Abstract
Background: There is currently no universal consensus on nomenclature for spondyloarthropathy (SpA), or on activity and severity criteria for ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
Method: Points of agreement and majority opinions among 28 international experts in the field were identified by questionnaire. Agreement was defined as >80% concurrence, clear majority as >60% concurrence, and a majority or trend as >50% concurrence.
Results: Respondents agreed on the need for one term that reflects the inflammatory nature of the disease, but no agreement was reached on a specific term. Agreement included subdivision of patients with SpA into AS, psoriatic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease associated arthritis, and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis/spondyloarthropathy. A majority of experts defined active disease as fulfilling classification criteria for AS and/or a SpA, and disease activity measured by a Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) score >4 determined by two patient visits during a two month period, but no maximum radiographic score. The majority of participants considered failure of treatment response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) alone to be a prerequisite for active/severe AS, and 15/28 (54%) thought that NSAID treatment failure should be defined as lack of response to two or more NSAIDs.
Conclusions: Respondents agreed that a two to five year study is the ethical method to demonstrate effects of anti-tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) therapy on radiographic progression of AS, and that inclusion criteria should include a certain level of disease activity (measured by BASDAI) and failure of certain treatments. After the efficacy of anti-TNFα therapy in AS and psoriatic arthritis is proved, respondents agreed that more studies will be needed to show efficacy for other SpA subsets.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (267.8 KB).
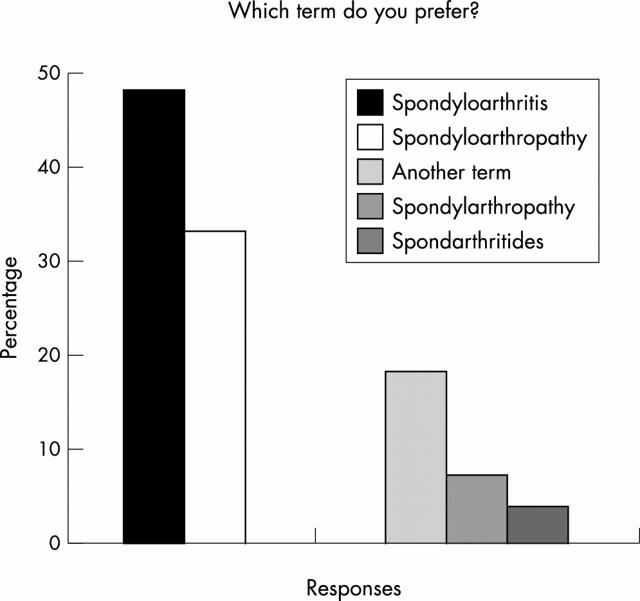
Figure 1 .
Respondents' preferences for the terms "spondyloarthritis" and "spondyloarthropathy."
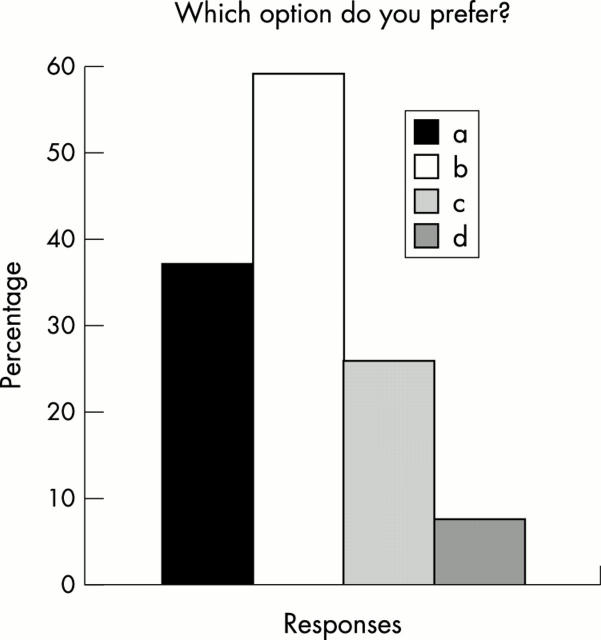
Figure 2 .
