Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (202.0 KB).
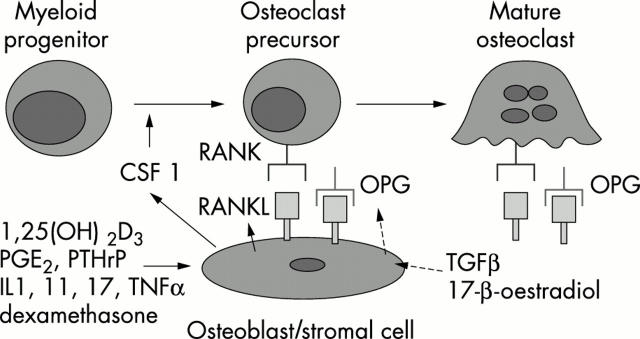
Figure 1 .
Regulation of osteoclast formation. Calciotropic factors such as vitamin D3, prostaglandin E2, IL1, IL11, TNFα and glucocorticoid induce RANKL expression on osteoblasts. RANKL binding to the RANK expressed on haematopoietic progenitors activates a signal transduction cascade that leads to osteoclast differentiation in the presence of the survival factor CSF1. Moreover RANKL stimulates bone resorbing activity in mature osteoclasts via RANK. OPG produced by osteoblasts acts as a decoy receptor for RANKL and inhibits osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast activation by binding to RANKL. TGFß released from bone during active bone resorption has been suggested as one feedback mechanism for upregulating OPG. Oestrogen can increase OPG production on osteoblasts, which is a possible explanation of postmenopausal osteoporosis after oestrogen withdrawal.
Figure 2 .
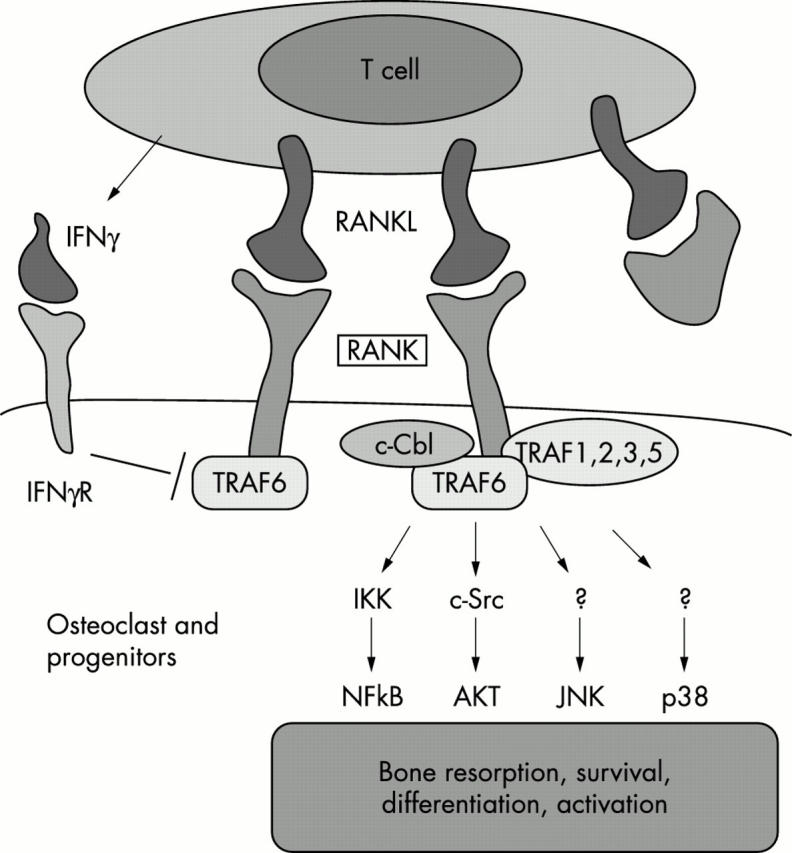
RANK signalling. After RANKL biding, the TNFR member RANK sends signals into the cells through tumour necrosis factor receptor associated factors (TRAFs) 1, 2, 3, 5, and 6. c-Src and Cbl proteins associate with the cytoplasmatic tail of RANK. These RANK associated molecules relay RANK dependent stimulation to downstream pathways such as NF-kB, JNK/SAPK, p38, and Akt/PKB that regulate bone resorption, activation, survival, and differentiation of osteoclasts and dendritic cells. Interferon gamma can inhibit RANKL mediated osteoclastogenesis presumably via induction of TRAF6 ubiquitination and proteolytic TRAF6 degradation. The scheme is based on Arron and Choi.92
Figure 3 .
