Abstract
Signal transduction pathways regulate cellular responses to stress and play a critical role in inflammation. The complexity and specificity of signalling mechanisms represent major hurdles for developing effective, safe therapeutic interventions that target specific molecules. One approach is to dissect the pathways methodically to determine their hierarchy in various cell types and diseases. This approach contributed to the identification and prioritisation of specific kinases that regulate NF-κB and the mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade as especially attractive targets. Although significant issues remain with regard to the discovery of truly selective kinase inhibitors, the risks that accompany inhibition of fundamental signal transduction mechanisms can potentially be decreased by careful dissection of the pathways and rational target selection.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (112.2 KB).
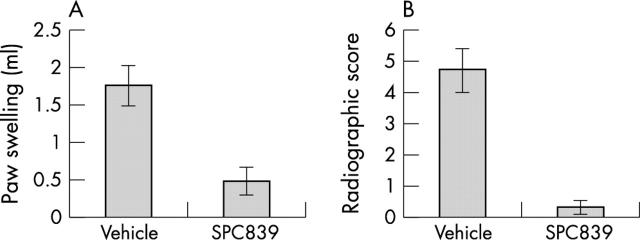
Figure 1.
Effect of the IKK2 inhibitor, SPC839, in rat adjuvant arthritis. Rats were immunised with complete Freund's adjuvant and treated with either vehicle or the IKK2 inhibitor SPC839 (100 mg/kg/day beginning on day 15). The experiment was ended on day 28. Paw swelling (A) was determined by water displacement plethysmometry and radiographic damage (B) was determined using a semiquantitative scoring system (maximum score=6). Clinical arthritis and radiographic damage were significantly decreased by the IKK2 inhibitor. Data adapted from reference 10.
Figure 2.
MAP kinase pathways. Complex parallel and interlocking signalling cascades link the three main MAP kinase families, ERK, JNK, and p38. The top level shows the MAP kinase kinase kinases (MAP3Ks), and the second tier shows the MAP kinase kinases (MAPKKs). MKK4 can also activate p38 under some circumstances.
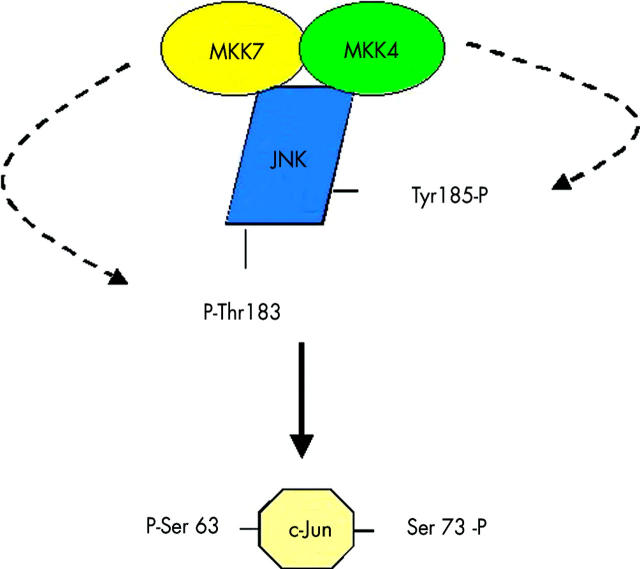
Figure 3.
