Abstract
Tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα) is a pivotal cytokine in host defences with broad ranging effects on the innate and adaptive immune systems. Clinically, TNFα inhibitors have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in a wide range of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders but clearly at the cost of heightened susceptibility to a variety of infections in those treated with these agents. Most reports to date have described increased susceptibility to intracellular pathogens in patients with underlying chronic viral infections, but little in the way of adverse event reporting in these patients has occurred. While the reported experience to date is rather limited, TNFα inhibitors have displayed a reasonable safety profile in the setting of some chronic viral infections and in certain circumstances have demonstrated adjunctive activity in the treatment of these infections. Given the high prevalence of chronic viral infections in patients who are candidates for anti-TNF therapy and the potential for these agents in the treatment of chronic viral illness, additional studies are urgently needed to assess the risks and benefits of such therapy in these populations.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (99.6 KB).
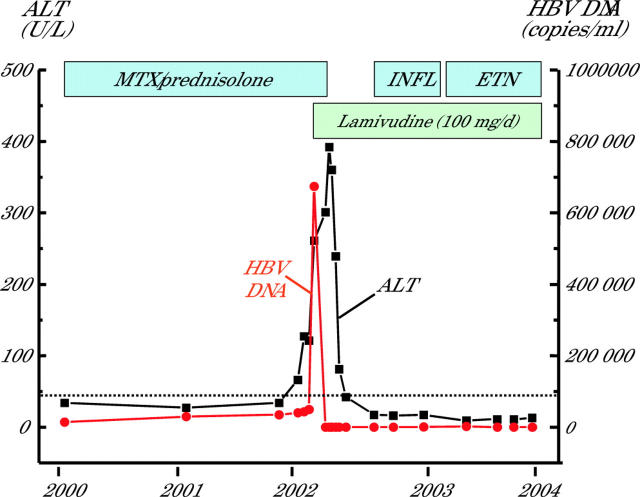
Figure 1.
A 58 year old woman with severe seropositive rheumatoid arthritis and chronic hepatitis B infection (HBeAg negative) was treated initially with methotrexate (MTX, 15 mg per week) and low dose prednisolone (<7.5 mg per day) without significant improvement of the joint disease. During treatment the hepatitis B infection exacerbated and was successfully managed with antiviral therapy (lamivudine 100 mg per day) and discontinuation of MTX and corticosteroids. After biochemical and virological remission was achieved, the patient was given infliximab (INFL, intravenous 3 mg/kg every eight weeks) for approximately six months. Despite the absence of hepatitis flare, infliximab was replaced with etanercept (ETN, 25 mg subcutaneously twice a week) due to resistant joint disease. The patient had a partial response to this regimen and she is still receiving etanercept and lamivudine without any evidence of biochemical or virological relapse. HBV DNA was measured with the Amplicor HBV monitor assay (Roche Molecular Systems, Nutely, NJ; sensitivity: 400 copies/ml). ALT, alanine aminotransferase.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aboulafia D. M., Bundow D., Wilske K., Ochs U. I. Etanercept for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus-associated psoriatic arthritis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000 Oct;75(10):1093–1098. doi: 10.4065/75.10.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter M. J., Kruszon-Moran D., Nainan O. V., McQuillan G. M., Gao F., Moyer L. A., Kaslow R. A., Margolis H. S. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1988 through 1994. N Engl J Med. 1999 Aug 19;341(8):556–562. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199908193410802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alter Miriam J. Epidemiology of hepatitis B in Europe and worldwide. J Hepatol. 2003;39 (Suppl 1):S64–S69. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett John A., Miralles G. Diego, Sevin Anne D., Silberman Martha, Pruitt Scott K., Ottinger Janet, Gryszowska Victoria, Fiscus Susan A., Bucy R. Pat, ACTG 380 Study Team Addition of cyclophosphamide to antiretroviral therapy does not diminish the cellular reservoir in HIV-infected persons. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2002 May 20;18(8):535–543. doi: 10.1089/088922202753747888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg L., Lampa J., Rogberg S., van Vollenhoven R., Klareskog L. Increased peripheral T cell reactivity to microbial antigens and collagen type II in rheumatoid arthritis after treatment with soluble TNFalpha receptors. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Feb;60(2):133–139. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.2.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. The biology of cachectin/TNF--a primary mediator of the host response. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:625–655. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese Leonard H., Lederman Michael M., Spritzler John, Coombs Robert W., Fox Lawrence, Schock Barbara, Yen-Lieberman Belinda, Johnson Ronald, Mildvan Donna, Parekh Namita. Placebo-controlled trial of cyclosporin-A in HIV-1 disease: implications for solid organ transplantation. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2002 Apr 1;29(4):356–362. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200204010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo Q. L., Kuo G., Weiner A. J., Overby L. R., Bradley D. W., Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):359–362. doi: 10.1126/science.2523562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope A. P., Londei M., Chu N. R., Cohen S. B., Elliott M. J., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Chronic exposure to tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in vitro impairs the activation of T cells through the T cell receptor/CD3 complex; reversal in vivo by anti-TNF antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1994 Aug;94(2):749–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI117394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cramp M. E., Rossol S., Chokshi S., Carucci P., Williams R., Naoumov N. V. Hepatitis C virus-specific T-cell reactivity during interferon and ribavirin treatment in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2000 Feb;118(2):346–355. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(00)70217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezube B. J., Lederman M. M., Chapman B., Georges D. L., Dogon A. L., Mudido P., Reis-Lishing J., Cheng S. L., Silberman S. L., Crumpacker C. S. The effect of tenidap on cytokines, acute-phase proteins, and virus load in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients: correlation between plasma HIV-1 RNA and proinflammatory cytokine levels. J Infect Dis. 1997 Sep;176(3):807–810. doi: 10.1086/517308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Bisceglie Adrian M., Hoofnagle Jay H. Optimal therapy of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002 Nov;36(5 Suppl 1):S121–S127. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.36228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl A. M. Cytokine regulation of liver injury and repair. Immunol Rev. 2000 Apr;174:160–171. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0528.2002.017411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diepolder H. M., Zachoval R., Hoffmann R. M., Wierenga E. A., Santantonio T., Jung M. C., Eichenlaub D., Pape G. R. Possible mechanism involving T-lymphocyte response to non-structural protein 3 in viral clearance in acute hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet. 1995 Oct 14;346(8981):1006–1007. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91691-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Serag Hashem B. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis C in the United States. Hepatology. 2002 Nov;36(5 Suppl 1):S74–S83. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.36807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellerin Todd, Rubin Robert H., Weinblatt Michael E. Infections and anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Nov;48(11):3013–3022. doi: 10.1002/art.11301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang J. W., Shen W. W., Meager A., Lau J. Y. Activation of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha system in the liver in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Apr;91(4):748–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried Michael W., Shiffman Mitchell L., Reddy K. Rajender, Smith Coleman, Marinos George, Gonçales Fernando L., Jr, Häussinger Dieter, Diago Moises, Carosi Giampiero, Dhumeaux Daniel. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002 Sep 26;347(13):975–982. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa020047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda R., Ishimura N., Ishihara S., Chowdhury A., Morlyama N., Nogami C., Miyake T., Niigaki M., Tokuda A., Satoh S. Intrahepatic expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNAs and interferon efficacy in chronic hepatitis C. Liver. 1996 Dec;16(6):390–399. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0676.1996.tb00768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaylis Norman. Infliximab in the treatment of an HIV positive patient with Reiter's syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2003 Feb;30(2):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginès Pere, Guevara Mónica. Good news for hepatorenal syndrome. Hepatology. 2002 Aug;36(2):504–506. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.35273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti L. G., Ishikawa T., Hobbs M. V., Matzke B., Schreiber R., Chisari F. V. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity. 1996 Jan;4(1):25–36. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadziyannis S. J., Vassilopoulos D. Hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2001 Oct;34(4 Pt 1):617–624. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.27834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadziyannis Stephanos J., Sette Hoel, Jr, Morgan Timothy R., Balan Vijayan, Diago Moises, Marcellin Patrick, Ramadori Giuliano, Bodenheimer Henry, Jr, Bernstein David, Rizzetto Mario. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med. 2004 Mar 2;140(5):346–355. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-5-200403020-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbein G., O'Brien W. A. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and TNF receptors in viral pathogenesis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 2000 Mar;223(3):241–257. doi: 10.1177/153537020022300305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle Jay H. Course and outcome of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002 Nov;36(5 Suppl 1):S21–S29. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.36227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain M. J., Lau J. Y., Williams R., Vergani D. Hepatic expression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Clin Pathol. 1994 Dec;47(12):1112–1115. doi: 10.1136/jcp.47.12.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson J. M., Greenspan J. S., Spritzler J., Ketter N., Fahey J. L., Jackson J. B., Fox L., Chernoff M., Wu A. W., MacPhail L. A. Thalidomide for the treatment of oral aphthous ulcers in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases AIDS Clinical Trials Group. N Engl J Med. 1997 May 22;336(21):1487–1493. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199705223362103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallinowski B., Haseroth K., Marinos G., Hanck C., Stremmel W., Theilmann L., Singer M. V., Rossol S. Induction of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type p55 and p75 in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998 Feb;111(2):269–277. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00469.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamal Sanaa M., Fehr Jutta, Roesler Bernd, Peters Thomas, Rasenack Jens W. Peginterferon alone or with ribavirin enhances HCV-specific CD4 T-helper 1 responses in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2002 Oct;123(4):1070–1083. doi: 10.1053/gast.2002.36045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasahara Senji, Ando Kazuki, Saito Kuniaki, Sekikawa Kenji, Ito Hiroyasu, Ishikawa Tetsuya, Ohnishi Hiroo, Seishima Mitsuru, Kakumu Shinichi, Moriwaki Hisataka. Lack of tumor necrosis factor alpha induces impaired proliferation of hepatitis B virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Virol. 2003 Feb;77(4):2469–2476. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.4.2469-2476.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Kyun-Hwan, Seong Baik L. Pro-apoptotic function of HBV X protein is mediated by interaction with c-FLIP and enhancement of death-inducing signal. EMBO J. 2003 May 1;22(9):2104–2116. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishihara Y., Hayashi J., Yoshimura E., Yamaji K., Nakashima K., Kashiwagi S. IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha produced by peripheral blood mononuclear cells before and during interferon therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci. 1996 Feb;41(2):315–321. doi: 10.1007/BF02093821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrea E., Garcia N., Qian C., Civeira M. P., Prieto J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression and the response to interferon in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 1996 Feb;23(2):210–217. doi: 10.1002/hep.510230203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay Karen L. Introduction to therapy of hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2002 Nov;36(5 Suppl 1):S114–S120. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.36226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lok A. S., McMahon B. J., Practice Guidelines Committee, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases Chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 2001 Dec;34(6):1225–1241. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.29401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manns M. P., McHutchison J. G., Gordon S. C., Rustgi V. K., Shiffman M., Reindollar R., Goodman Z. D., Koury K., Ling M., Albrecht J. K. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001 Sep 22;358(9286):958–965. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(01)06102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinos G., Naoumov N. V., Rossol S., Torre F., Wong P. Y., Gallati H., Portmann B., Williams R. Tumor necrosis factor receptors in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1995 May;108(5):1453–1463. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90694-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marriott J. B., Cookson S., Carlin E., Youle M., Hawkins D. A., Nelson M., Pearson M., Vaughan A. N., Gazzard B., Dalgleish A. G. A double-blind placebo-controlled phase II trial of thalidomide in asymptomatic HIV-positive patients: clinical tolerance and effect on activation markers and cytokines. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1997 Dec 10;13(18):1625–1631. doi: 10.1089/aid.1997.13.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurice M. M., van der Graaff W. L., Leow A., Breedveld F. C., van Lier R. A., Verweij C. L. Treatment with monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibody results in an accumulation of Th1 CD4+ T cells in the peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Oct;42(10):2166–2173. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199910)42:10<2166::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel Marc, Duvoux Cristophe, Hezode Cristophe, Cherqui Daniel. Fulminant hepatitis after infliximab in a patient with hepatitis B virus treated for an adult onset still's disease. J Rheumatol. 2003 Jul;30(7):1624–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monsalve-De Castillo Francisca, Romero Tania A., Estévez Jesús, Costa Luciana L., Atencio Ricardo, Porto Leticia, Callejas Diana. Concentrations of cytokines, soluble interleukin-2 receptor, and soluble CD30 in sera of patients with hepatitis B virus infection during acute and convalescent phases. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002 Nov;9(6):1372–1375. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.9.6.1372-1375.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Lim H. L., Marousis C. G., Fang J. W., Davis G. L., Shen L., Urdea M. S., Kolberg J. A., Lau J. Y. Activation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha system in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Dec;42(12):2487–2494. doi: 10.1023/a:1018804426724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Gullberg U., Lantz M., Peetre C. A tumor necrosis factor binding protein (TNF-BP)-physiological antagonist of TNF. Biotherapy. 1991;3(2):159–165. doi: 10.1007/BF02172088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oniankitan Owonayo, Duvoux Christophe, Challine Dominique, Mallat Arianne, Chevalier Xavier, Pawlotsky Jean-Michel, Claudepierre Pascal. Infliximab therapy for rheumatic diseases in patients with chronic hepatitis B or C. J Rheumatol. 2004 Jan;31(1):107–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostuni P., Botsios C., Punzi L., Sfriso P., Todesco S. Hepatitis B reactivation in a chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carrier with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab and low dose methotrexate. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Jul;62(7):686–687. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.7.686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palella F. J., Jr, Delaney K. M., Moorman A. C., Loveless M. O., Fuhrer J., Satten G. A., Aschman D. J., Holmberg S. D. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998 Mar 26;338(13):853–860. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199803263381301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson D. L., Georghiou P. R., Allworth A. M., Kemp R. J. Thalidomide as treatment of refractory aphthous ulceration related to human immunodeficiency virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 1995 Feb;20(2):250–254. doi: 10.1093/clinids/20.2.250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. R., Hsu F. C., Simkin P. A., Wener M. H. Effect of tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonists on serum transaminases and viraemia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and chronic hepatitis C infection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Nov;62(11):1078–1082. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.11.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlüter D., Deckert M. The divergent role of tumor necrosis factor receptors in infectious diseases. Microbes Infect. 2000 Aug;2(10):1285–1292. doi: 10.1016/s1286-4579(00)01282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha Beverly E., Valdez Hernan, Gelman Rebecca S., Landay Alan L., Agosti Jan, Mitsuyasu Ronald, Pollard Richard B., Mildvan Donna, Namkung Ann, Ogata-Arakaki Debra M. Effect of etanercept (Enbrel) on interleukin 6, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and markers of immune activation in HIV-infected subjects receiving interleukin 2. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2002 Jun 10;18(9):661–665. doi: 10.1089/088922202760019365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Lau J., Daniels H., Goka J., Eddleston A., Alexander G. J., Williams R. Increased production of tumour necrosis factor alpha in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol. 1991 Mar;12(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90945-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengler U., Zachoval R., Gallati H., Jung M. C., Hoffmann R., Riethmüller G., Pape G. Serum levels and in situ expression of TNF-alpha and TNF-alpha binding proteins in inflammatory liver diseases. Cytokine. 