Abstract
Tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is a pleiotropic cytokine that mediates apoptosis, cell proliferation, immunomodulation, inflammation, viral replication, allergy, arthritis, septic shock, insulin resistance, autoimmune diseases, and other pathological conditions. TNF transduces these cellular responses through two distinct receptors: type I, which are expressed on all cell types, and type II, which are expressed only on cells of the immune system and endothelial cells. At the cellular level, these receptors activate the pathways leading to the activation of transcription factors NF-κB and AP-1, apoptosis and proliferation, and mitogen activated protein kinases. None of these receptors exhibit any enzymatic activity but the signals are transmitted through the recruitment of more than a dozen different signalling proteins, which together form signalling cascades. Inhibitors of TNF signalling have therapeutic value as indicated by the approval of the soluble TNF receptors and anti-TNF antibodies for rheumatoid arthritis and for inflammatory bowl disease.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (160.1 KB).
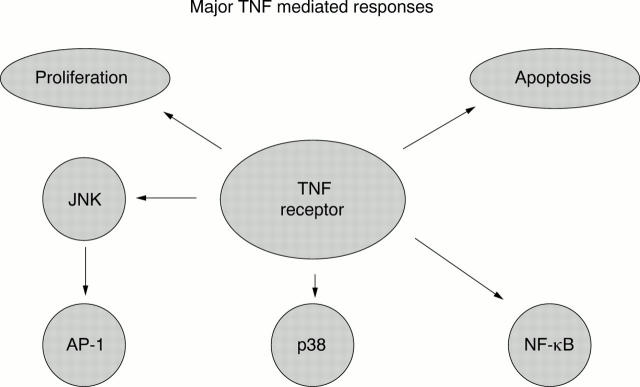
Figure 1 .
Major TNF receptor mediated cellular responses.
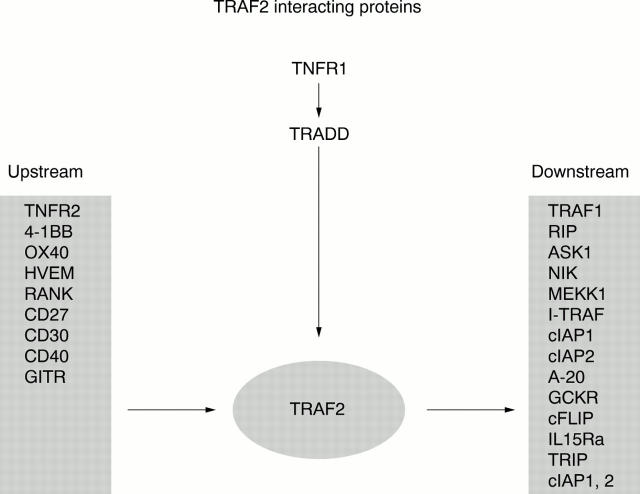
Figure 2 .
Interaction of TRAF2 with upstream and downstream signalling proteins.
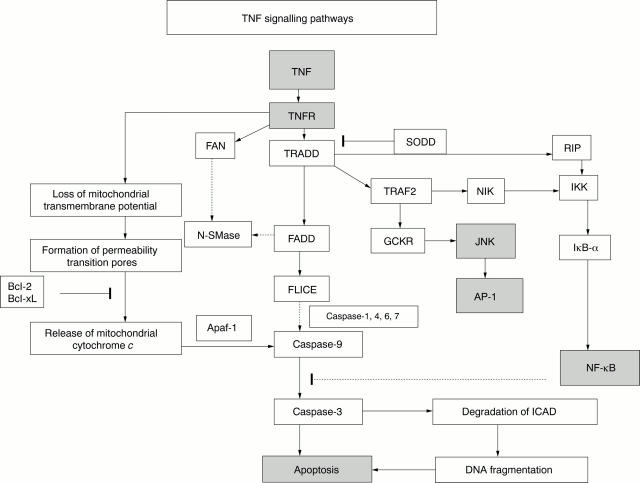
Figure 3 .
TNF signalling pathways leading to the activation of apoptosis, NF-kB, JNK and AP-1.