Percentages of respondents choosing to (a) abandon the term "Reiter's disease"; (b) use the term "reactive arthritis"; (c) use only the term, "Reiter's disease" in reference to the classic triad of arthritis, urethritis, and conjunctivitis; or (d) not change the terminology.
Figure 3 .
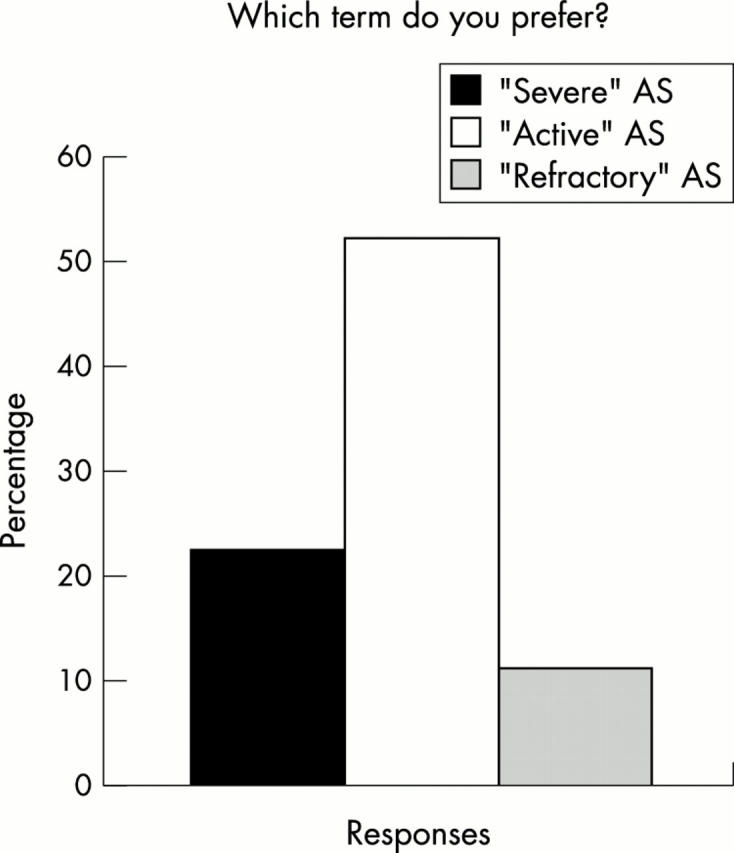
Percentages of respondents preferring the term "severe," "active," or refractory" ankylosing spondylitis in the context of indication for anti-TNF treatment.
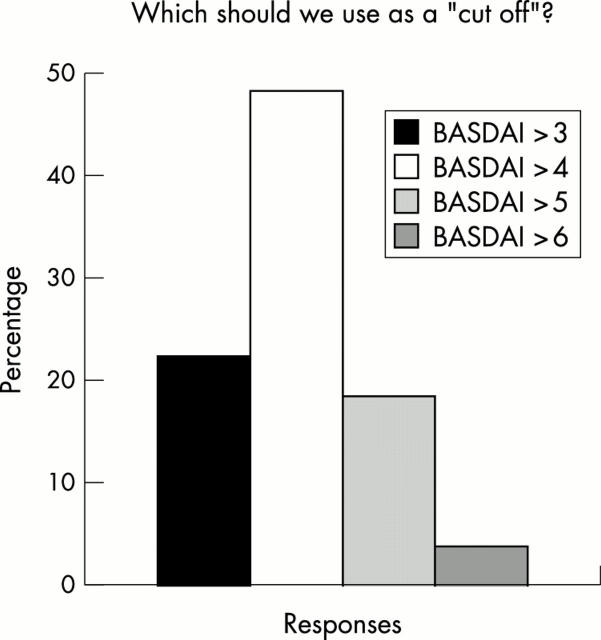
Figure 4 .
Percentages of respondents in favour of BASDAI scores >3, >4, >5, or >6 for definition of active/severe AS.
Figure 5 .
