Abstract
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin 1 (IL1) are considered as master cytokines in chronic, destructive arthritis. Therapeutic approaches in rheumatic arthritis (RA) patients so far mainly focused on TNF. Although TNF is a major inflammatory mediator in RA and a potent inducer of IL1, anti-TNF treatment is not effective in all patients, nor does it fully control the arthritic process in affected joints of good responders. Analysis of cytokine patterns in early synovial biopsy specimens of RA patients reveals prominent TNF staining in 50% of the patients, whereas IL1b staining was evident in 100%. This argues that TNF independent IL1 production occurs in some of the patients. Studies in a range of experimental arthritis models in mice make it clear that TNF is involved in early joint swelling. However, TNF alone is not arthritogenic nor destructive and exerts its arthritogenic potential through IL1 induction. Intriguingly, TNF independent IL1 production is found in many models. Its relevance is further underlined by the greater efficacy of anti-IL1 treatment as compared with anti-TNF treatment and the total lack of chronic, erosive arthritis in IL1b deficient mice. IL1b is not necessarily involved in early joint swelling, but is a crucial mediator in chronic arthritis and cartilage erosion in all models studied so far. This makes ILb an attractive target in chronic, destructive arthritis.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (102.1 KB).
Figure 1 .
IL1b levels in tissue washouts six hours after injection of SCW fragments into the knee joint of mice. The first set depicts IL1 levels in control and anti-TNFa treated mice (see also van den Berg6). The second set depicts values in control and TNF-/- mice. Although some reduction is consistently noted in TNF -/- mice, it does not reach statistical significance, implying that most of the IL1 is produced in a TNF independent fashion.
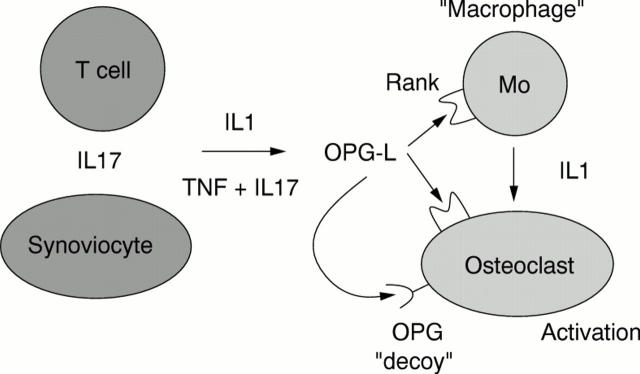
Figure 2 .
Simplified version of cytokine involvement in osteoclast activation.
Figure 3 .
Potential pathways of TNF overproduction. Note that general T cell/macrophage triggering, as studied in arthritis models, gives rise to both TNF and IL1, with considerable TNF independent IL1 production, and extreme skewing to IL1 when immune complexes are used as stimulus.
Figure 4 .
Amplifying elements in erosive processes. Immune complexes generate high levels of IL1 and through Fc interaction also provide additional mediators to activate pro-MMPs (metalloproteinases). T cells may be involved in enhanced bone erosion through TNF, IL17 and direct OPG-L production. T cells come close to the bone at erosion sites. IL17 also promotes cartilage erosion, a role of OPG-L in this remains to be seen.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakker A. C., Joosten L. A., Arntz O. J., Helsen M. M., Bendele A. M., van de Loo F. A., van den Berg W. B. Prevention of murine collagen-induced arthritis in the knee and ipsilateral paw by local expression of human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein in the knee. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 May;40(5):893–900. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Chantry D., Jackson A., Maini R., Feldmann M. Inhibitory effect of TNF alpha antibodies on synovial cell interleukin-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1989 Jul 29;2(8657):244–247. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Cobby M., Doherty M., Domljan Z., Emery P., Nuki G., Pavelka K., Rau R., Rozman B. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Dec;41(12):2196–2204. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199812)41:12<2196::AID-ART15>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horai R., Saijo S., Tanioka H., Nakae S., Sudo K., Okahara A., Ikuse T., Asano M., Iwakura Y. Development of chronic inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in interleukin 1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 2000 Jan 17;191(2):313–320. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Lacey D. L., Dunstan C. R., Solovyev I., Colombero A., Timms E., Tan H. L., Elliott G., Kelley M. J., Sarosi I. Tumor necrosis factor receptor family member RANK mediates osteoclast differentiation and activation induced by osteoprotegerin ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 30;96(7):3540–3545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joosten L. A., Helsen M. M., Saxne T., van De Loo F. A., Heinegard D., van Den Berg W. B. IL-1 alpha beta blockade prevents cartilage and bone destruction in murine type II collagen-induced arthritis, whereas TNF-alpha blockade only ameliorates joint inflammation. J Immunol. 1999 Nov 1;163(9):5049–5055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joosten L. A., Helsen M. M., van de Loo F. A., van den Berg W. B. Anticytokine treatment of established type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. A comparative study using anti-TNF alpha, anti-IL-1 alpha/beta, and IL-1Ra. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 May;39(5):797–809. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkham B., Portek I., Lee C. S., Stavros B., Lenarczyk A., Lassere M., Edmonds J. Intraarticular variability of synovial membrane histology, immunohistology, and cytokine mRNA expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1999 Apr;26(4):777–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korganow A. S., Ji H., Mangialaio S., Duchatelle V., Pelanda R., Martin T., Degott C., Kikutani H., Rajewsky K., Pasquali J. L. From systemic T cell self-reactivity to organ-specific autoimmune disease via immunoglobulins. Immunity. 1999 Apr;10(4):451–461. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuiper S., Joosten L. A., Bendele A. M., Edwards C. K., 3rd, Arntz O. J., Helsen M. M., Van de Loo F. A., Van den Berg W. B. Different roles of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 in murine streptococcal cell wall arthritis. Cytokine. 1998 Sep;10(9):690–702. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1998.0372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubberts E., Joosten L. A., Chabaud M., van Den Bersselaar L., Oppers B., Coenen-De Roo C. J., Richards C. D., Miossec P., van Den Berg W. B. IL-4 gene therapy for collagen arthritis suppresses synovial IL-17 and osteoprotegerin ligand and prevents bone erosion. J Clin Invest. 