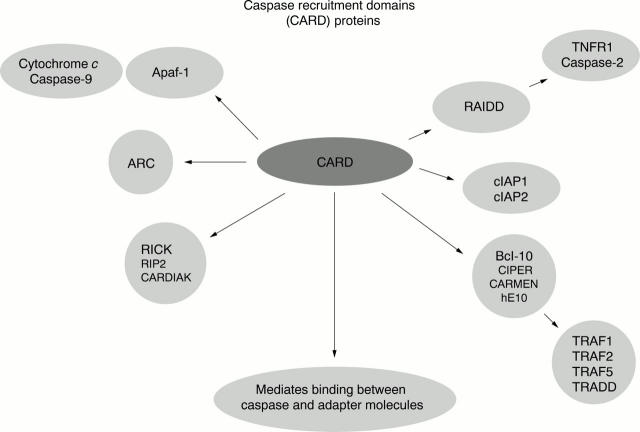
Figure 4 .
Interaction of various caspase recruitment domain (CARD) proteins.
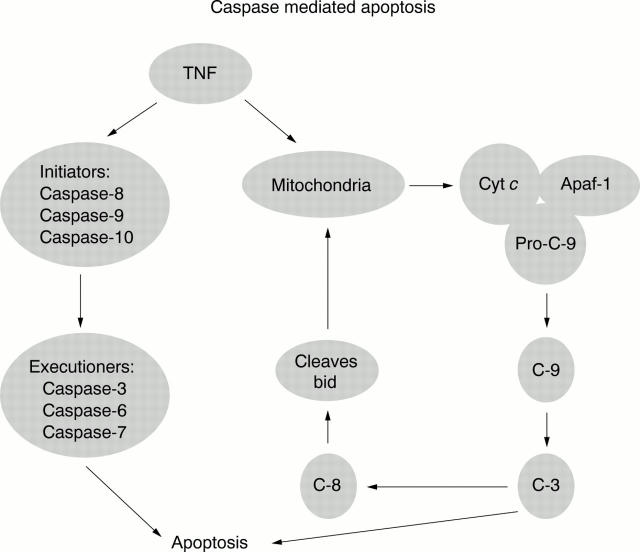
Figure 5 .
Role of various caspases in TNF induced apoptosis.
Figure 6 .
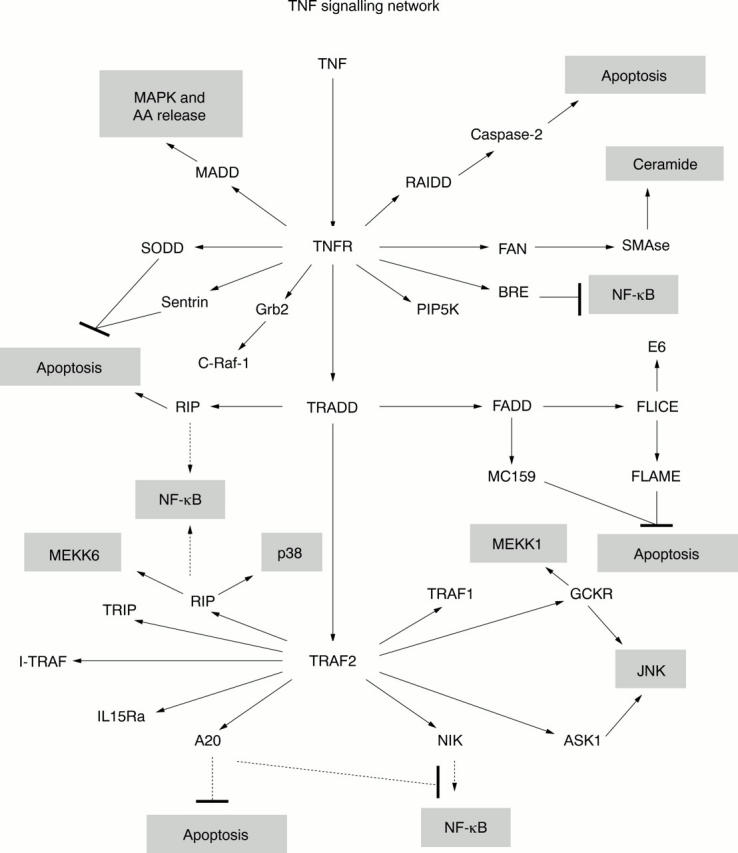
A network of TNF signalling proteins leading to various cellular responses.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam-Klages S., Adam D., Wiegmann K., Struve S., Kolanus W., Schneider-Mergener J., Krönke M. FAN, a novel WD-repeat protein, couples the p55 TNF-receptor to neutral sphingomyelinase. Cell. 1996 Sep 20;86(6):937–947. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80169-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal B. B., Eessalu T. E., Hass P. E. Characterization of receptors for human tumour necrosis factor and their regulation by gamma-interferon. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):665–667. doi: 10.1038/318665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal B. B., Kohr W. J., Hass P. E., Moffat B., Spencer S. A., Henzel W. J., Bringman T. S., Nedwin G. E., Goeddel D. V., Harkins R. N. Human tumor necrosis factor. Production, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2345–2354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal B. B., Natarajan K. Tumor necrosis factors: developments during the last decade. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1996 Apr-Jun;7(2):93–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad M., Srinivasula S. M., Wang L., Talanian R. V., Litwack G., Fernandes-Alnemri T., Alnemri E. S. CRADD, a novel human apoptotic adaptor molecule for caspase-2, and FasL/tumor necrosis factor receptor-interacting protein RIP. Cancer Res. 1997 Feb 15;57(4):615–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baud V., Liu Z. G., Bennett B., Suzuki N., Xia Y., Karin M. Signaling by proinflammatory cytokines: oligomerization of TRAF2 and TRAF6 is sufficient for JNK and IKK activation and target gene induction via an amino-terminal effector domain. Genes Dev. 1999 May 15;13(10):1297–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.10.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron L., Perez G. I., Macdonald G., Shi L., Sun Y., Jurisicova A., Varmuza S., Latham K. E., Flaws J. A., Salter J. C. Defects in regulation of apoptosis in caspase-2-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 1998 May 1;12(9):1304–1314. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.9.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldin M. P., Goncharov T. M., Goltsev Y. V., Wallach D. Involvement of MACH, a novel MORT1/FADD-interacting protease, in Fas/APO-1- and TNF receptor-induced cell death. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):803–815. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boldin M. P., Varfolomeev E. E., Pancer Z., Mett I. L., Camonis J. H., Wallach D. A novel protein that interacts with the death domain of Fas/APO1 contains a sequence motif related to the death domain. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):7795–7798. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.14.7795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino A. M., Parker G. J., Boronenkov I. V., Anderson R. A., Chao M. V. A novel interaction between the juxtamembrane region of the p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor and phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1997 Feb 28;272(9):5861–5870. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.5861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin A. I., Shu J., Shan Shi C., Yao Z., Kehrl J. H., Cheng G. TANK potentiates tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase activation through the germinal center kinase pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;19(10):6665–6672. doi: 10.1128/mcb.19.10.6665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnaiyan A. M., O'Rourke K., Tewari M., Dixit V. M. FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):505–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90071-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delhase M., Hayakawa M., Chen Y., Karin M. Positive and negative regulation of IkappaB kinase activity through IKKbeta subunit phosphorylation. Science. 1999 Apr 9;284(5412):309–313. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5412.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deveraux Q. L., Takahashi R., Salvesen G. S., Reed J. C. X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature. 