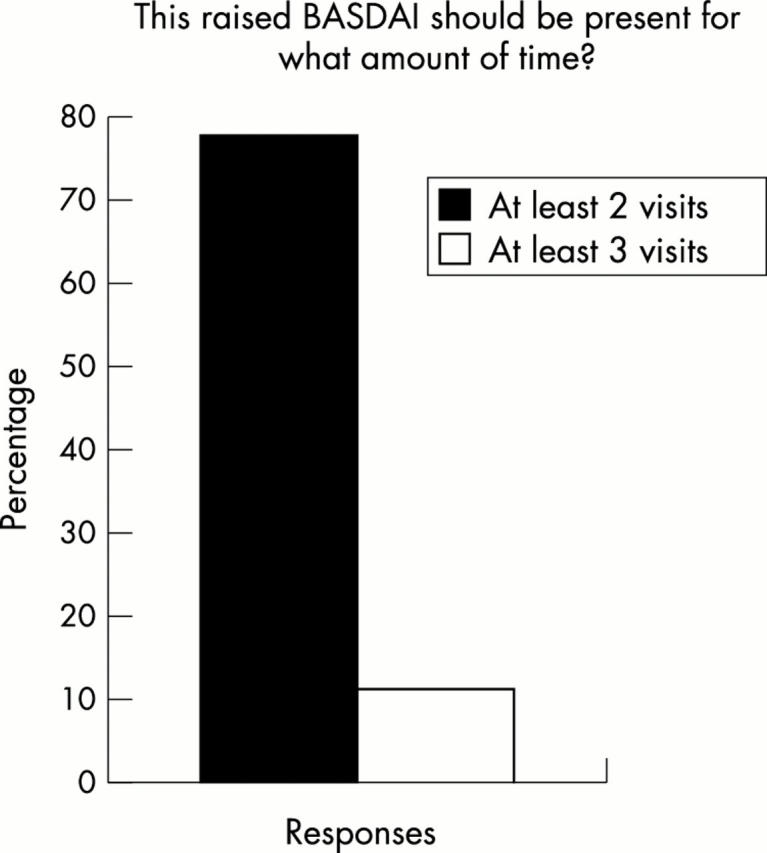
Percentages of respondents in favour of duration of raised BASDAI scores for at least two or at least three office visits. No respondent voted for more than three visits.
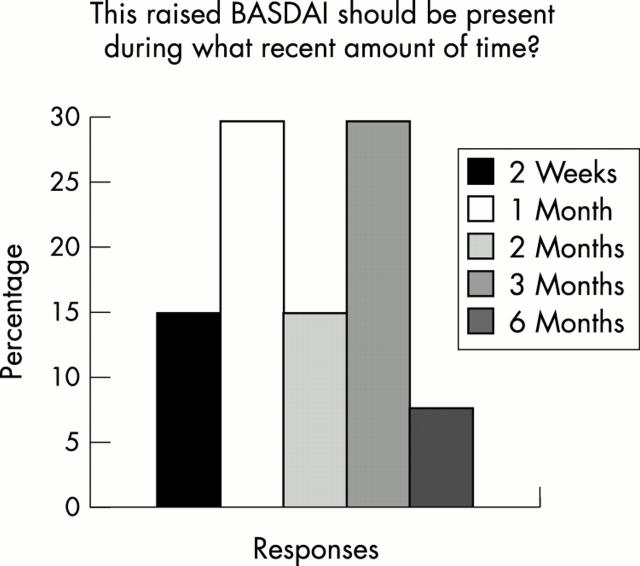
Figure 6 .
Distribution of responses to question about the duration of raised BASDAI scores at presentation.