Components of the JNK signalling complex. A JNK signalling complex, or signalsome, facilitates the phosphorylation of threonine and tyrosine on JNK by MKK4 and MKK7. The activated complex can then phosphorylate c-Jun on two sites and markedly increase the transcriptional activity of AP1.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aupperle K. R., Yamanishi Y., Bennett B. L., Mercurio F., Boyle D. L., Firestein G. S. Expression and regulation of inducible IkappaB kinase (IKK-i) in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cell Immunol. 2001 Nov 25;214(1):54–59. doi: 10.1006/cimm.2002.1885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aupperle K., Bennett B., Han Z., Boyle D., Manning A., Firestein G. NF-kappa B regulation by I kappa B kinase-2 in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. J Immunol. 2001 Feb 15;166(4):2705–2711. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.4.2705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger A. M., Griswold D. E., Kapadia R., Blake S., Swift B. A., Hoffman S. J., Stroup G. B., Webb E., Rieman D. J., Gowen M. Disease-modifying activity of SB 242235, a selective inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):175–183. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<175::AID-ANR22>3.0.CO;2-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L., Karin M. Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature. 2001 Mar 1;410(6824):37–40. doi: 10.1038/35065000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuenda A., Rouse J., Doza Y. N., Meier R., Cohen P., Gallagher T. F., Young P. R., Lee J. C. SB 203580 is a specific inhibitor of a MAP kinase homologue which is stimulated by cellular stresses and interleukin-1. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 8;364(2):229–233. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00357-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger G. R., Gerwins P., Widmann C., Jarpe M. B., Johnson G. L. MEKKs, GCKs, MLKs, PAKs, TAKs, and tpls: upstream regulators of the c-Jun amino-terminal kinases? Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997 Feb;7(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(97)80111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng Y., Schreiner G. F., Chakravarty S., Liu D. Y., Joly A. H. Inhibition of the mitogen activated protein kinase, p38 alpha, prevents proinflammatory cytokine induction by human adherent mononuclear leukocytes in response to lipid loading. Atherosclerosis. 2001 Oct;158(2):331–338. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9150(01)00453-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fijen J. W., Zijlstra J. G., De Boer P., Spanjersberg R., Tervaert J. W., Van Der Werf T. S., Ligtenberg J. J., Tulleken J. E. Suppression of the clinical and cytokine response to endotoxin by RWJ-67657, a p38 mitogen-activated protein-kinase inhibitor, in healthy human volunteers. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Apr;124(1):16–20. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming Y., Armstrong C. G., Morrice N., Paterson A., Goedert M., Cohen P. Synergistic activation of stress-activated protein kinase 1/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (SAPK1/JNK) isoforms by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MKK4) and MKK7. Biochem J. 2000 Nov 15;352(Pt 1):145–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Z., Boyle D. L., Aupperle K. R., Bennett B., Manning A. M., Firestein G. S. Jun N-terminal kinase in rheumatoid arthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Oct;291(1):124–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Z., Boyle D. L., Chang L., Bennett B., Karin M., Yang L., Manning A. M., Firestein G. S. c-Jun N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2001 Jul;108(1):73–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI12466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Z., Boyle D. L., Manning A. M., Firestein G. S. AP-1 and NF-kappaB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity. 1998;28(4):197–208. doi: 10.3109/08916939808995367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han Zuoning, Chang Lufen, Yamanishi Yuji, Karin Michael, Firestein Gary S. Joint damage and inflammation in c-Jun N-terminal kinase 2 knockout mice with passive murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):818–823. doi: 10.1002/art.10104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson Gary L., Lapadat Razvan. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and p38 protein kinases. Science. 2002 Dec 6;298(5600):1911–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.1072682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotlyarov A., Neininger A., Schubert C., Eckert R., Birchmeier C., Volk H. D., Gaestel M. MAPKAP kinase 2 is essential for LPS-induced TNF-alpha biosynthesis. Nat Cell Biol. 1999 Jun;1(2):94–97. doi: 10.1038/10061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavon I., Goldberg I., Amit S., Landsman L., Jung S., Tsuberi B. Z., Barshack I., Kopolovic J., Galun E., Bujard H. High susceptibility to bacterial infection, but no liver dysfunction, in mice compromised for hepatocyte NF-kappaB activation. Nat Med. 2000 May;6(5):573–577. doi: 10.1038/75057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler S., Fleming Y., Goedert M., Cohen P. Synergistic activation of SAPK1/JNK1 by two MAP kinase kinases in vitro. Curr Biol. 1998 Dec 17;8(25):1387–1390. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(98)00019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. W., Chu W., Hu Y., Delhase M., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Johnson R., Karin M. The IKKbeta subunit of IkappaB kinase (IKK) is essential for nuclear factor kappaB activation and prevention of apoptosis. J Exp Med. 1999 Jun 7;189(11):1839–1845. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.11.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manna S. K., Aggarwal B. B. Immunosuppressive leflunomide metabolite (A77 1726) blocks TNF-dependent nuclear factor-kappa B activation and gene expression. J Immunol. 1999 Feb 15;162(4):2095–2102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miagkov A. V., Kovalenko D. V., Brown C. E., Didsbury J. R., Cogswell J. P., Stimpson S. A., Baldwin A. S., Makarov S. S. NF-kappaB activation provides the potential link between inflammation and hyperplasia in the arthritic joint. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Nov 10;95(23):13859–13864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. J., Cobb M. H. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;9(2):180–186. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(97)80061-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer H. J., Catling A. D., Eblen S. T., Collier L. S., Krauss A., Weber M. J. MP1: a MEK binding partner that enhances enzymatic activation of the MAP kinase cascade. Science. 1998 Sep 11;281(5383):1668–1671. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schett G., Tohidast-Akrad M., Smolen J. S., Schmid B. J., Steiner C. W., Bitzan P., Zenz P., Redlich K., Xu Q., Steiner G. Activation, differential localization, and regulation of the stress-activated protein kinases, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-JUN N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, in synovial tissue and cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Nov;43(11):2501–2512. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200011)43:11<2501::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seetharaman R., Mora A. L., Nabozny G., Boothby M., Chen J. Essential role of T cell NF-kappa B activation in collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 1999 Aug 1;163(3):1577–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Krebs E. G. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995 Jun;9(9):726–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada T., Kawai T., Takeda K., Matsumoto M., Inoue J., Tatsumi Y., Kanamaru A., Akira S. IKK-i, a novel lipopolysaccharide-inducible kinase that is related to IkappaB kinases. Int Immunol. 1999 Aug;11(8):1357–1362. doi: 10.1093/intimm/11.8.1357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shouda T., Yoshida T., Hanada T., Wakioka T., Oishi M., Miyoshi K., Komiya S., Kosai K., Hanakawa Y., Hashimoto K. Induction of the cytokine signal regulator SOCS3/CIS3 as a therapeutic strategy for treating inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2001 Dec;108(12):1781–1788. doi: 10.1172/JCI13568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sioud M., Mellbye O., Førre O. Analysis of the NF-kappa B p65 subunit, Fas antigen, Fas ligand and Bcl-2-related proteins in the synovium of RA and polyarticular JRA. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998 Mar-Apr;16(2):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundarrajan Monisha, Boyle David L., Chabaud-Riou Martine, Hammaker Deepa, Firestein Gary S. Expression of the MAPK kinases MKK-4 and MKK-7 in rheumatoid arthritis and their role as key regulators of JNK. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Sep;48(9):2450–2460. doi: 10.1002/art.11228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Firestein G. S. NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001 Jan;107(1):7–11. doi: 10.1172/JCI11830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Gerlag D. M., Aupperle K. R., van de Geest D. A., Overbeek M., Bennett B. L., Boyle D. L., Manning A. M., Firestein G. S. Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappaB kinase beta is a key regulator of synovial inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Aug;44(8):1897–1907. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200108)44:8<1897::AID-ART328>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston Claire R., Davis Roger J. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002 Feb;12(1):14–21. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(01)00258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmarsh A. J., Cavanagh J., Tournier C., Yasuda J., Davis R. J. A mammalian scaffold complex that selectively mediates MAP kinase activation. Science. 1998 Sep 11;281(5383):1671–1674. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H., Merchant A. M., Tye B. K. Cell cycle-regulated nuclear localization of MCM2 and MCM3, which are required for the initiation of DNA synthesis at chromosomal replication origins in yeast. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2149–2160. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin M. J., Yamamoto Y., Gaynor R. B. The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of I(kappa)B kinase-beta. Nature. 1998 Nov 5;396(6706):77–80. doi: 10.1038/23948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]