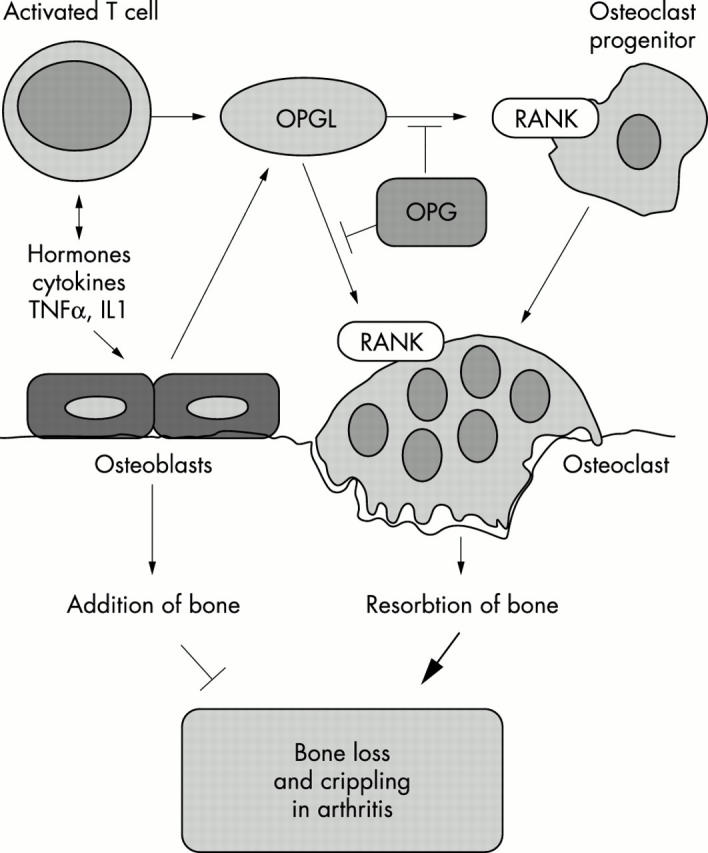
Rational drug design to interfere with arthritic disease. Activated T cells produce cytokines such as TNFα, IL1, IL11, and IL17 that lead to RANKL expression on osteoblasts. Moreover, activated T cells directly express and produce RANKL that induces osteoclast formation and activation. The soluble decoy receptor for RANKL, OPG, blocks both pathways. In addition to inhibiting the functions of cytokines to alleviate inflammation, inhibition of RANKL via OPG might be useful to block osteoclast activation and crippling in arthritis irrespective of the disease trigger.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu-Amer Y. IL-4 abrogates osteoclastogenesis through STAT6-dependent inhibition of NF-kappaB. J Clin Invest. 2001 Jun;107(11):1375–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI10530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. M., Maraskovsky E., Billingsley W. L., Dougall W. C., Tometsko M. E., Roux E. R., Teepe M. C., DuBose R. F., Cosman D., Galibert L. A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature. 1997 Nov 13;390(6656):175–179. doi: 10.1038/36593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arron J. R., Choi Y. Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000 Nov 30;408(6812):535–536. doi: 10.1038/35046196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins G. J., Bouralexis S., Haynes D. R., Graves S. E., Geary S. M., Evdokiou A., Zannettino A. C., Hay S., Findlay D. M. Osteoprotegerin inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorbing activity in giant cell tumors of bone. Bone. 2001 Apr;28(4):370–377. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00404-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azuma Y., Kaji K., Katogi R., Takeshita S., Kudo A. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha induces differentiation of and bone resorption by osteoclasts. J Biol Chem. 2000 Feb 18;275(7):4858–4864. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.7.4858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M. F., Wong B. R., Josien R., Steinman R. M., Oxenius A., Choi Y. TRANCE, a tumor necrosis factor family member critical for CD40 ligand-independent T helper cell activation. J Exp Med. 1999 Apr 5;189(7):1025–1031. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.7.1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendele A., McComb J., Gould T., McAbee T., Sennello G., Chlipala E., Guy M. Animal models of arthritis: relevance to human disease. Toxicol Pathol. 1999 Jan-Feb;27(1):134–142. doi: 10.1177/019262339902700125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen A. C., Shevde N. K., Dienger K. M., Willson T. M., Funk C. D., Pike J. W. IL-4 inhibits osteoclast formation through a direct action on osteoclast precursors via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 20;98(5):2443–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.041493198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Mathis D. A revival of the B cell paradigm for rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis? Arthritis Res. 2000 Feb 24;2(2):90–94. doi: 10.1186/ar73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändström H., Jonsson K. B., Ohlsson C., Vidal O., Ljunghall S., Ljunggren O. Regulation of osteoprotegerin mRNA levels by prostaglandin E2 in human bone marrow stroma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Jun 18;247(2):338–341. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändström H., Jonsson K. B., Vidal O., Ljunghall S., Ohlsson C., Ljunggren O. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and -beta upregulate the levels of osteoprotegerin mRNA in human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Jul 30;248(3):454–457. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucay N., Sarosi I., Dunstan C. R., Morony S., Tarpley J., Capparelli C., Scully S., Tan H. L., Xu W., Lacey D. L. osteoprotegerin-deficient mice develop early onset osteoporosis and arterial calcification. Genes Dev. 1998 May 1;12(9):1260–1268. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.9.