1997 Jul 17;388(6639):300–304. doi: 10.1038/40901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devin A., Cook A., Lin Y., Rodriguez Y., Kelliher M., Liu Z. The distinct roles of TRAF2 and RIP in IKK activation by TNF-R1: TRAF2 recruits IKK to TNF-R1 while RIP mediates IKK activation. Immunity. 2000 Apr;12(4):419–429. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douni E., Kollias G. A critical role of the p75 tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75TNF-R) in organ inflammation independent of TNF, lymphotoxin alpha, or the p55TNF-R. J Exp Med. 1998 Oct 5;188(7):1343–1352. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.7.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan H., Dixit V. M. RAIDD is a new 'death' adaptor molecule. Nature. 1997 Jan 2;385(6611):86–89. doi: 10.1038/385086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enari M., Sakahira H., Yokoyama H., Okawa K., Iwamatsu A., Nagata S. A caspase-activated DNase that degrades DNA during apoptosis, and its inhibitor ICAD. Nature. 1998 Jan 1;391(6662):43–50. doi: 10.1038/34112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Aderka D., Rubinstein M., Rotman D., Wallach D. A tumor necrosis factor-binding protein purified to homogeneity from human urine protects cells from tumor necrosis factor toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11974–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson S. L., de Sauvage F. J., Kikly K., Carver-Moore K., Pitts-Meek S., Gillett N., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Goeddel D. V., Moore M. W. Decreased sensitivity to tumour-necrosis factor but normal T-cell development in TNF receptor-2-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 Dec 8;372(6506):560–563. doi: 10.1038/372560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes-Alnemri T., Litwack G., Alnemri E. S. CPP32, a novel human apoptotic protein with homology to Caenorhabditis elegans cell death protein Ced-3 and mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30761–30764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goeddel D. V., Aggarwal B. B., Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Nedwin G. E., Palladino M. A., Patton J. S., Pennica D., Shepard H. M., Sugarman B. J. Tumor necrosis factors: gene structure and biological activities. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):597–609. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu C., Castellino A., Chan J. Y., Chao M. V. BRE: a modulator of TNF-alpha action. FASEB J. 1998 Sep;12(12):1101–1108. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.12.12.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakem R., Hakem A., Duncan G. S., Henderson J. T., Woo M., Soengas M. S., Elia A., de la Pompa J. L., Kagi D., Khoo W. Differential requirement for caspase 9 in apoptotic pathways in vivo. Cell. 1998 Aug 7;94(3):339–352. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han D. K., Chaudhary P. M., Wright M. E., Friedman C., Trask B. J., Riedel R. T., Baskin D. G., Schwartz S. M., Hood L. MRIT, a novel death-effector domain-containing protein, interacts with caspases and BclXL and initiates cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Oct 14;94(21):11333–11338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.21.11333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haridas V., Darnay B. G., Natarajan K., Heller R., Aggarwal B. B. Overexpression of the p80 TNF receptor leads to TNF-dependent apoptosis, nuclear factor-kappa B activation, and c-Jun kinase activation. J Immunol. 1998 Apr 1;160(7):3152–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildt E., Oess S. Identification of Grb2 as a novel binding partner of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor I. J Exp Med. 1999 Jun 7;189(11):1707–1714. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Huang J., Shu H. B., Baichwal V., Goeddel D. V. TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity. 1996 Apr;4(4):387–396. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Shu H. B., Pan M. G., Goeddel D. V. TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):299–308. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80984-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Xiong J., Goeddel D. V. The TNF receptor 1-associated protein TRADD signals cell death and NF-kappa B activation. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):495–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S., Vincenz C., Buller M., Dixit V. M. A novel family of viral death effector domain-containing molecules that inhibit both CD-95- and tumor necrosis factor receptor-1-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997 Apr 11;272(15):9621–9624. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.15.9621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y., Baud V., Delhase M., Zhang P., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Johnson R., Karin M. Abnormal morphogenesis but intact IKK activation in mice lacking the IKKalpha subunit of IkappaB kinase. Science. 1999 Apr 9;284(5412):316–320. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5412.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inohara N., Koseki T., Hu Y., Chen S., Núez G. CLARP, a death effector domain-containing protein interacts with caspase-8 and regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Sep 30;94(20):10717–10722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.10717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inohara N., del Peso L., Koseki T., Chen S., Núez G. RICK, a novel protein kinase containing a caspase recruitment domain, interacts with CLARP and regulates CD95-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1998 May 15;273(20):12296–12300. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.20.12296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irmler M., Thome M., Hahne M., Schneider P., Hofmann K., Steiner V., Bodmer J. L., Schröter M., Burns K., Mattmann C. Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature. 1997 Jul 10;388(6638):190–195. doi: 10.1038/40657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., Woronicz J. D., Liu W., Goeddel D. V. Prevention of constitutive TNF receptor 1 signaling by silencer of death domains. Science. 1999 Jan 22;283(5401):543–546. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5401.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelliher M. A., Grimm S., Ishida Y., Kuo F., Stanger B. Z., Leder P. The death domain kinase RIP mediates the TNF-induced NF-kappaB signal. Immunity. 1998 Mar;8(3):297–303. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80535-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno T., Brewer M. T., Baker S. L., Schwartz P. E., King M. W., Hale K. K., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Vannice J. L. A second tumor necrosis factor receptor gene product can shed a naturally occurring tumor necrosis factor inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8331–8335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreder D., Krut O., Adam-Klages S., Wiegmann K., Scherer G., Plitz T., Jensen J. M., Proksch E., Steinmann J., Pfeffer K. Impaired neutral sphingomyelinase activation and cutaneous barrier repair in FAN-deficient mice. EMBO J. 1999 May 4;18(9):2472–2479. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.9.2472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuida K., Haydar T. F., Kuan C. Y., Gu Y., Taya C., Karasuyama H., Su M. S., Rakic P., Flavell R. A. Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell. 1998 Aug 7;94(3):325–337. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81476-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuida K., Lippke J. A., Ku G., Harding M. W., Livingston D. J., Su M. S., Flavell R. A. Altered cytokine export and apoptosis in mice deficient in interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):2000–2003. doi: 10.1126/science.7535475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuida K., Zheng T. S., Na S., Kuan C., Yang D., Karasuyama H., Rakic P., Flavell R. A. Decreased apoptosis in the brain and premature lethality in CPP32-deficient mice. Nature. 1996 Nov 28;384(6607):368–372. doi: 10.1038/384368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz M., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Characterization in vitro of a human tumor necrosis factor-binding protein. A soluble form of a tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1396–1402. doi: 10.1172/JCI114853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Lee S. Y., Choi Y. TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP): a novel component of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)- and CD30-TRAF signaling complexes that inhibits TRAF2-mediated NF-kappaB activation. J Exp Med. 1997 Apr 7;185(7):1275–1285. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.7.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Reichlin A., Santana A., Sokol K. A., Nussenzweig M. C., Choi Y. TRAF2 is essential for JNK but not NF-kappaB activation and regulates lymphocyte proliferation and survival. Immunity. 1997 Nov;7(5):703–713. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Bergeron L., Cryns V., Pasternack M. S., Zhu H., Shi L., Greenberg A., Yuan J. Activation of caspase-2 in apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 22;272(34):21010–21017. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.34.21010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Van Antwerp D., Mercurio F., Lee K. F., Verma I. M. Severe liver degeneration in mice lacking the IkappaB kinase 2 gene. Science. 1999 Apr 9;284(5412):321–325. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5412.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. W., Chu W., Hu Y., Delhase M., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Johnson R., Karin M. The IKKbeta subunit of IkappaB kinase (IKK) is essential for nuclear factor kappaB activation and prevention of apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1999 Jun 7;189(11):1839–1845. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling L., Cao Z., Goeddel D. V. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activates IKK-alpha by phosphorylation of Ser-176. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 31;95(7):3792–3797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Tabuchi H., Lesslauer W. Molecular cloning and expression of the human 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90815-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo X., Budihardjo I., Zou H., Slaughter C., Wang X. Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell. 1998 Aug 21;94(4):481–490. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81589-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinin N. L., Boldin M. P., Kovalenko A. V., Wallach D. MAP3K-related kinase involved in NF-kappaB induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature. 1997 Feb 6;385(6616):540–544. doi: 10.1038/385540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. A., Siegel R. M., Zheng L., Lenardo M. J. Membrane oligomerization and cleavage activates the caspase-8 (FLICE/MACHalpha1) death signal. J Biol Chem. 1998 Feb 20;273(8):4345–4349. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.8.4345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. V., Ni J., Dixit V. M. RIP2 is a novel NF-kappaB-activating and cell death-inducing kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jul 3;273(27):16968–16975. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.27.16968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muzio M., Chinnaiyan A. M., Kischkel F. C., O'Rourke K., Shevchenko A., Ni J., Scaffidi C., Bretz J. D., Zhang M., Gentz R. FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death--inducing signaling complex. Cell. 1996 Jun 14;85(6):817–827. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81266-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natoli G., Costanzo A., Moretti F., Fulco M., Balsano C., Levrero M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor 1 signaling downstream of TNF receptor-associated factor 2. Nuclear factor kappaB (NFkappaB)-inducing kinase requirement for activation of activating protein 1 and NFkappaB but not of c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 17;272(42):26079–26082. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.42.26079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navas T. A., Baldwin D. T., Stewart T. A. RIP2 is a Raf1-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999 Nov 19;274(47):33684–33690. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.47.33684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishitoh H., Saitoh M., Mochida Y., Takeda K., Nakano H., Rothe M., Miyazono K., Ichijo H. ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2. Mol Cell. 1998 Sep;2(3):389–395. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nophar Y., Kemper O., Brakebusch C., Englemann H., Zwang R., Aderka D., Holtmann H., Wallach D. Soluble forms of tumor necrosis factor receptors (TNF-Rs). The cDNA for the type I TNF-R, cloned using amino acid sequence data of its soluble form, encodes both the cell surface and a soluble form of the receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3269–3278. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okura T., Gong L., Kamitani T., Wada T., Okura I., Wei C. F., Chang H. M., Yeh E. T. Protection against Fas/APO-1- and tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death by a novel protein, sentrin. J Immunol. 1996 Nov 15;157(10):4277–4281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Lantz M., Nilsson E., Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Adolf G. Isolation and characterization of a tumor necrosis factor binding protein from urine. Eur J Haematol. 1989 Mar;42(3):270–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1989.