Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (100.7 KB).
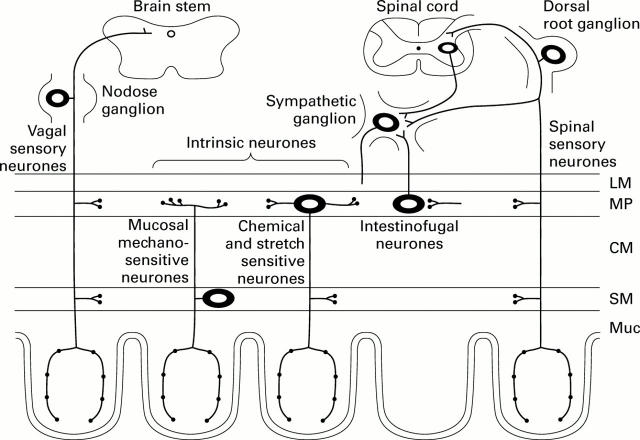
Figure 1 .
Representation of the types of sensory neurones of the gastrointestinal tract. Extrinsic sensory neurones: some have cell bodies in the nodose ganglion, and supply the stomach through the vagus nerves, while others have cell bodies in spinal (dorsal root) ganglia, and supply the stomach, and small and large intestines. Intrinsic sensory neurones have cell bodies in the gut wall. These have only been demonstrated recently. Another type of afferent pathway, that of intestinofugal neurones, conducts sensory information from the gut to prevertebral sympathetic ganglia. The layers of the gut wall are represented: LM, CM (longitudinal and circular muscle); MP, myenteric plexus; SM, submucosa; Muc, mucosa.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baidan L. V., Fertel R. H., Wood J. D. Effects of brain-gut related peptides on cAMP levels in myenteric ganglia of guinea-pig small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;225(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90034-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand P. P., Galligan J. J. Signal-transduction pathways causing slow synaptic excitation in guinea pig myenteric AH neurons. Am J Physiol. 1995 Nov;269(5 Pt 1):G710–G720. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.269.5.G710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer R. D., Connor J. H., Brown G. P., Wong T., Shenolikar S., Iyengar R., Landau E. M. Gating of CaMKII by cAMP-regulated protein phosphatase activity during LTP. Science. 1998 Jun 19;280(5371):1940–1942. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5371.1940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradette M., Delvaux M., Staumont G., Fioramonti J., Bueno L., Frexinos J. Evaluation of colonic sensory thresholds in IBS patients using a barostat. Definition of optimal conditions and comparison with healthy subjects. Dig Dis Sci. 1994 Mar;39(3):449–457. doi: 10.1007/BF02088327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueno L., Fioramonti J., Delvaux M., Frexinos J. Mediators and pharmacology of visceral sensitivity: from basic to clinical investigations. Gastroenterology. 1997 May;112(5):1714–1743. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri M., Choi M. G. Review article: irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1997 Feb;11(1):3–15. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.1997.84256000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc N., Furness J. B., Kunze W. A., Thomas E. A., Bertrand P. P. Long-term effects of synaptic activation at low frequency on excitability of myenteric AH neurons. Neuroscience. 1999 Apr;90(1):279–289. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Kunze W. A., Bertrand P. P., Clerc N., Bornstein J. C. Intrinsic primary afferent neurons of the intestine. Prog Neurobiol. 1998 Jan;54(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(97)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grady E. F., Gamp P. D., Jones E., Baluk P., McDonald D. M., Payan D. G., Bunnett N. W. Endocytosis and recycling of neurokinin 1 receptors in enteric neurons. Neuroscience. 1996 Dec;75(4):1239–1254. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(96)00357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Ascending enteric reflex: multiple neurotransmitter systems and interactions. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 1):G540–G545. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.3.G540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze W. A., Bertrand P. P., Furness J. B., Bornstein J. C. Influence of the mucosa on the excitability of myenteric neurons. Neuroscience. 1997 Jan;76(2):619–634. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(96)00408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze W. A., Clerc N., Bertrand P. P., Furness J. B. Contractile activity in intestinal muscle evokes action potential discharge in guinea-pig myenteric neurons. J Physiol. 1999 Jun 1;517(Pt 2):547–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0547t.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze W. A., Clerc N., Furness J. B., Gola M. The soma and neurites of primary afferent neurons in the guinea-pig intestine respond differentially to deformation. J Physiol. 2000 Jul 15;526(Pt 2):375–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze W. A., Furness J. B., Bertrand P. P., Bornstein J. C. Intracellular recording from myenteric neurons of the guinea-pig ileum that respond to stretch. J Physiol. 1998 Feb 1;506(Pt 3):827–842. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.827bv.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze W. A., Furness J. B. The enteric nervous system and regulation of intestinal motility. Annu Rev Physiol. 1999;61:117–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.61.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y. M., Roder J. C., Davidow J., Salter M. W. Src activation in the induction of long-term potentiation in CA1 hippocampal neurons. Science. 1998 Feb 27;279(5355):1363–1367. doi: 10.1126/science.279.5355.1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manseau F., Sossin W. S., Castellucci V. F. Long-term changes in excitability induced by protein kinase C activation in Aplysia sensory neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1998 Mar;79(3):1210–1218. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.3.1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer E. A., Raybould H. E. Role of visceral afferent mechanisms in functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 1990 Dec;99(6):1688–1704. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90475-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean P. G., Garcia-Villar R., Fioramonti J., Buéno L. Effects of tachykinin receptor antagonists on the rat jejunal distension pain response. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998 Mar 26;345(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munakata J., Naliboff B., Harraf F., Kodner A., Lembo T., Chang L., Silverman D. H., Mayer E. A. Repetitive sigmoid stimulation induces rectal hyperalgesia in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1997 Jan;112(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70219-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P. R., Palmer J. M., Wood J. D., Zafirov D. H. Effects of forskolin on electrical behaviour of myenteric neurones in guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:439–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness T. J., Gebhart G. F. Visceral pain: a review of experimental studies. Pain. 1990 May;41(2):167–234. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(90)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otmakhov N., Griffith L. C., Lisman J. E. Postsynaptic inhibitors of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II block induction but not maintenance of pairing-induced long-term potentiation. J Neurosci. 1997 Jul 15;17(14):5357–5365. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-14-05357.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Wood J. D., Zafirov D. H. Elevation of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate mimics slow synaptic excitation in myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:451–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan H., Wang H. Y., Friedman E., Gershon M. D. Mediation by protein kinases C and A of Go-linked slow responses of enteric neurons to 5-HT. J Neurosci. 1997 Feb 1;17(3):1011–1024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-03-01011.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedarzani P., Krause M., Haug T., Storm J. F., Stühmer W. Modulation of the Ca2+-activated K+ current sIAHP by a phosphatase-kinase balance under basal conditions in rat CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1998 Jun;79(6):3252–3256. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.6.3252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serra J., Azpiroz F., Malagelada J. R. Perception and reflex responses to intestinal distention in humans are modified by simultaneous or previous stimulation. Gastroenterology. 1995 Dec;109(6):1742–1749. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90739-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Feng D. P. Postsynaptic protein kinase C essential to induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation in the hippocampal CA1 region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2576–2580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]