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess T. L., Qian Y., Kaufman S., Ring B. D., Van G., Capparelli C., Kelley M., Hsu H., Boyle W. J., Dunstan C. R. The ligand for osteoprotegerin (OPGL) directly activates mature osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 1999 May 3;145(3):527–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.145.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. E. How can we improve the treatment of bone metastases further? Curr Opin Oncol. 1998 Aug;10 (Suppl 1):S7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway J. G., Wakefield J. A., Brown R. H., Marron B. E., Sekut L., Stimpson S. A., McElroy A., Menius J. A., Jeffreys J. J., Clark R. L. Inhibition of cartilage and bone destruction in adjuvant arthritis in the rat by a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1995 Aug 1;182(2):449–457. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnay B. G., Haridas V., Ni J., Moore P. A., Aggarwal B. B. Characterization of the intracellular domain of receptor activator of NF-kappaB (RANK). Interaction with tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors and activation of NF-kappab and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 7;273(32):20551–20555. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.32.20551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougall W. C., Glaccum M., Charrier K., Rohrbach K., Brasel K., De Smedt T., Daro E., Smith J., Tometsko M. E., Maliszewski C. R. RANK is essential for osteoclast and lymph node development. Genes Dev. 1999 Sep 15;13(18):2412–2424. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.18.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling P. R., Erbas B., Hopper J. L., Wark J. D., Rubinfeld A. R. Bone mineral density and bone turnover in asthmatics treated with long-term inhaled or oral glucocorticoids. J Bone Miner Res. 1998 Aug;13(8):1283–1289. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.8.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery J. G., McDonnell P., Burke M. B., Deen K. C., Lyn S., Silverman C., Dul E., Appelbaum E. R., Eichman C., DiPrinzio R. Osteoprotegerin is a receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. J Biol Chem. 1998 Jun 5;273(23):14363–14367. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.23.14363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fata J. E., Kong Y. Y., Li J., Sasaki T., Irie-Sasaki J., Moorehead R. A., Elliott R., Scully S., Voura E. B., Lacey D. L. The osteoclast differentiation factor osteoprotegerin-ligand is essential for mammary gland development. Cell. 2000 Sep 29;103(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.14.1.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzoso G., Carlson L., Xing L., Poljak L., Shores E. W., Brown K. D., Leonardi A., Tran T., Boyce B. F., Siebenlist U. Requirement for NF-kappaB in osteoclast and B-cell development. Genes Dev. 1997 Dec 15;11(24):3482–3496. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.24.3482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fye K. H. New treatments for rheumatoid arthritis. Available and upcoming slow-acting antirheumatic drugs. Postgrad Med. 1999 Oct 1;106(4):82-5, 88-90, 92. doi: 10.3810/pgm.1999.10.1.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert L., Tometsko M. E., Anderson D. M., Cosman D., Dougall W. C. The involvement of multiple tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-associated factors in the signaling mechanisms of receptor activator of NF-kappaB, a member of the TNFR superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1998 Dec 18;273(51):34120–34127. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.51.34120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes D. R., Crotti T. N., Loric M., Bain G. I., Atkins G. J., Findlay D. M. Osteoprotegerin and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL) regulate osteoclast formation by cells in the human rheumatoid arthritic joint. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Jun;40(6):623–630. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.6.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer L. C., Khosla S., Dunstan C. R., Lacey D. L., Spelsberg T. C., Riggs B. L. Estrogen stimulates gene expression and protein production of osteoprotegerin in human osteoblastic cells. Endocrinology. 1999 Sep;140(9):4367–4370. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.9.7131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer L. C., Lacey D. L., Dunstan C. R., Spelsberg T. C., Riggs B. L., Khosla S. Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, but not interleukin-6, stimulate osteoprotegerin ligand gene expression in human osteoblastic cells. Bone. 1999 Sep;25(3):255–259. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(99)00162-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honore P., Luger N. M., Sabino M. A., Schwei M. J., Rogers S. D., Mach D. B., O'keefe P. F., Ramnaraine M. L., Clohisy D. R., Mantyh P. W. Osteoprotegerin blocks bone cancer-induced skeletal destruction, skeletal pain and pain-related neurochemical reorganization of the spinal cord. Nat Med. 2000 May;6(5):521–528. doi: 10.1038/74999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwood N. J., Elliott J., Martin T. J., Gillespie M. T. IL-12 alone and in synergy with IL-18 inhibits osteoclast formation in vitro. J Immunol. 2001 Apr 15;166(8):4915–4921. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.8.4915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H., Lacey D. L., Dunstan C. R., Solovyev I., Colombero A., Timms E., Tan H. L., Elliott G., Kelley M. J., Sarosi I. Tumor necrosis factor receptor family member RANK mediates osteoclast differentiation and activation induced by osteoprotegerin ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 30;96(7):3540–3545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.3540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. E., Ralston S. H., Marken J., Bell C., MacPherson H., Wallace R. G., van Hul W., Whyte M. P., Nakatsuka K., Hovy L. Mutations in TNFRSF11A, affecting the signal peptide of RANK, cause familial expansile osteolysis. Nat Genet. 2000 Jan;24(1):45–48. doi: 10.1038/71667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iotsova V., Caamaño J., Loy J., Yang Y., Lewin A., Bravo R. Osteopetrosis in mice lacking NF-kappaB1 and NF-kappaB2. Nat Med. 1997 Nov;3(11):1285–1289. doi: 10.1038/nm1197-1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Hong, Pettit Allison, Ohmura Koichiro, Ortiz-Lopez Adriana, Duchatelle Veronique, Degott Claude, Gravallese Ellen, Mathis Diane, Benoist Christophe. Critical roles for interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in antibody-induced arthritis. J Exp Med. 2002 Jul 1;196(1):77–85. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josien R., Li H. L., Ingulli E., Sarma S., Wong B. R., Vologodskaia M., Steinman R. M., Choi Y. TRANCE, a tumor necrosis factor family member, enhances the longevity and adjuvant properties of dendritic cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 2000 Feb 7;191(3):495–502. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josien R., Wong B. R., Li H. L., Steinman R. M., Choi Y. TRANCE, a TNF family member, is differentially expressed on T cell subsets and induces cytokine production in dendritic cells. J Immunol. 1999 Mar 1;162(5):2562–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen L., Engstad T., Jacobsen B. K. Bone mineral density in acute stroke patients: low bone mineral density may predict first stroke in women. Stroke. 2001 Jan;32(1):47–51. doi: 10.1161/01.str.32.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartsogiannis V., Zhou H., Horwood N. J., Thomas R. J., Hards D. K., Quinn J. M., Niforas P., Ng K. W., Martin T. J., Gillespie M. T. Localization of RANKL (receptor activator of NF kappa B ligand) mRNA and protein in skeletal and extraskeletal tissues. Bone. 1999 Nov;25(5):525–534. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(99)00214-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T., Naka T., Yoshida K., Tanaka T., Fujiwara H., Suematsu S., Yoshida N., Kishimoto T., Kikutani H. The immune responses in CD40-deficient mice: impaired immunoglobulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity. 1994 Jun;1(3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keffer J., Probert L., Cazlaris H., Georgopoulos S., Kaslaris E., Kioussis D., Kollias G. Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: a predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4025–4031. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim D., Mebius R. E., MacMicking J. D., Jung S., Cupedo T., Castellanos Y., Rho J., Wong B. R., Josien R., Kim N. Regulation of peripheral lymph node genesis by the tumor necrosis factor family member TRANCE. J Exp Med. 2000 Nov 20;192(10):1467–1478. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.10.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim N., Odgren P. R., Kim D. K., Marks S. C., Jr, Choi Y. Diverse roles of the tumor necrosis factor family member TRANCE in skeletal physiology revealed by TRANCE deficiency and partial rescue by a lymphocyte-expressed TRANCE transgene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Sep 26;97(20):10905–10910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.200294797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi K., Takahashi N., Jimi E., Udagawa N., Takami M., Kotake S., Nakagawa N., Kinosaki M., Yamaguchi K., Shima N. Tumor necrosis factor alpha stimulates osteoclast differentiation by a mechanism independent of the ODF/RANKL-RANK interaction. J Exp Med. 2000 Jan 17;191(2):275–286. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.2.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi N., Kadono Y., Naito A., Matsumoto K., Yamamoto T., Tanaka S., Inoue J. Segregation of TRAF6-mediated signaling pathways clarifies its role in osteoclastogenesis. EMBO J. 2001 Mar 15;20(6):1271–1280. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.6.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro H., Olee T., Kühn K., Quach J., Brinson D. C., Shikhman A., Valbracht J., Creighton-Achermann L., Lotz M. The osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand system in cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Dec;44(12):2768–2776. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200112)44:12<2768::aid-art464>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong Y. Y., Feige U., Sarosi I., Bolon B., Tafuri A., Morony S., Capparelli C., Li J., Elliott R., McCabe S. Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. Nature. 1999 Nov 18;402(6759):304–309. doi: 10.1038/46303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong Y. Y., Yoshida H., Sarosi I., Tan H. L., Timms E., Capparelli C., Morony S., Oliveira-dos-Santos A. J., Van G., Itie A. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 1999 Jan 28;397(6717):315–323. doi: 10.1038/16852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotake S., Udagawa N., Hakoda M., Mogi M., Yano K., Tsuda E., Takahashi K., Furuya T., Ishiyama S., Kim K. J. Activated human T cells directly induce osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes: possible role of T cells in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 May;44(5):1003–1012. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200105)44:5<1003::AID-ANR179>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouskoff V., Korganow A. S., Duchatelle V., Degott C., Benoist C., Mathis D. Organ-specific disease provoked by systemic autoimmunity. Cell. 1996 Nov 29;87(5):811–822. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81989-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey D. L., Timms E., Tan H. L., Kelley M. J., Dunstan C. R., Burgess T., Elliott R., Colombero A., Elliott G., Scully S. Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 1998 Apr 17;93(2):165–176. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81569-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagasse E., Weissman I. L. Enforced expression of Bcl-2 in monocytes rescues macrophages and partially reverses osteopetrosis in op/op mice. Cell. 1997 Jun 27;89(7):1021–1031. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80290-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Z. H., Kwack K., Kim K. K., Lee S. H., Kim H. H. Activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and activator protein 1 by receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB. Mol Pharmacol. 2000 Dec;58(6):1536–1545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Sarosi I., Yan X. Q., Morony S., Capparelli C., Tan H. L., McCabe S., Elliott R., Scully S., Van G. RANK is the intrinsic hematopoietic cell surface receptor that controls osteoclastogenesis and regulation of bone mass and calcium metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Feb 15;97(4):1566–1571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.4.