1996 Nov;8(11):864–872. doi: 10.1006/cyto.1996.0115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su F., Schneider R. J. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein sensitizes cells to apoptotic killing by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Aug 5;94(16):8744–8749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.16.8744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam R. C., Pai B., Bard J., Lim C., Averett D. R., Phan U. T., Milovanovic T. Ribavirin polarizes human T cell responses towards a Type 1 cytokine profile. J Hepatol. 1999 Mar;30(3):376–382. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang T. J., Kwekkeboom J., Laman J. D., Niesters H. G. M., Zondervan P. E., de Man R. A., Schalm S. W., Janssen H. L. A. The role of intrahepatic immune effector cells in inflammatory liver injury and viral control during chronic hepatitis B infection. J Viral Hepat. 2003 May;10(3):159–167. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.2003.00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torre D., Zeroli C., Giola M., Ferrario G., Fiori G. P., Bonetta G., Tambini R. Serum levels of interleukin-1 alpha, interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor in patients with acute viral hepatitis. Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Feb;18(2):194–198. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. L., Liaw Y. F., Chen M. H., Huang C. Y., Kuo G. C. Detection of type 2-like T-helper cells in hepatitis C virus infection: implications for hepatitis C virus chronicity. Hepatology. 1997 Feb;25(2):449–458. doi: 10.1002/hep.510250233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdez H., Lederman M. M. Cytokines and cytokine therapies in HIV infection. AIDS Clin Rev. 1997:187–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vento Sandro, Cainelli Francesca, Longhi Maria Serena. Reactivation of replication of hepatitis B and C viruses after immunosuppressive therapy: an unresolved issue. Lancet Oncol. 2002 Jun;3(6):333–340. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(02)00773-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. E., Spooner K. M., Kelly G., McCloskey R. V., Woody J. N., Falloon J., Baseler M., Piscitelli S. C., Davey R. T., Jr, Polis M. A. Inhibition of immunoreactive tumor necrosis factor-alpha by a chimeric antibody in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Infect Dis. 1996 Jul;174(1):63–68. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis R. S., Nsubuga P., Whalen C., Mugerwa R. D., Okwera A., Oette D., Jackson J. B., Johnson J. L., Ellner J. J. Pentoxifylline therapy in human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive persons with tuberculosis: a randomized, controlled trial. J Infect Dis. 1996 Oct;174(4):727–733. doi: 10.1093/infdis/174.4.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis Robert S., Kalayjian Robert, Jacobson Jeffrey M., Fox Lawrence, Purdue Lynette, Shikuma Cecilia M., Arakaki Richard, Snyder Stuart, Coombs Robert W., Bosch Ronald J. A study of the immunology, virology, and safety of prednisone in HIV-1-infected subjects with CD4 cell counts of 200 to 700 mm(-3). J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2003 Mar 1;32(3):281–286. doi: 10.1097/00126334-200303010-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis Robert S., Kyambadde Peter, Johnson John L., Horter Libby, Kittle Rodney, Pohle Monika, Ducar Constance, Millard Monica, Mayanja-Kizza Harriet, Whalen Christopher. A study of the safety, immunology, virology, and microbiology of adjunctive etanercept in HIV-1-associated tuberculosis. AIDS. 2004 Jan 23;18(2):257–264. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200401230-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen C., Horsburgh C. R., Hom D., Lahart C., Simberkoff M., Ellner J. Accelerated course of human immunodeficiency virus infection after tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995 Jan;151(1):129–135. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.151.1.7812542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka K., Kakumu S., Arao M., Tsutsumi Y., Inoue M., Wakita T., Ishikawa T., Mizokami M. Immunohistochemical studies of intrahepatic tumour necrosis factor alpha in chronic liver disease. J Clin Pathol. 1990 Apr;43(4):298–302. doi: 10.1136/jcp.43.4.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Franchis Roberto, Hadengue Antoine, Lau George, Lavanchy Daniel, Lok Anna, McIntyre Neil, Mele Alfonso, Paumgartner Gustav, Pietrangelo Antonello, Rodés Juan. EASL International Consensus Conference on Hepatitis B. 13-14 September, 2002 Geneva, Switzerland. Consensus statement (long version). J Hepatol. 2003;39 (Suppl 1):S3–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]