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opipari A. W., Jr, Hu H. M., Yabkowitz R., Dixit V. M. The A20 zinc finger protein protects cells from tumor necrosis factor cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12424–12427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Nedwin G. E., Hayflick J. S., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R., Palladino M. A., Kohr W. J., Aggarwal B. B., Goeddel D. V. Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):724–729. doi: 10.1038/312724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Matsuyama T., Kündig T. M., Wakeham A., Kishihara K., Shahinian A., Wiegmann K., Ohashi P. S., Krönke M., Mak T. W. Mice deficient for the 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor are resistant to endotoxic shock, yet succumb to L. monocytogenes infection. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90134-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe J., Lesslauer W., Lötscher H., Lang Y., Koebel P., Köntgen F., Althage A., Zinkernagel R., Steinmetz M., Bluethmann H. Mice lacking the tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 are resistant to TNF-mediated toxicity but highly susceptible to infection by Listeria monocytogenes. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):798–802. doi: 10.1038/364798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Pan M. G., Henzel W. J., Ayres T. M., Goeddel D. V. The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins. Cell. 1995 Dec 29;83(7):1243–1252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Sarma V., Dixit V. M., Goeddel D. V. TRAF2-mediated activation of NF-kappa B by TNF receptor 2 and CD40. Science. 1995 Sep 8;269(5229):1424–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.7544915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Sarma V., Dixit V. M., Goeddel D. V. TRAF2-mediated activation of NF-kappa B by TNF receptor 2 and CD40. Science. 1995 Sep 8;269(5229):1424–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.7544915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Wong S. C., Henzel W. J., Goeddel D. V. A novel family of putative signal transducers associated with the cytoplasmic domain of the 75 kDa tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):681–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Xiong J., Shu H. B., Williamson K., Goddard A., Goeddel D. V. I-TRAF is a novel TRAF-interacting protein that regulates TRAF-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Aug 6;93(16):8241–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.16.8241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Régnier C. H., Song H. Y., Gao X., Goeddel D. V., Cao Z., Rothe M. Identification and characterization of an IkappaB kinase. Cell. 1997 Jul 25;90(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G. S., Dixit V. M. Caspase activation: the induced-proximity model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Sep 28;96(20):10964–10967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.10964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scaffidi C., Medema J. P., Krammer P. H., Peter M. E. FLICE is predominantly expressed as two functionally active isoforms, caspase-8/a and caspase-8/b. J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 24;272(43):26953–26958. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.43.26953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schievella A. R., Chen J. H., Graham J. R., Lin L. L. MADD, a novel death domain protein that interacts with the type 1 tumor necrosis factor receptor and activates mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1997 May 2;272(18):12069–12075. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.18.12069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11966–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Zhang J. H., Hauptmann B., Dayer J. M. Characterization of a tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) inhibitor: evidence of immunological cross-reactivity with the TNF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5188–5192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkura R., Kitada K., Matsuda F., Tashiro K., Ikuta K., Suzuki M., Kogishi K., Serikawa T., Honjo T. Alymphoplasia is caused by a point mutation in the mouse gene encoding Nf-kappa b-inducing kinase. Nat Genet. 1999 May;22(1):74–77. doi: 10.1038/8780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. B., Halpin D. R., Goeddel D. V. Casper is a FADD- and caspase-related inducer of apoptosis. Immunity. 1997 Jun;6(6):751–763. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80450-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu H. B., Takeuchi M., Goeddel D. V. The tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 signal transducers TRAF2 and c-IAP1 are components of the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Nov 26;93(24):13973–13978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.24.13973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Davis T., Anderson D., Solam L., Beckmann M. P., Jerzy R., Dower S. K., Cosman D., Goodwin R. G. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990 May 25;248(4958):1019–1023. doi: 10.1126/science.2160731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song H. Y., Rothe M., Goeddel D. V. The tumor necrosis factor-inducible zinc finger protein A20 interacts with TRAF1/TRAF2 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 25;93(13):6721–6725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.13.6721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song H. Y., Régnier C. H., Kirschning C. J., Goeddel D. V., Rothe M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated kinase cascades: bifurcation of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK) pathways at TNF receptor-associated factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Sep 2;94(18):9792–9796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.18.9792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser D. E., Bachmann M. F., Frick T. W., McKall-Faienza K., Griffiths E., Pfeffer K., Mak T. W., Ohashi P. S. TNF receptor p55 controls early acute graft-versus-host disease. J Immunol. 1997 Jun 1;158(11):5185–5190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasula S. M., Ahmad M., Ottilie S., Bullrich F., Banks S., Wang Y., Fernandes-Alnemri T., Croce C. M., Litwack G., Tomaselli K. J. FLAME-1, a novel FADD-like anti-apoptotic molecule that regulates Fas/TNFR1-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997 Jul 25;272(30):18542–18545. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.30.18542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanger B. Z., Leder P., Lee T. H., Kim E., Seed B. RIP: a novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-1 (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell. 1995 May 19;81(4):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber G. B., Aiyer R. A., Aggarwal B. B. Human tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor. Purification by immunoaffinity chromatography and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19098–19104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., Lee J., Navas T., Baldwin D. T., Stewart T. A., Dixit V. M. RIP3, a novel apoptosis-inducing kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999 Jun 11;274(24):16871–16875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.24.16871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Fuentes M. E., Yamaguchi K., Durnin M. H., Dalrymple S. A., Hardy K. L., Goeddel D. V. Embryonic lethality, liver degeneration, and impaired NF-kappa B activation in IKK-beta-deficient mice. Immunity. 1999 Apr;10(4):421–429. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia L. A., Ayres T. M., Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. A novel domain within the 55 kd TNF receptor signals cell death. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):845–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Quan L. T., O'Rourke K., Desnoyers S., Zeng Z., Beidler D. R., Poirier G. G., Salvesen G. S., Dixit V. M. Yama/CPP32 beta, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90541-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Wolf F. W., Seldin M. F., O'Shea K. S., Dixit V. M., Turka L. A. Lymphoid expression and regulation of A20, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 15;154(4):1699–1706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thome M., Hofmann K., Burns K., Martinon F., Bodmer J. L., Mattmann C., Tschopp J. Identification of CARDIAK, a RIP-like kinase that associates with caspase-1. Curr Biol. 1998 Jul 16;8(15):885–888. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(07)00352-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ting A. T., Pimentel-Muiños F. X., Seed B. RIP mediates tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 activation of NF-kappaB but not Fas/APO-1-initiated apoptosis. EMBO J. 1996 Nov 15;15(22):6189–6196. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varfolomeev E. E., Schuchmann M., Luria V., Chiannilkulchai N., Beckmann J. S., Mett I. L., Rebrikov D., Brodianski V. M., Kemper O. C., Kollet O. Targeted disruption of the mouse Caspase 8 gene ablates cell death induction by the TNF receptors, Fas/Apo1, and DR3 and is lethal prenatally. Immunity. 