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomaga M. A., Yeh W. C., Sarosi I., Duncan G. S., Furlonger C., Ho A., Morony S., Capparelli C., Van G., Kaufman S. TRAF6 deficiency results in osteopetrosis and defective interleukin-1, CD40, and LPS signaling. Genes Dev. 1999 Apr 15;13(8):1015–1024. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.8.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lum L., Wong B. R., Josien R., Becherer J. D., Erdjument-Bromage H., Schlöndorff J., Tempst P., Choi Y., Blobel C. P. Evidence for a role of a tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-converting enzyme-like protease in shedding of TRANCE, a TNF family member involved in osteoclastogenesis and dendritic cell survival. J Biol Chem. 1999 May 7;274(19):13613–13618. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.19.13613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach F., Schönbeck U., Sukhova G. K., Atkinson E., Libby P. Reduction of atherosclerosis in mice by inhibition of CD40 signalling. Nature. 1998 Jul 9;394(6689):200–203. doi: 10.1038/28204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto M., Sudo T., Saito T., Osada H., Tsujimoto M. Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL). J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 6;275(40):31155–31161. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001229200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min H., Morony S., Sarosi I., Dunstan C. R., Capparelli C., Scully S., Van G., Kaufman S., Kostenuik P. J., Lacey D. L. Osteoprotegerin reverses osteoporosis by inhibiting endosteal osteoclasts and prevents vascular calcification by blocking a process resembling osteoclastogenesis. J Exp Med. 2000 Aug 21;192(4):463–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.4.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno A., Murakami A., Nakagawa N., Yasuda H., Tsuda E., Morinaga T., Higashio K. Structure of the mouse osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCIF) gene and its expression in embryogenesis. Gene. 1998 Jul 30;215(2):339–343. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00295-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Hiroyuki, Kitazawa Riko, Mizuki Shinichi, Nose Masato, Maeda Sakan, Kitazawa Sohei. RANK ligand, RANK, and OPG expression in type II collagen-induced arthritis mouse. Histochem Cell Biol. 2002 Jan 26;117(3):283–292. doi: 10.1007/s00418-001-0376-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morony S., Capparelli C., Lee R., Shimamoto G., Boone T., Lacey D. L., Dunstan C. R. A chimeric form of osteoprotegerin inhibits hypercalcemia and bone resorption induced by IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, PTH, PTHrP, and 1, 25(OH)2D3. J Bone Miner Res. 1999 Sep;14(9):1478–1485. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.9.1478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morony S., Capparelli C., Sarosi I., Lacey D. L., Dunstan C. R., Kostenuik P. J. Osteoprotegerin inhibits osteolysis and decreases skeletal tumor burden in syngeneic and nude mouse models of experimental bone metastasis. Cancer Res. 2001 Jun 1;61(11):4432–4436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito A., Azuma S., Tanaka S., Miyazaki T., Takaki S., Takatsu K., Nakao K., Nakamura K., Katsuki M., Yamamoto T. Severe osteopetrosis, defective interleukin-1 signalling and lymph node organogenesis in TRAF6-deficient mice. Genes Cells. 1999 Jun;4(6):353–362. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1999.00265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa N., Kinosaki M., Yamaguchi K., Shima N., Yasuda H., Yano K., Morinaga T., Higashio K. RANK is the essential signaling receptor for osteoclast differentiation factor in osteoclastogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998 Dec 18;253(2):395–400. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.9788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima T., Kobayashi Y., Yamasaki S., Kawakami A., Eguchi K., Sasaki H., Sakai H. Protein expression and functional difference of membrane-bound and soluble receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand: modulation of the expression by osteotropic factors and cytokines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Sep 7;275(3):768–775. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveri M. B., Mautalen C. A., Rodriguez Fuchs C. A., Romanelli M. C. Vertebral compression fractures at the onset of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in a child. Henry Ford Hosp Med J. 1991;39(1):45–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panayi G. S., Lanchbury J. S., Kingsley G. H. The importance of the T cell in initiating and maintaining the chronic synovitis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):729–735. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parhami F., Demer L. L. Arterial calcification in face of osteoporosis in ageing: can we blame oxidized lipids? Curr Opin Lipidol. 1997 Oct;8(5):312–314. doi: 10.1097/00041433-199710000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit A. R., Ji H., von Stechow D., Müller R., Goldring S. R., Choi Y., Benoist C., Gravallese E. M. TRANCE/RANKL knockout mice are protected from bone erosion in a serum transfer model of arthritis. Am J Pathol. 2001 Nov;159(5):1689–1699. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63016-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piepkorn B., Kann P., Forst T., Andreas J., Pfützner A., Beyer J. Bone mineral density and bone metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res. 1997 Nov;29(11):584–591. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-979106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redlich Kurt, Hayer Silvia, Maier Andrea, Dunstan Colin R., Tohidast-Akrad Makiyeh, Lang Susanne, Türk Birgit, Pietschmann Peter, Woloszczuk Wolfgang, Haralambous Silva. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated joint destruction is inhibited by targeting osteoclasts with osteoprotegerin. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):785–792. doi: 10.1002/art.10097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggia C., Gao Y., Cenci S., Weitzmann M. N., Toraldo G., Isaia G., Pacifici R. Up-regulation of TNF-producing T cells in the bone marrow: a key mechanism by which estrogen deficiency induces bone loss in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Nov 20;98(24):13960–13965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.251534698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romas E., Gillespie M. T., Martin T. J. Involvement of receptor activator of NFkappaB ligand and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Bone. 2002 Feb;30(2):340–346. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00682-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roodman G. D. Cell biology of the osteoclast. Exp Hematol. 1999 Aug;27(8):1229–1241. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross F. P. RANKing the importance of measles virus in Paget's disease. J Clin Invest. 2000 Mar;105(5):555–558. doi: 10.1172/JCI9557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy M., Waldschmidt T., Aruffo A., Ledbetter J. A., Noelle R. J. The regulation of the expression of gp39, the CD40 ligand, on normal and cloned CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2497–2510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saika M., Inoue D., Kido S., Matsumoto T. 17beta-estradiol stimulates expression of osteoprotegerin by a mouse stromal cell line, ST-2, via estrogen receptor-alpha. Endocrinology. 2001 Jun;142(6):2205–2212. doi: 10.1210/endo.142.6.8220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seitz M., Hunstein W. Enhanced prostanoid release from monocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and active systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Jul;44(7):438–445. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.7.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonet W. S., Lacey D. L., Dunstan C. R., Kelley M., Chang M. S., Lüthy R., Nguyen H. Q., Wooden S., Bennett L., Boone T. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997 Apr 18;89(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80209-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayanagi H., Ogasawara K., Hida S., Chiba T., Murata S., Sato K., Takaoka A., Yokochi T., Oda H., Tanaka K. T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature. 