Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (184.1 KB).
Figure 1 .
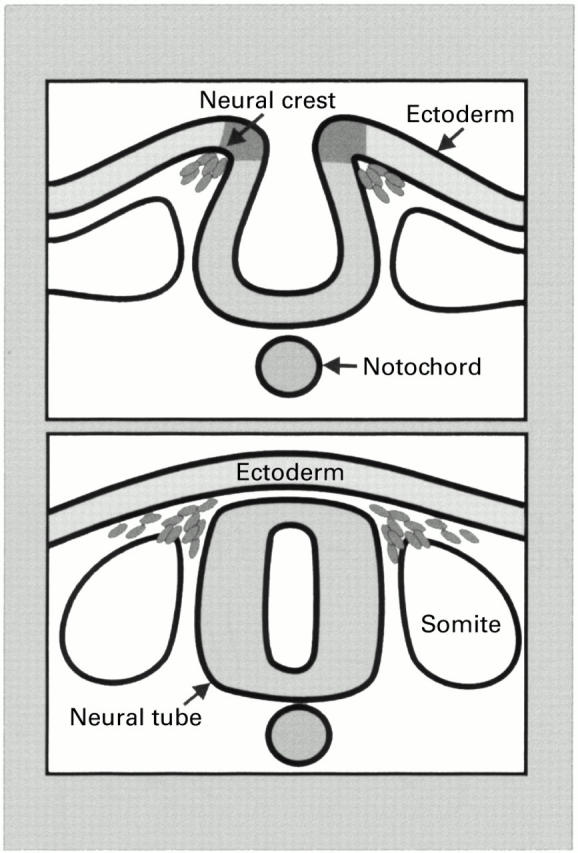
Development of the enteric nervous system from the neural crest.
Figure 2 .
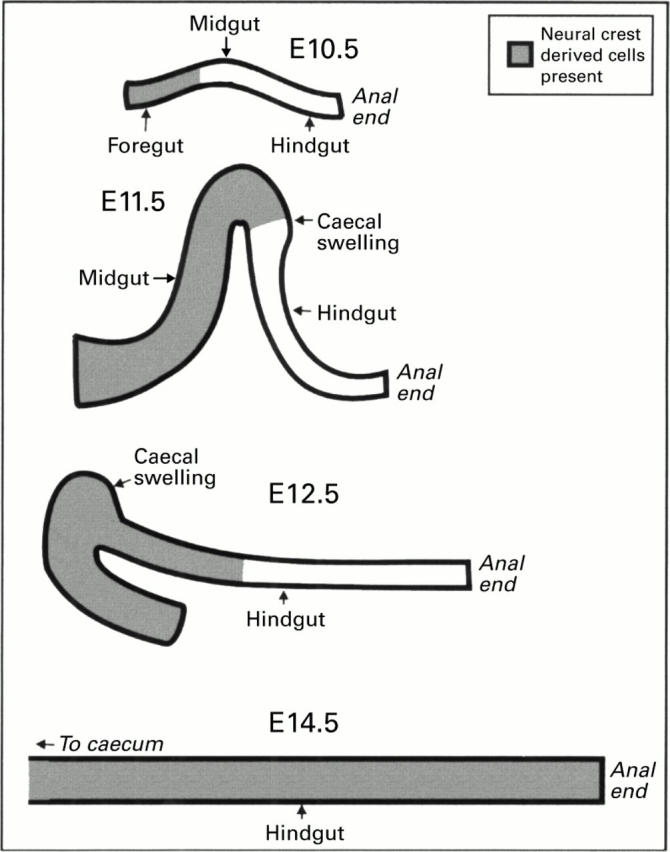
Colonisation of the gut by vagal level neural crest cells.
Figure 3 .
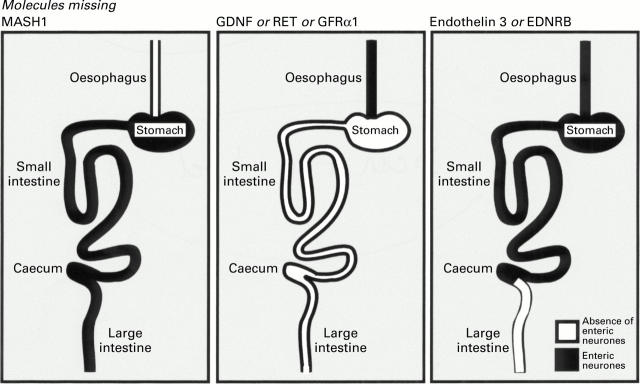
Use of gene knockout studies to identify molecules which are essential for the development of the enteric nervous system in different regions of the gut. GDNF, glial derived neurotrophic factor; GFRα1, GDNF family receptor α1; EDNRB, endothelin B.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan I. J., Newgreen D. F. The origin and differentiation of enteric neurons of the intestine of the fowl embryo. Am J Anat. 1980 Feb;157(2):137–154. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001570203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannerman P. G., Pleasure D. Protein growth factor requirements of rat neural crest cells. J Neurosci Res. 1993 Sep 1;36(1):46–57. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490360106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branchek T. A., Gershon M. D. Time course of expression of neuropeptide Y, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and NADPH diaphorase activity in neurons of the developing murine bowel and the appearance of 5-hydroxytryptamine in mucosal enterochromaffin cells. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Jul 8;285(2):262–273. doi: 10.1002/cne.902850208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns A. J., Douarin N. M. The sacral neural crest contributes neurons and glia to the post-umbilical gut: spatiotemporal analysis of the development of the enteric nervous system. Development. 1998 Nov;125(21):4335–4347. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.21.4335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalazonitis A., Rothman T. P., Chen J., Lamballe F., Barbacid M., Gershon M. D. Neurotrophin-3 induces neural crest-derived cells from fetal rat gut to develop in vitro as neurons or glia. J Neurosci. 1994 Nov;14(11 Pt 1):6571–6584. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-11-06571.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariepy C. E., Williams S. C., Richardson J. A., Hammer R. E., Yanagisawa M. Transgenic expression of the endothelin-B receptor prevents congenital intestinal aganglionosis in a rat model of Hirschsprung disease. J Clin Invest. 1998 Sep 15;102(6):1092–1101. doi: 10.1172/JCI3702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D. Genes and lineages in the formation of the enteric nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1997 Feb;7(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(97)80127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearn C. J., Young H. M., Ciampoli D., Lomax A. E., Newgreen D. Catenary cultures of embryonic gastrointestinal tract support organ morphogenesis, motility, neural crest cell migration, and cell differentiation. Dev Dyn. 1999 Mar;214(3):239–247. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0177(199903)214:3<239::AID-AJA7>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbarth B., Pingault V., Bondurand N., Kuhlbrodt K., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Puliti A., Lemort N., Goossens M., Wegner M. Mutation of the Sry-related Sox10 gene in Dominant megacolon, a mouse model for human Hirschsprung disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Apr 28;95(9):5161–5165. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.9.5161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jing S., Wen D., Yu Y., Holst P. L., Luo Y., Fang M., Tamir R., Antonio L., Hu Z., Cupples R. GDNF-induced activation of the ret protein tyrosine kinase is mediated by GDNFR-alpha, a novel receptor for GDNF. Cell. 1996 Jun 28;85(7):1113–1124. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapur R. P., Yost C., Palmiter R. D. A transgenic model for studying development of the enteric nervous system in normal and aganglionic mice. Development. 1992 Sep;116(1):167–175. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.Supplement.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. M., Teillet M. A. The migration of neural crest cells to the wall of the digestive tract in avian embryo. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1973 Aug;30(1):31–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo L. C., Johnson J. E., Wuenschell C. W., Saito T., Anderson D. J. Mammalian achaete-scute homolog 1 is transiently expressed by spatially restricted subsets of early neuroepithelial and neural crest cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1524–1537. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijers J. H., Tibboel D., van der Kamp A. W., van Haperen-Heuts I. C., Molenaar J. C. A model for aganglionosis in the chicken embryo. J Pediatr Surg. 1989 Jun;24(6):557–561. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(89)80505-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachnis V., Mankoo B., Costantini F. Expression of the c-ret proto-oncogene during mouse embryogenesis. Development. 1993 Dec;119(4):1005–1017. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.4.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattyn A., Morin X., Cremer H., Goridis C., Brunet J. F. Expression and interactions of the two closely related homeobox genes Phox2a and Phox2b during neurogenesis. Development. 1997 Oct;124(20):4065–4075. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.20.4065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomeranz H. D., Rothman T. P., Gershon M. D. Colonization of the post-umbilical bowel by cells derived from the sacral neural crest: direct tracing of cell migration using an intercalating probe and a replication-deficient retrovirus. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):647–655. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serbedzija G. N., Burgan S., Fraser S. E., Bronner-Fraser M. Vital dye labelling demonstrates a sacral neural crest contribution to the enteric nervous system of chick and mouse embryos. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):857–866. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southard-Smith E. M., Kos L., Pavan W. J. Sox10 mutation disrupts neural crest development in Dom Hirschsprung mouse model. Nat Genet. 1998 Jan;18(1):60–64. doi: 10.1038/ng0198-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiveron M. C., Hirsch M. R., Brunet J. F. The expression pattern of the transcription factor Phox2 delineates synaptic pathways of the autonomic nervous system. J Neurosci. 1996 Dec 1;16(23):7649–7660. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-23-07649.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treanor J. J., Goodman L., de Sauvage F., Stone D. M., Poulsen K. T., Beck C. D., Gray C., Armanini M. P., Pollock R. A., Hefti F. Characterization of a multicomponent receptor for GDNF. Nature. 1996 Jul 4;382(6586):80–83. doi: 10.1038/382080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YNTEMA C. L., HAMMOND W. S. The origin of intrinsic ganglia of trunk viscera from vagal neural crest in the chick embryo. J Comp Neurol. 1954 Oct;101(2):515–541. doi: 10.1002/cne.901010212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. M., Ciampoli D., Southwell B. R., Newgreen D. F. Origin of interstitial cells of Cajal in the mouse intestine. Dev Biol. 1996 Nov 25;180(1):97–107. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. M., Ciampoli D. Transient expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase by neurons of the submucous plexus of the mouse small intestine. Cell Tissue Res. 1998 Mar;291(3):395–401. doi: 10.1007/s004410051009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. M., Hearn C. J., Ciampoli D., Southwell B. R., Brunet J. F., Newgreen D. F. A single rostrocaudal colonization of the rodent intestine by enteric neuron precursors is revealed by the expression of Phox2b, Ret, and p75 and by explants grown under the kidney capsule or in organ culture. Dev Biol. 1998 Oct 1;202(1):67–84. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.8987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]