1998 Aug;9(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80609-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B., Fujisawa H., Zhuang L., Kondo S., Shivji G. M., Kim C. S., Mak T. W., Sauder D. N. Depressed Langerhans cell migration and reduced contact hypersensitivity response in mice lacking TNF receptor p75. J Immunol. 1997 Dec 15;159(12):6148–6155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Mayo M. W., Korneluk R. G., Goeddel D. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science. 1998 Sep 11;281(5383):1680–1683. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts A. D., Hunt N. H., Wanigasekara Y., Bloomfield G., Wallach D., Roufogalis B. D., Chaudhri G. A casein kinase I motif present in the cytoplasmic domain of members of the tumour necrosis factor ligand family is implicated in 'reverse signalling'. EMBO J. 1999 Apr 15;18(8):2119–2126. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.8.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo M., Hakem R., Soengas M. S., Duncan G. S., Shahinian A., Kägi D., Hakem A., McCurrach M., Khoo W., Kaufman S. A. Essential contribution of caspase 3/CPP32 to apoptosis and its associated nuclear changes. Genes Dev. 1998 Mar 15;12(6):806–819. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.6.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woronicz J. D., Gao X., Cao Z., Rothe M., Goeddel D. V. IkappaB kinase-beta: NF-kappaB activation and complex formation with IkappaB kinase-alpha and NIK. Science. 1997 Oct 31;278(5339):866–869. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5339.866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka S., Courtois G., Bessia C., Whiteside S. T., Weil R., Agou F., Kirk H. E., Kay R. J., Israël A. Complementation cloning of NEMO, a component of the IkappaB kinase complex essential for NF-kappaB activation. Cell. 1998 Jun 26;93(7):1231–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. C., Shahinian A., Speiser D., Kraunus J., Billia F., Wakeham A., de la Pompa J. L., Ferrick D., Hum B., Iscove N. Early lethality, functional NF-kappaB activation, and increased sensitivity to TNF-induced cell death in TRAF2-deficient mice. Immunity. 1997 Nov;7(5):715–725. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80391-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. C., de la Pompa J. L., McCurrach M. E., Shu H. B., Elia A. J., Shahinian A., Ng M., Wakeham A., Khoo W., Mitchell K. FADD: essential for embryo development and signaling from some, but not all, inducers of apoptosis. Science. 1998 Mar 20;279(5358):1954–1958. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5358.1954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Kong Y. Y., Yoshida R., Elia A. J., Hakem A., Hakem R., Penninger J. M., Mak T. W. Apaf1 is required for mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and brain development. Cell. 1998 Sep 18;94(6):739–750. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81733-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa T., Ohno S., Kehrl J. H., Kyriakis J. M. Tumor necrosis factor signaling to stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK)/Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38. Germinal center kinase couples TRAF2 to mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase kinase 1 and SAPK while receptor interacting protein associates with a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase upstream of MKK6 and p38. J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 28;273(35):22681–22692. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.35.22681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zandi E., Rothwarf D. M., Delhase M., Hayakawa M., Karin M. The IkappaB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase subunits, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, necessary for IkappaB phosphorylation and NF-kappaB activation. Cell. 1997 Oct 17;91(2):243–252. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Cado D., Chen A., Kabra N. H., Winoto A. Fas-mediated apoptosis and activation-induced T-cell proliferation are defective in mice lacking FADD/Mort1. Nature. 1998 Mar 19;392(6673):296–300. doi: 10.1038/32681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou H., Henzel W. J., Liu X., Lutschg A., Wang X. Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell. 1997 Aug 8;90(3):405–413. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80501-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou H., Li Y., Liu X., Wang X. An APAF-1.cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 1999 Apr 23;274(17):11549–11556. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.17.11549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]