2000 Nov 30;408(6812):600–605. doi: 10.1038/35046102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal N. O., Brändström H., Jonsson K. B., Ohlsson C. Osteoprotegerin mRNA is expressed in primary human osteoblast-like cells: down-regulation by glucocorticoids. J Endocrinol. 1998 Oct;159(1):191–195. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1590191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Bone K., Dennison E., Cooper C. Epidemiology of osteoporosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2001 Feb;27(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. R., Besser D., Kim N., Arron J. R., Vologodskaia M., Hanafusa H., Choi Y. TRANCE, a TNF family member, activates Akt/PKB through a signaling complex involving TRAF6 and c-Src. Mol Cell. 1999 Dec;4(6):1041–1049. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80232-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. R., Josien R., Lee S. Y., Sauter B., Li H. L., Steinman R. M., Choi Y. TRANCE (tumor necrosis factor [TNF]-related activation-induced cytokine), a new TNF family member predominantly expressed in T cells, is a dendritic cell-specific survival factor. J Exp Med. 1997 Dec 15;186(12):2075–2080. doi: 10.1084/jem.186.12.2075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. R., Josien R., Lee S. Y., Vologodskaia M., Steinman R. M., Choi Y. The TRAF family of signal transducers mediates NF-kappaB activation by the TRANCE receptor. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 23;273(43):28355–28359. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.43.28355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. R., Rho J., Arron J., Robinson E., Orlinick J., Chao M., Kalachikov S., Cayani E., Bartlett F. S., 3rd, Frankel W. N. TRANCE is a novel ligand of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family that activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase in T cells. J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 3;272(40):25190–25194. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.40.25190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu J., Foy T. M., Laman J. D., Elliott E. A., Dunn J. J., Waldschmidt T. J., Elsemore J., Noelle R. J., Flavell R. A. Mice deficient for the CD40 ligand. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):423–431. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda H., Shima N., Nakagawa N., Mochizuki S. I., Yano K., Fujise N., Sato Y., Goto M., Yamaguchi K., Kuriyama M. Identity of osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor (OCIF) and osteoprotegerin (OPG): a mechanism by which OPG/OCIF inhibits osteoclastogenesis in vitro. Endocrinology. 1998 Mar;139(3):1329–1337. doi: 10.1210/endo.139.3.5837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda H., Shima N., Nakagawa N., Yamaguchi K., Kinosaki M., Mochizuki S., Tomoyasu A., Yano K., Goto M., Murakami A. Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Mar 31;95(7):3597–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.7.3597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun T. J., Chaudhary P. M., Shu G. L., Frazer J. K., Ewings M. K., Schwartz S. M., Pascual V., Hood L. E., Clark E. A. OPG/FDCR-1, a TNF receptor family member, is expressed in lymphoid cells and is up-regulated by ligating CD40. J Immunol. 1998 Dec 1;161(11):6113–6121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Dai J., Qi Y., Lin D. L., Smith P., Strayhorn C., Mizokami A., Fu Z., Westman J., Keller E. T. Osteoprotegerin inhibits prostate cancer-induced osteoclastogenesis and prevents prostate tumor growth in the bone. J Clin Invest. 2001 May;107(10):1235–1244. doi: 10.1172/JCI11685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Heulsmann A., Tondravi M. M., Mukherjee A., Abu-Amer Y. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF) stimulates RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via coupling of TNF type 1 receptor and RANK signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 5;276(1):563–568. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008198200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]