2000 Jun;105(12):1697–1710. doi: 10.1172/JCI7739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubberts E., Joosten L. A., van Den Bersselaar L., Helsen M. M., Bakker A. C., van Meurs J. B., Graham F. L., Richards C. D., van Den Berg W. B. Adenoviral vector-mediated overexpression of IL-4 in the knee joint of mice with collagen-induced arthritis prevents cartilage destruction. J Immunol. 1999 Oct 15;163(8):4546–4556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y., Thornton S., Boivin G. P., Hirsh D., Hirsch R., Hirsch E. Altered susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis in transgenic mice with aberrant expression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Oct;41(10):1798–1805. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199810)41:10<1798::AID-ART11>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probert L., Plows D., Kontogeorgos G., Kollias G. The type I interleukin-1 receptor acts in series with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) to induce arthritis in TNF-transgenic mice. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Jun;25(6):1794–1797. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Brown R. R., Dalldorf F. G., Thompson R. C. Pro- and anti-inflammatory roles of interleukin-1 in recurrence of bacterial cell wall-induced arthritis in rats. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4436–4442. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4436-4442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lent P. L., Van De Loo F. A., Holthuysen A. E., Van Den Bersselaar L. A., Vermeer H., Van Den Berg W. B. Major role for interleukin 1 but not for tumor necrosis factor in early cartilage damage in immune complex arthritis in mice. J Rheumatol. 1995 Dec;22(12):2250–2258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9784–9788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Dutcher J., Widmer M. B., Gillis S. Influence of a recombinant human soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor FC fusion protein on type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 1;151(11):6602–6607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Whalen J. D., Chapman D. L., Berger A. E., Richard K. A., Aspar D. G., Staite N. D. The effect of an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein on type II collagen-induced arthritis and antigen-induced arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Sep;36(9):1305–1314. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lent P. L., van Vuuren A. J., Blom A. B., Holthuysen A. E., van de Putte L. B., van de Winkel J. G., van den Berg W. B. Role of Fc receptor gamma chain in inflammation and cartilage damage during experimental antigen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Apr;43(4):740–752. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<740::AID-ANR4>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meurs J. B., van Lent P. L., Holthuysen A. E., Singer I. I., Bayne E. K., van den Berg W. B. Kinetics of aggrecanase- and metalloproteinase-induced neoepitopes in various stages of cartilage destruction in murine arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jun;42(6):1128–1139. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1128::AID-ANR9>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meurs J. B., van Lent P. L., Singer I. I., Bayne E. K., van de Loo F. A., van den Berg W. B. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist prevents expression of the metalloproteinase-generated neoepitope VDIPEN in antigen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Apr;41(4):647–656. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199804)41:4<647::AID-ART11>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meurs J., van Lent P., Holthuysen A., Lambrou D., Bayne E., Singer I., van den Berg W. Active matrix metalloproteinases are present in cartilage during immune complex-mediated arthritis: a pivotal role for stromelysin-1 in cartilage destruction. J Immunol. 1999 Nov 15;163(10):5633–5639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meurs J., van Lent P., Stoop R., Holthuysen A., Singer I., Bayne E., Mudgett J., Poole R., Billinghurst C., van der Kraan P. Cleavage of aggrecan at the Asn341-Phe342 site coincides with the initiation of collagen damage in murine antigen-induced arthritis: a pivotal role for stromelysin 1 in matrix metalloproteinase activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Oct;42(10):2074–2084. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199910)42:10<2074::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Loo A. A., Arntz O. J., Bakker A. C., van Lent P. L., Jacobs M. J., van den Berg W. B. Role of interleukin 1 in antigen-induced exacerbations of murine arthritis. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jan;146(1):239–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Loo A. A., van den Berg W. B. Effects of murine recombinant interleukin 1 on synovial joints in mice: measurement of patellar cartilage metabolism and joint inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990 Apr;49(4):238–245. doi: 10.1136/ard.49.4.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Loo F. A., Joosten L. A., van Lent P. L., Arntz O. J., van den Berg W. B. Role of interleukin-1, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-6 in cartilage proteoglycan metabolism and destruction. Effect of in situ blocking in murine antigen- and zymosan-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Feb;38(2):164–172. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., Bresnihan B. Pathogenesis of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence of a dominant role for interleukin-I. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 1999 Dec;13(4):577–597. doi: 10.1053/berh.1999.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B. Joint inflammation and cartilage destruction may occur uncoupled. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1998;20(1-2):149–164. doi: 10.1007/BF00832004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., Joosten L. A., Helsen M., van de Loo F. A. Amelioration of established murine collagen-induced arthritis with anti-IL-1 treatment. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Feb;95(2):237–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]