Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (143.7 KB).
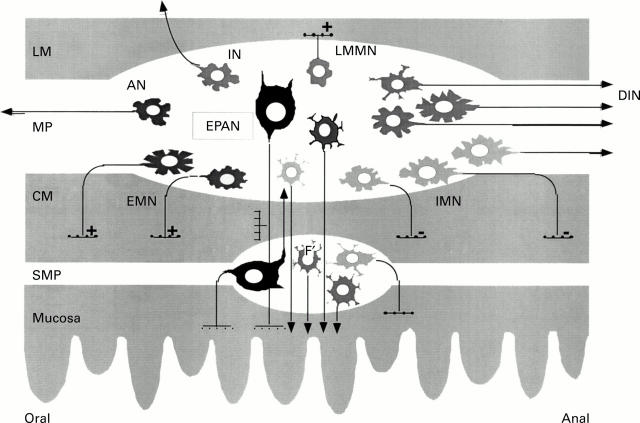
Figure 1 .
Classes of myenteric neurones. LM, longitudinal muscle; CM, circular muscle; MP, myenteric plexus; SMP, submucous plexus; AN, ascending neurones; IN, intestinofugal neurones; DIN, descending interneurones; EPAN, enteric primary afferent neurones; EMN, excitatory motorneurones; IMN, inhibitory motorneurones; LMMN, longitudinal motorneurones. The secretomotor and vasomotor neurones in the myenteric and submucous plexuses are not labelled (modified from Costa and colleagues6).
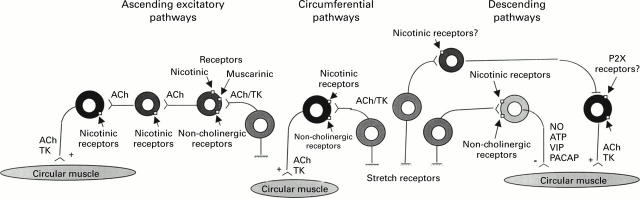
Figure 2 .
Polarised enteric motor pathways involved in control of intestinal motor activity. ACh, acetylcholine; TK, tachykinins; NO, nitric oxide; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide; PACAP, pituitary activating cyclic AMP peptide; P2X, subclass of purinergic receptors.
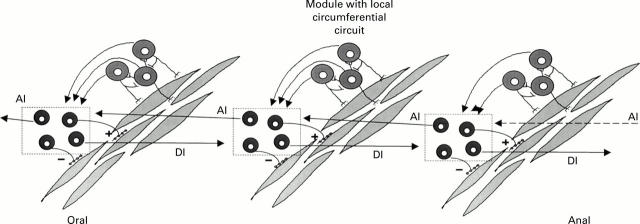
Figure 3 .
Modular organisation of the enteric nervous system with repeated and overlapping circumferential, ascending, and descending neural pathways. AI, ascending pathways; DI, descending pathways.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayliss W. M., Starling E. H. The movements and innervation of the small intestine. J Physiol. 1899 May 11;24(2):99–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1899.sp000752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes S. J., Chen B. N., Costa M., Humphreys C. M. Initiation of peristalsis by circumferential stretch of flat sheets of guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1999 Apr 15;516(Pt 2):525–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0525v.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes S. J., Meedeniya A. C., Jobling P., Costa M. Orally projecting interneurones in the guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1997 Dec 1;505(Pt 2):473–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1997.473bb.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes S. J., Song Z. M., Ramsay G. A., Costa M. Long aboral projections of Dogiel type II, AH neurons within the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig small intestine. J Neurosci. 1995 May;15(5 Pt 2):4013–4022. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-04013.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes S. J., Song Z. M., Steele P. A., Costa M. Identification of motor neurons to the longitudinal muscle of the guinea pig ileum. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):961–973. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90030-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes S. J., Steele P. A., Costa M. Identification and immunohistochemistry of cholinergic and non-cholinergic circular muscle motor neurons in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience. 1991;42(3):863–878. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimponeriu D., LoPresti P., Lavelanet M., Roistacher K., Remigio P., Marfatia S., Glatt A. E. Gastrointestinal histoplasmosis in HIV infection: two cases of colonic pseudocancer and review of the literature. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jan;89(1):129–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa M., Brookes S. J., Steele P. A., Gibbins I., Burcher E., Kandiah C. J. Neurochemical classification of myenteric neurons in the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience. 1996 Dec;75(3):949–967. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(96)00275-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Bornstein J. C., Murphy R., Pompolo S. Roles of peptides in transmission in the enteric nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992 Feb;15(2):66–71. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Kunze W. A., Bertrand P. P., Clerc N., Bornstein J. C. Intrinsic primary afferent neurons of the intestine. Prog Neurobiol. 1998 Jan;54(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(97)00051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennig G. W., Costa M., Chen B. N., Brookes S. J. Quantitative analysis of peristalsis in the guinea-pig small intestine using spatio-temporal maps. J Physiol. 1999 Jun 1;517(Pt 2):575–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0575t.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders K. M. A case for interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers and mediators of neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1996 Aug;111(2):492–515. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v111.pm8690216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna S. K. Cyclic motor activity; migrating motor complex: 1985. Gastroenterology. 1985 Oct;89(4):894–913. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90589-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Z. M., Brookes S. J., Costa M. Projections of specific morphological types of neurons within the myenteric plexus of the small intestine of the guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res. 1996 Jul;285(1):149–156. doi: 10.1007/s004410050630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele P. A., Brookes S. J., Costa M. Immunohistochemical identification of cholinergic neurons in the myenteric plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience. 1991;45(1):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonini M., Costa M., Brookes S. J., Humphreys C. M. Dissociation of the ascending excitatory reflex from peristalsis in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience. 1996 Jul;73(1):287–297. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(96)00040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman S. A., Costa M. The role of enteric inhibitory motoneurons in peristalsis in the isolated guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1994 Jun 15;477(Pt 3):459–468. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman S. A., Costa M., Tonini M. Accommodation mediated by enteric inhibitory reflexes in the isolated guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 1;474(3):539–546. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman S. A., Tonini M., Costa M. The role of ascending excitatory and descending inhibitory pathways in peristalsis in the isolated guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 15;481(Pt 1):223–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]