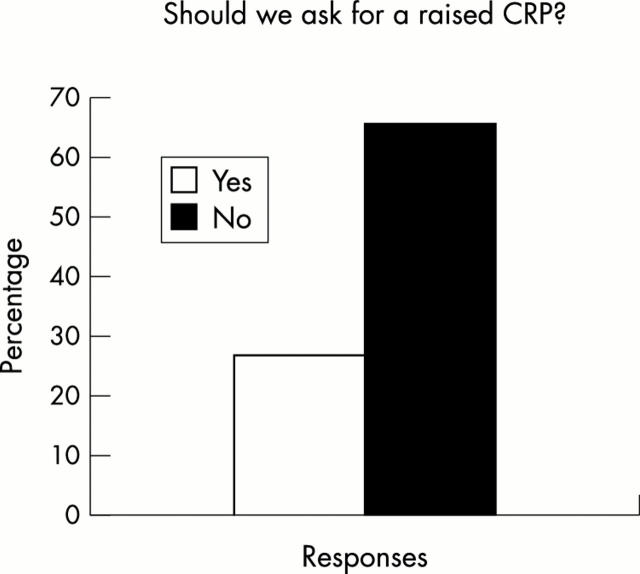
Figure 7 .
Percentages of respondents in favour of (Yes) and against (No) the requirement of raised CRP for definition of active/severe AS.
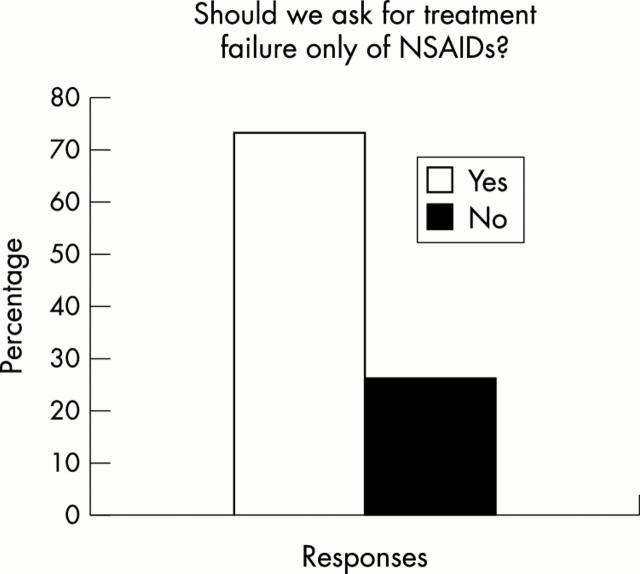
Figure 8 .
Percentages of respondents supporting failure of NSAID treatment alone to be sufficient for definition of active/severe AS.
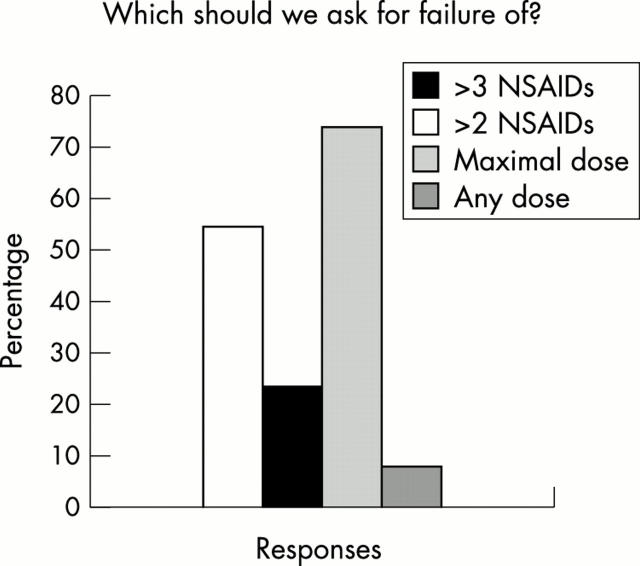
Figure 9 .
Percentages of respondents in favour of failure of >2 NSAIDs, >3 NSAIDs, maximal NSAID dose, or any NSAID dose as a prerequisite for definition of active/severe AS.
