetch J. V. Uncoupling of immune complex formation and kidney damage in autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Science. 1998 Feb 13;279(5353):1052–1054. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5353.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope A. P., Liblau R. S., Yang X. D., Congia M., Laudanna C., Schreiber R. D., Probert L., Kollias G., McDevitt H. O. Chronic tumor necrosis factor alters T cell responses by attenuating T cell receptor signaling. J Exp Med. 1997 May 5;185(9):1573–1584. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.9.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope A. P. Regulation of autoimmunity by proinflammatory cytokines. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998 Dec;10(6):669–676. doi: 10.1016/s0952-7915(98)80087-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauphinée M. J., Kipper S. B., Wofsy D., Talal N. Interleukin 2 deficiency is a common feature of autoimmune mice. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2483–2487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. F., Calkins C., Hügins A., Giese T., Holmes K. L. Cytokine secretion by C3H-lpr and -gld T cells. Hypersecretion of IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha by stimulated CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4138–4148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. F., Roths J. B., Holmes K. L., Rudikoff E., Morse H. C., 3rd Dissociation of severe lupus-like disease from polyclonal B cell activation and IL 2 deficiency in C3H-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):1048–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi Y., Kishimoto S. Tumour necrosis factor/cachectin plays a key role in autoimmune pulmonary inflammation in lupus-prone mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Sep;85(3):392–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörner T., Hucko M., Mayet W. J., Trefzer U., Burmester G. R., Hiepe F. Enhanced membrane expression of the 52 kDa Ro(SS-A) and La(SS-B) antigens by human keratinocytes induced by TNF alpha. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Nov;54(11):904–909. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.11.904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards C. K., 3rd, Zhou T., Zhang J., Baker T. J., De M., Long R. E., Borcherding D. R., Bowlin T. L., Bluethmann H., Mountz J. D. Inhibition of superantigen-induced proinflammatory cytokine production and inflammatory arthritis in MRL-lpr/lpr mice by a transcriptional inhibitor of TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 1996 Aug 15;157(4):1758–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan X., Oertli B., Wüthrich R. P. Up-regulation of tubular epithelial interleukin-12 in autoimmune MRL-Fas(lpr) mice with renal injury. Kidney Int. 1997 Jan;51(1):79–86. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finck B. K., Chan B., Wofsy D. Interleukin 6 promotes murine lupus in NZB/NZW F1 mice. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):585–591. doi: 10.1172/JCI117373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Hirose S., Jiang Y., Kodera S., Ohmuro H., Zhang D., Hamano Y., Ishida H., Furukawa S., Shirai T. Dissection of the effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and class II gene polymorphisms within the MHC on murine systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Int Immunol. 1998 Oct;10(10):1467–1472. doi: 10.1093/intimm/10.10.1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgescu L., Vakkalanka R. K., Elkon K. B., Crow M. K. Interleukin-10 promotes activation-induced cell death of SLE lymphocytes mediated by Fas ligand. J Clin Invest. 1997 Nov 15;100(10):2622–2633. doi: 10.1172/JCI119806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C., Ranges G. E., Greenspan J. S., Wofsy D. Chronic therapy with recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in autoimmune NZB/NZW F1 mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Sep;52(3):421–434. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon C., Wofsy D. Effects of recombinant murine tumor necrosis factor-alpha on immune function. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1753–1758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Ramos J. C., Andreu J. L., Revilla Y., Viñuela E., Martinez C. Recovery from autoimmunity of MRL/lpr mice after infection with an interleukin-2/vaccinia recombinant virus. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):271–274. doi: 10.1038/346271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas C., Ryffel B., Le Hir M. IFN-gamma is essential for the development of autoimmune glomerulonephritis in MRL/Ipr mice. J Immunol. 1997 Jun 1;158(11):5484–5491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas C., Ryffel B., Le Hir M. IFN-gamma receptor deletion prevents autoantibody production and glomerulonephritis in lupus-prone (NZB x NZW)F1 mice. J Immunol. 1998 Apr 15;160(8):3713–3718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. M., Lunec J. The TNF-ligand and receptor superfamilies: controllers of immunity and the Trojan horses of autoimmune disease? Mol Aspects Med. 1996 Oct;17(5):455–509. doi: 10.1016/s0098-2997(96)00011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Lo D., Glimcher L. H. c-maf promotes T helper cell type 2 (Th2) and attenuates Th1 differentiation by both interleukin 4-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Exp Med. 1998 Nov 16;188(10):1859–1866. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.10.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. P., Feng G. J., Lindop G., Stott D. I., Liew F. Y. The role of interleukin 12 and nitric oxide in the development of spontaneous autoimmune disease in MRL/MP-lpr/lpr mice. J Exp Med. 1996 Apr 1;183(4):1447–1459. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.4.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang F. P., Stott D. I. Restoration of an early, progressive defect in responsiveness to T-cell activation in lupus mice by exogenous IL-2. Autoimmunity. 1993;15(1):19–29. doi: 10.3109/08916939309004835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggins M. L., Huang F. P., Xu D., Lindop G., Stott D. I. Modulation of autoimmune disease in the MRL-lpr/lpr mouse by IL-2 and TGF-beta1 gene therapy using attenuated Salmonella typhimurium as gene carrier. Lupus. 1999;8(1):29–38. doi: 10.1191/096120399678847308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunger R. E., Carnaud C., Garcia I., Vassalli P., Mueller C. Prevention of autoimmune diabetes mellitus in NOD mice by transgenic expression of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor p55. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Jan;27(1):255–261. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunger R. E., Müller S., Laissue J. A., Hess M. W., Carnaud C., Garcia I., Mueller C. Inhibition of submandibular and lacrimal gland infiltration in nonobese diabetic mice by transgenic expression of soluble TNF-receptor p55. J Clin Invest. 1996 Aug 15;98(4):954–961. doi: 10.1172/JCI118879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida H., Muchamuel T., Sakaguchi S., Andrade S., Menon S., Howard M. Continuous administration of anti-interleukin 10 antibodies delays onset of autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):305–310. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Hwang F., Lewis G. D., Stall A. M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in murine systemic lupus erythematosus disease models: implications for genetic predisposition and immune regulation. Cytokine. 1991 Nov;3(6):551–561. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90481-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Lee S. K., Strassmann G. Mutational analysis of TNF-alpha gene reveals a regulatory role for the 3'-untranslated region in the genetic predisposition to lupus-like autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 1996 Apr 15;156(8):3043–3050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., McDevitt H. O. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha in murine autoimmune 'lupus' nephritis. Nature. 1988 Jan 28;331(6154):356–358. doi: 10.1038/331356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Tashman N. B. Disruption in the AU motif of the mouse TNF-alpha 3' UTR correlates with reduced TNF production by macrophages in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 11;21(11):2761–2766. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.11.2761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in autoimmunity: pretty girl or old witch? Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):122–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90107-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., van der Meide P. H., McDevitt H. O. In vivo treatment of (NZB X NZW)F1 lupus-like nephritis with monoclonal antibody to gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):798–803. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalechman Y., Gafter U., Da J. P., Albeck M., Alarcon-Segovia D., Sredni B. Delay in the onset of systemic lupus erythematosus following treatment with the immunomodulator AS101: association with IL-10 inhibition and increase in TNF-alpha levels. J Immunol. 1997 Sep 15;159(6):2658–2667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Gaulton G. N., Hattori M., Ikegami H., Eisenbarth G., Strom T. B. Anti-interleukin 2 receptor antibody suppresses murine diabetic insulitis and lupus nephritis. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):59–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiberd B. A. Interleukin-6 receptor blockage ameliorates murine lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1993 Jul;4(1):58–61. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V4158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiberd B. A., Stadnyk A. W. Established murine lupus nephritis does not respond to exogenous interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; a role for the endogenous molecule? Immunopharmacology. 1995 Aug;30(2):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(95)00014-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebedeva T. V., Singh A. K. Increased responsiveness of B. cells in the murine MRL/lpr model of lupus nephritis to interleukin-1 beta. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995 Jan;5(7):1530–1534. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V571530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang H. E., Hsueh Y. P., Wu C. C., Hsu S. C., Han S. H., Lai M. Z. Atypical signaling defects prevent IL-2 gene expression in lpr/lpr CD4-CD8- cells. J Biomed Sci. 1998 Jul-Aug;5(4):297–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02255862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llorente L., Zou W., Levy Y., Richaud-Patin Y., Wijdenes J., Alcocer-Varela J., Morel-Fourrier B., Brouet J. C., Alarcon-Segovia D., Galanaud P. Role of interleukin 10 in the B lymphocyte hyperactivity and autoantibody production of human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1995 Mar 1;181(3):839–844. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.3.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance J. H., O'Sullivan F. X., Caver T. E., Waegell W., Gresham H. D. Spontaneous elaboration of transforming growth factor beta suppresses host defense against bacterial infection in autoimmune MRL/lpr mice. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1693–1703. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malide D., Russo P., Bendayan M. Presence of tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in renal mesangial cells of lupus nephritis patients. Hum Pathol. 1995 May;26(5):558–564. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C., Singh A. K. IL-1 beta gene expression in B cells derived from the murine MRL/lpr model of lupus. Autoimmunity. 1996;24(2):71–79. doi: 10.3109/08916939609001949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurray R. W., Hoffman R. W., Nelson W., Walker S. E. Cytokine mRNA expression in the B/W mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus--analyses of strain, gender, and age effects. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1997 Sep;84(3):260–268. doi: 10.1006/clin.1997.4390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer C., Huysen V., Smeenk R. T., Swaak A. J. Profiles of cytokines (TNF alpha and IL-6) and acute phase proteins (CRP and alpha 1AG) related to the disease course in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1993 Dec;2(6):359–365. doi: 10.1177/096120339300200605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. J., Yeh K., Naito T., Kelley V. R. TNF-alpha enhances colony-stimulating factor-1-induced macrophage accumulation in autoimmune renal disease. J Immunol. 1996 Jul 1;157(1):427–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima A., Hirose S., Yagita H., Okumura K. Roles of IL-4 and IL-12 in the development of lupus in NZB/W F1 mice. J Immunol. 1997 Feb 1;158(3):1466–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ebihara I., Fukui M., Osada S., Tomino Y., Masaki T., Goto K., Furuichi Y., Koide H. Renal expression of mRNAs for endothelin-1, endothelin-3 and endothelin receptors in NZB/W F1 mice. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1993 Sep-Oct;16(5):233–243. doi: 10.1159/000173768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohteki T., Okamoto S., Nakamura M., Nemoto E., Kumagai K. Elevated production of interleukin 6 by hepatic MNC correlates with ICAM-1 expression on the hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells in autoimmune MRL/lpr mice. Immunol Lett. 1993 May;36(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(93)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen K. L., Shibata T., Izui S., Walker S. E. Recombinant interleukin-2 therapy of systemic lupus erythematosus in the New Zealand black/New Zealand white mouse. J Biol Response Mod. 1989 Aug;8(4):366–374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozmen L., Roman D., Fountoulakis M., Schmid G., Ryffel B., Garotta G. Experimental therapy of systemic lupus erythematosus: the treatment of NZB/W mice with mouse soluble interferon-gamma receptor inhibits the onset of glomerulonephritis. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jan;25(1):6–12. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng S. L., Moslehi J., Craft J. Roles of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4 in murine lupus. J Clin Invest. 1997 Apr 15;99(8):1936–1946. doi: 10.1172/JCI119361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prud'homme G. J., Kono D. H., Theofilopoulos A. N. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis reveals marked overexpression of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-1 and interferon-gamma mRNA in the lymph nodes of lupus-prone mice. Mol Immunol. 1995 May;32(7):495–503. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(95)00024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radvanyi L. G., Raju K., Spaner D., Mills G. B., Miller R. G. Interleukin-2 reverses the defect in activation-induced apoptosis in T cells from autoimmune lpr mice. Cell Immunol. 1998 Jan 10;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1997.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz E., Dudler J., Lotz M., Baird S. M., Berry C. C., Eisenberg R. A., Carson D. A. Modulation of disease activity in murine systemic lupus erythematosus by cytokine gene delivery. Lupus. 1995 Aug;4(4):286–292. doi: 10.1177/096120339500400409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter G., Qin Z. H., Diamantstein T., Blankenstein T. Analysis of restriction fragment length polymorphism in lymphokine genes of normal and autoimmune mice. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1439–1443. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincón M., Enslen H., Raingeaud J., Recht M., Zapton T., Su M. S., Penix L. A., Davis R. J., Flavell R. A. Interferon-gamma expression by Th1 effector T cells mediated by the p38 MAP kinase signaling pathway. EMBO J. 1998 May 15;17(10):2817–2829. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.10.2817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincón M., Flavell R. A. T-cell subsets: transcriptional control in the Th1/Th2 decision. Curr Biol. 1997 Nov 1;7(11):R729–R732. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00368-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel B., Car B. D., Gunn H., Roman D., Hiestand P., Mihatsch M. J. Interleukin-6 exacerbates glomerulonephritis in (NZB x NZW)F1 mice. Am J Pathol. 1994 May;144(5):927–937. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabzevari H., Propp S., Kono D. H., Theofilopoulos A. N. G1 arrest and high expression of cyclin kinase and apoptosis inhibitors in accumulated activated/memory phenotype CD4+ cells of older lupus mice. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Aug;27(8):1901–1910. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadlack B., Löhler J., Schorle H., Klebb G., Haber H., Sickel E., Noelle R. J., Horak I. Generalized autoimmune disease in interleukin-2-deficient mice is triggered by an uncontrolled activation and proliferation of CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Nov;25(11):3053–3059. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago M. L., Fossati L., Jacquet C., Müller W., Izui S., Reininger L. Interleukin-4 protects against a genetically linked lupus-like autoimmune syndrome. J Exp Med. 1997 Jan 6;185(1):65–70. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorlemmer H. U., Kanzy E. J., Langner K. D., Kurrle R. Immunoregulation of SLE-like disease by the IL-1 receptor: disease modifying activity on BDF1 hybrid mice and MRL autoimmune mice. Agents Actions. 1993;39(Spec No):C117–C120. doi: 10.1007/BF01972740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting A., Wada T., Kinoshita K., Tesch G., Kelley V. R. IFN-gamma receptor signaling is essential for the initiation, acceleration, and destruction of autoimmune kidney disease in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice. J Immunol. 1998 Jul 1;161(1):494–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Conover J., Klinman D. M. Increased activation and altered ratio of interferon-gamma: interleukin-4 secreting cells in MRL-lpr/lpr mice. Autoimmunity. 1995;21(2):107–116. doi: 10.3109/08916939508993357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. K., Lebedeva T. V. Interleukin-1 contributes to high level IgG production in the murine MRL/lpr lupus model. Immunol Invest. 1994 Aug;23(4-5):281–292. doi: 10.3109/08820139409066824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh A. K., Mao C., Lebedeva T. V. In vitro role of IL-1 in heightened IgG, anti-DNA, and nephritogenic idiotype production by B cells derived from the murine MRL/lpr lupus model. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Sep;72(3):410–415. doi: 10.1006/clin.1994.1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studnicka-Benke A., Steiner G., Petera P., Smolen J. S. Tumour necrosis factor alpha and its soluble receptors parallel clinical disease and autoimmune activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Nov;35(11):1067–1074. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.11.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su X., Zhou T., Yang P., Edwards C. K., 3rd, Mountz J. D. Reduction of arthritis and pneumonitis in motheaten mice by soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jan;41(1):139–149. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199801)41:1<139::AID-ART17>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kündig T. M., Furlonger C., Wakeham A., Timms E., Matsuyama T., Schmits R., Simard J. J., Ohashi P. S., Griesser H. Deregulated T cell activation and autoimmunity in mice lacking interleukin-2 receptor beta. Science. 1995 Jun 9;268(5216):1472–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.7770771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Fossati L., Iwamoto M., Merino R., Motta R., Kobayakawa T., Izui S. Imbalance towards Th1 predominance is associated with acceleration of lupus-like autoimmune syndrome in MRL mice. J Clin Invest. 1996 Apr 1;97(7):1597–1604. doi: 10.1172/JCI118584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Nagasaka Y., Kitamura F., Kuida K., Suwa H., Miyasaka M. The role of the interleukin-2 (IL-2)/IL-2 receptor pathway in MRL/lpr lymphadenopathy: the expanded CD4-8- T cell subset completely lacks functional IL-2 receptors. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jun;23(6):1378–1380. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. A., Carballo E., Lee D. M., Lai W. S., Thompson M. J., Patel D. D., Schenkman D. I., Gilkeson G. S., Broxmeyer H. E., Haynes B. F. A pathogenetic role for TNF alpha in the syndrome of cachexia, arthritis, and autoimmunity resulting from tristetraprolin (TTP) deficiency. Immunity. 1996 May;4(5):445–454. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80411-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe Y., Jacob C. O. Regulation of MHC class II antigen expression. Opposing effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on IFN-gamma-induced HLA-DR and Ia expression depends on the maturation and differentiation stage of the cell. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):899–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Granger D. L., Pisetsky D. S., Seldin M. F., Misukonis M. A., Mason S. N., Pippen A. M., Ruiz P., Wood E. R., Gilkeson G. S. The role of nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of spontaneous murine autoimmune disease: increased nitric oxide production and nitric oxide synthase expression in MRL-lpr/lpr mice, and reduction of spontaneous glomerulonephritis and arthritis by orally administered NG-monomethyl-L-arginine. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):651–660. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willerford D. M., Chen J., Ferry J. A., Davidson L., Ma A., Alt F. W. Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain regulates the size and content of the peripheral lymphoid compartment. Immunity. 1995 Oct;3(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang X. D., Tisch R., Singer S. M., Cao Z. A., Liblau R. S., Schreiber R. D., McDevitt H. O. Effect of tumor necrosis factor alpha on insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in NOD mice. I. The early development of autoimmunity and the diabetogenic process. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):995–1004. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama H., Kreft B., Kelley V. R. Biphasic increase in circulating and renal TNF-alpha in MRL-lpr mice with differing regulatory mechanisms. Kidney Int. 1995 Jan;47(1):122–130. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng W., Flavell R. A. The transcription factor GATA-3 is necessary and sufficient for Th2 cytokine gene expression in CD4 T cells. Cell. 1997 May 16;89(4):587–596. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]