Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (119.9 KB).
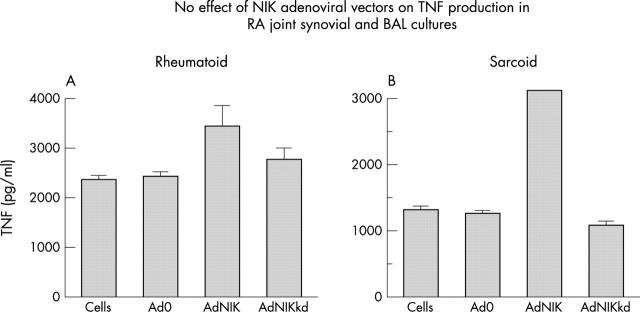
Figure 1.
NIK is inessential for constitutive TNF production by primary rheumatoid synoviocytes (A) and sarcoid bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) (B). Dissociated rheumatoid synoviocytes or cells from a BAL were uninfected or infected with an empty adenovirus (Ad0) or adenoviruses expressing NIK (AdNIK), or the kinase dead version of NIK (AdNIKkd) (multiplicity of infection (moi)=100 (A); moi=150 (B)). Cell supernatants were collected after 24 hours, and secreted TNF levels were determined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Data represent one experiment and are representative of three independent experiments using separate donors (SEM).
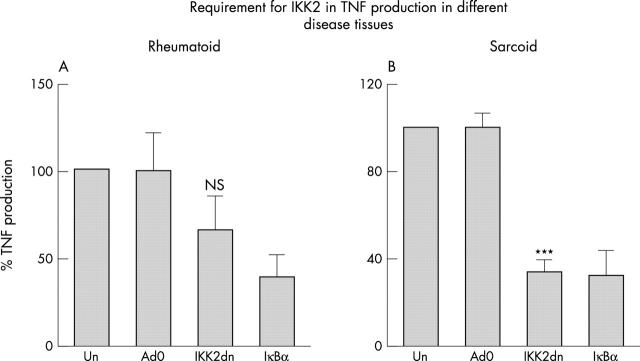
Figure 2.
IKK2 has varying roles for constitutive TNF production by primary rheumatoid synoviocytes (A) and sarcoid BAL (B). Dissociated rheumatoid synoviocytes or cells from a BAL were uninfected (un) or infected with an empty adenovirus (Ad0) or adenoviruses expressing kinase dead version of IKK2 (IKK2dn), or IκBα (moi=100 (A); moi=150, (B)). Cell supernatants were collected after 24 hours, and secreted TNF levels were determined by ELISA. Data represent one experiment and are representative of three independent experiments using separate donors (SEM). The data are given as a percentage of TNF production by infected cells.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M., Svensson L., Roach M., Hambor J., McNeish J., Gabel C. A. Deficiency of the stress kinase p38alpha results in embryonic lethality: characterization of the kinase dependence of stress responses of enzyme-deficient embryonic stem cells. J Exp Med. 2000 Mar 6;191(5):859–870. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreakos Evangelos T., Foxwell Brian M., Brennan Fionula M., Maini Ravinder N., Feldmann Marc. Cytokines and anti-cytokine biologicals in autoimmunity: present and future. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2002 Aug-Oct;13(4-5):299–313. doi: 10.1016/s1359-6101(02)00018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreakos Evangelos, Smith Clive, Kiriakidis Serafim, Monaco Claudia, de Martin Rainer, Brennan Fionula M., Paleolog Ewa, Feldmann Marc, Foxwell Brian M. Heterogeneous requirement of IkappaB kinase 2 for inflammatory cytokine and matrix metalloproteinase production in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Jul;48(7):1901–1912. doi: 10.1002/art.11044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreakos Evangelos, Smith Clive, Monaco Claudia, Brennan Fionula M., Foxwell Brian M., Feldmann Marc. Ikappa B kinase 2 but not NF-kappa B-inducing kinase is essential for effective DC antigen presentation in the allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction. Blood. 2002 Sep 19;101(3):983–991. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asadullah Khusru, Volk Hans-Dieter, Sterry Wolfram. Novel immunotherapies for psoriasis. Trends Immunol. 2002 Jan;23(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4906(01)02119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain Jenny, McLauchlan Hilary, Elliott Matthew, Cohen Philip. The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update. Biochem J. 2003 Apr 1;371(Pt 1):199–204. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baud V., Karin M. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol. 2001 Sep;11(9):372–377. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(01)02064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M., Bloom O., Raabe T., Cohen P. S., Chesney J., Sherry B., Schmidtmayerova H., Calandra T., Zhang X., Bukrinsky M. Suppression of proinflammatory cytokines in monocytes by a tetravalent guanylhydrazone. J Exp Med. 1996 Mar 1;183(3):927–936. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borovikova L. V., Ivanova S., Nardi D., Zhang M., Yang H., Ombrellino M., Tracey K. J. Role of vagus nerve signaling in CNI-1493-mediated suppression of acute inflammation. Auton Neurosci. 2000 Dec 20;85(1-3):141–147. doi: 10.1016/S1566-0702(00)00233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Golder W., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Krause A., Schneider M. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002 Apr 6;359(9313):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Guoqing, Goeddel David V. TNF-R1 signaling: a beautiful pathway. Science. 2002 May 31;296(5573):1634–1635. doi: 10.1126/science.1071924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Schmidtmayerova H., Dennis J., Dubrovsky L., Sherry B., Wang H., Bukrinsky M., Tracey K. J. The critical role of p38 MAP kinase in T cell HIV-1 replication. Mol Med. 1997 May;3(5):339–346. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conron Matthew, Andreakos Evangelos, Pantelidis Panagiotis, Smith Clive, Beynon Huw L. C., Dubois Roland M., Foxwell Brian M. J. Nuclear factor-kappaB activation in alveolar macrophages requires IkappaB kinase-beta, but not nuclear factor-kappaB inducing kinase. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002 Apr 1;165(7):996–1004. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.7.2107058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. P., Reddy H., Caivano M., Cohen P. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J. 2000 Oct 1;351(Pt 1):95–105. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3510095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Maini R. N., Bondeson J., Taylor P., Foxwell B. M., Brennan F. M. Cytokine blockade in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2001;490:119–127. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1243-1_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwood Nicole J., Mahon Tara, McDaid John P., Campbell Jamie, Mano Hiroyuki, Brennan Fionula M., Webster David, Foxwell Brian M. J. Bruton's tyrosine kinase is required for lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha production. J Exp Med. 2003 Jun 16;197(12):1603–1611. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt A. E., Lali F. V., Lord J. D., Nelson B. H., Miyazaki T., Tracey K. J., Foxwell B. M. Role of interleukin (IL)-2 receptor beta-chain subdomains and Shc in p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and p54 MAP kinase (stress-activated protein Kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase) activation. IL-2-driven proliferation is independent of p38 and p54 MAP kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1999 Mar 12;274(11):7591–7597. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.11.7591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs Douglas A., Griffiths Paul D. Fomivirsen for the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002 Apr;133(4):552–556. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(02)01325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis B., Faulds D. Etanercept: a review of its use in rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs. 1999 Jun;57(6):945–966. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199957060-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami Y., Miura T., Bissonnette R., Hata D., Khan W. N., Kitamura T., Maeda-Yamamoto M., Hartman S. E., Yao L., Alt F. W. Bruton's tyrosine kinase regulates apoptosis and JNK/SAPK kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 15;94(8):3938–3942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.3938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keane J., Gershon S., Wise R. P., Mirabile-Levens E., Kasznica J., Schwieterman W. D., Siegel J. N., Braun M. M. Tuberculosis associated with infliximab, a tumor necrosis factor alpha-neutralizing agent. N Engl J Med. 2001 Oct 11;345(15):1098–1104. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa011110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Laydon J. T., McDonnell P. C., Gallagher T. F., Kumar S., Green D., McNulty D., Blumenthal M. J., Heys J. R., Landvatter S. W. A protein kinase involved in the regulation of inflammatory cytokine biosynthesis. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):739–746. doi: 10.1038/372739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Q., Van Antwerp D., Mercurio F., Lee K. F., Verma I. M. Severe liver degeneration in mice lacking the IkappaB kinase 2 gene. Science. 1999 Apr 9;284(5412):321–325. doi: 10.1126/science.284.5412.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell D. J., Giannini E. H., Reiff A., Cawkwell G. D., Silverman E. D., Nocton J. J., Stein L. D., Gedalia A., Ilowite N. T., Wallace C. A. Etanercept in children with polyarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000 Mar 16;342(11):763–769. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200003163421103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinin N. L., Boldin M. P., Kovalenko A. V., Wallach D. MAP3K-related kinase involved in NF-kappaB induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature. 1997 Feb 6;385(6616):540–544. doi: 10.1038/385540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima A., Kaisho T., Rennert P. D., Nakano H., Kurosawa K., Uchida D., Takeda K., Akira S., Matsumoto M. Essential role of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-inducing kinase and inhibitor of kappaB (IkappaB) kinase alpha in NF-kappaB activation through lymphotoxin beta receptor, but not through tumor necrosis factor receptor I. J Exp Med. 2001 Mar 5;193(5):631–636. doi: 10.1084/jem.193.5.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mease P. J., Goffe B. S., Metz J., VanderStoep A., Finck B., Burge D. J. Etanercept in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2000 Jul 29;356(9227):385–390. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02530-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poltorak A., He X., Smirnova I., Liu M. Y., Van Huffel C., Du X., Birdwell D., Alejos E., Silva M., Galanos C. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998 Dec 11;282(5396):2085–2088. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5396.2085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot Amanda E. I. Chemokine receptors: multifaceted therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002 Feb;2(2):106–115. doi: 10.1038/nri722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi S. T., Larivière L., Leveque G., Clermont S., Moore K. J., Gros P., Malo D. Endotoxin-tolerant mice have mutations in Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4) J Exp Med. 1999 Feb 15;189(4):615–625. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.4.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C., Andreakos E., Crawley J. B., Brennan F. M., Feldmann M., Foxwell B. M. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase is dispensable for activation of NF-kappaB in inflammatory settings but essential for lymphotoxin beta receptor activation of NF-kappaB in primary human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 2001 Nov 15;167(10):5895–5903. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.10.5895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Sudo T., Senftleben U., Dadak A. M., Johnson R., Karin M. Requirement for p38alpha in erythropoietin expression: a role for stress kinases in erythropoiesis. Cell. 2000 Jul 21;102(2):221–231. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Fuentes M. E., Yamaguchi K., Durnin M. H., Dalrymple S. A., Hardy K. L., Goeddel D. V. Embryonic lethality, liver degeneration, and impaired NF-kappa B activation in IKK-beta-deficient mice. Immunity. 1999 Apr;10(4):421–429. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutuncu Z., Morgan G. J., Jr, Kavanaugh A. Anti-TNF therapy for other inflammatory conditions. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002 Nov-Dec;20(6 Suppl 28):S146–S151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin L., Wu L., Wesche H., Arthur C. D., White J. M., Goeddel D. V., Schreiber R. D. Defective lymphotoxin-beta receptor-induced NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in NIK-deficient mice. Science. 2001 Mar 16;291(5511):2162–2165. doi: 10.1126/science.1058453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]