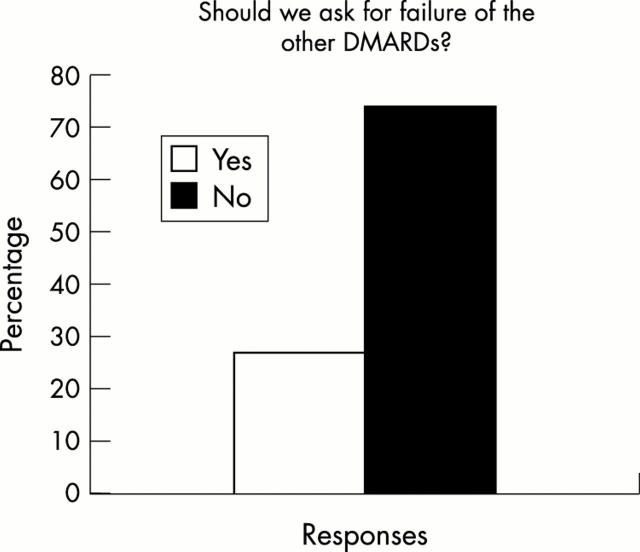
Figure 10 .
Percentages of respondents in favour of (Yes) and against (No) failure of treatment with other DMARDs as a prerequisite for classification as active/severe AS.
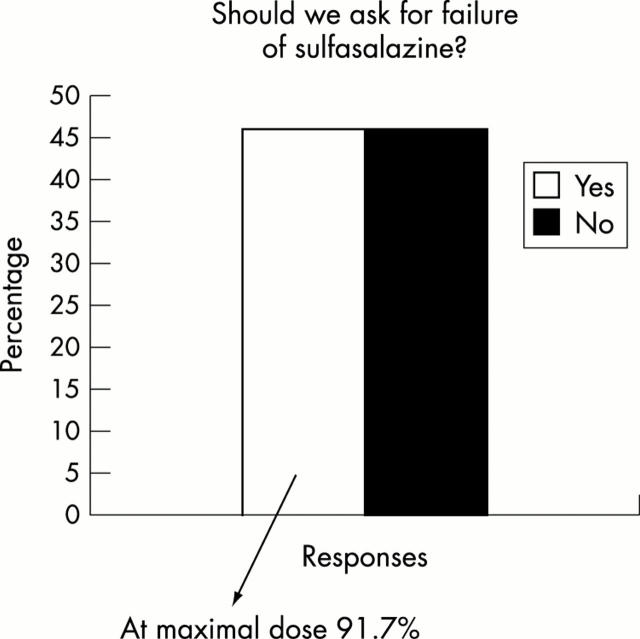
Figure 11 .
Disagreement among respondents as to whether failure of sulfasalazine should be a prerequisite for classification as active/severe AS.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C. Ankylosing spondylitis 1992: from Connor to transgenes. J Ir Coll Physicians Surg. 1993 Jul;22(3):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeten D., Van Damme N., Van den Bosch F., Kruithof E., De Vos M., Mielants H., Veys E. M., De Keyser F. Impaired Th1 cytokine production in spondyloarthropathy is restored by anti-TNFalpha. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Aug;60(8):750–755. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.8.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist M. Pierre Marie. Pioneer investigator in ankylosing spondylitis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1995 Apr 1;20(7):849–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Haibel H., Cornely D., Golder W., Gonzalez J., Reddig J., Thriene W., Sieper J., Braun J. Successful treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with the anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jun;43(6):1346–1352. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200006)43:6<1346::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Eggens U., König H., Distler A., Sieper J. Use of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with fast imaging in the detection of early and advanced sacroiliitis in spondylarthropathy patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jul;37(7):1039–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Remlinger G., Eggens U., Rudwaleit M., Distler A., Sieper J. Prevalence of spondylarthropathies in HLA-B27 positive and negative blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jan;41(1):58–67. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199801)41:1<58::AID-ART8>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Golder W., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Krause A., Schneider M. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002 Apr 6;359(9313):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Kingsley G., van der Heijde D., Sieper J. On the difficulties of establishing a consensus on the definition of and diagnostic investigations for reactive arthritis. Results and discussion of a questionnaire prepared for the 4th International Workshop on Reactive Arthritis, Berlin, Germany, July 3-6, 1999. J Rheumatol. 2000 Sep;27(9):2185–2192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Xiang J., Brandt J., Maetzel H., Haibel H., Wu P., Kohler S., Rudwaleit M., Siegert S., Radbruch A. Treatment of spondyloarthropathies with antibodies against tumour necrosis factor alpha: first clinical and laboratory experiences. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Nov;59 (Suppl 1):i85–i89. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.suppl_1.i85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calin A., Nakache J. P., Gueguen A., Zeidler H., Mielants H., Dougados M. Defining disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis: is a combination of variables (Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index) an appropriate instrument? Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Sep;38(9):878–882. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.9.878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg D. O., Reda D. J., Weisman M. H., Blackburn W. D., Cush J. J., Cannon G. W., Mahowald M. L., Schumacher H. R., Jr, Taylor T., Budiman-Mak E. Comparison of sulfasalazine and placebo in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. A Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Dec;39(12):2004–2012. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., Revel M., Khan M. A. Spondylarthropathy treatment: progress in medical treatment, physical therapy and rehabilitation. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1998 Nov;12(4):717–736. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(98)80046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M. Treatment of spondyloarthropathies. Recent advances and prospects in 2001. Joint Bone Spine. 2001 Dec;68(6):557–563. doi: 10.1016/s1297-319x(01)00328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., vam der Linden S., Leirisalo-Repo M., Huitfeldt B., Juhlin R., Veys E., Zeidler H., Kvien T. K., Olivieri I., Dijkmans B. Sulfasalazine in the treatment of spondylarthropathy. A randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 May;38(5):618–627. doi: 10.1002/art.1780380507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferraz M. B., Tugwell P., Goldsmith C. H., Atra E. Meta-analysis of sulfasalazine in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1990 Nov;17(11):1482–1486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François R. J., Braun J., Khan M. A. Entheses and enthesitis: a histopathologic review and relevance to spondyloarthritides. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001 Jul;13(4):255–264. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200107000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François R. J., Eulderink F., Bywaters E. G. Commented glossary for rheumatic spinal diseases, based on pathology. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995 Aug;54(8):615–625. doi: 10.1136/ard.54.8.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett S., Jenkinson T., Kennedy L. G., Whitelock H., Gaisford P., Calin A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol. 1994 Dec;21(12):2286–2291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leirisalo-Repo M. Therapeutic aspects of spondyloarthropathies -- a review. Scand J Rheumatol. 1998;27(5):323–328. doi: 10.1080/03009749850154320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maksymowych Walter P., Jhangri Gian S., Fitzgerald Avril A., LeClercq Sharon, Chiu Peter, Yan Alex, Skeith Kenneth J., Aaron Stephen L., Homik Joanne, Davis Paul. A six-month randomized, controlled, double-blind, dose-response comparison of intravenous pamidronate (60 mg versus 10 mg) in the treatment of nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug-refractory ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):766–773. doi: 10.1002/art.10139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzo-Ortega H., McGonagle D., O'Connor P., Emery P. Efficacy of etanercept in the treatment of the entheseal pathology in resistant spondylarthropathy: a clinical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Sep;44(9):2112–2117. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<2112::AID-ART363>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher H. R., Bardin T. The spondylarthropathies: classification and diagnosis. Do we need new terminologies? Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1998 Nov;12(4):551–565. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(98)80037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieper J., Braun J. New treatment options in ankylosing spondylitis: a role for anti-TNFalpha therapy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Nov;60 (Suppl 3):iii58–iii61. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.90003.iii58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoorenberg A., van der Heijde D., de Klerk E., Dougados M., de Vlam K., Mielants H., van der Tempel H., van der Linden S. Relative value of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in assessment of disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1999 Apr;26(4):980–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Bosch F., Kruithof E., Baeten D., De Keyser F., Mielants H., Veys E. M. Effects of a loading dose regimen of three infusions of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (infliximab) in spondyloarthropathy: an open pilot study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jun;59(6):428–433. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson L., Illingworth H., Smith D., Mowat A. Oral quinine in ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized placebo controlled double blind crossover trial. J Rheumatol. 2000 Aug;27(8):2054–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden S., Valkenburg H. A., Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Apr;27(4):361–368. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]