Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (2.4 MB).
Figure 1.
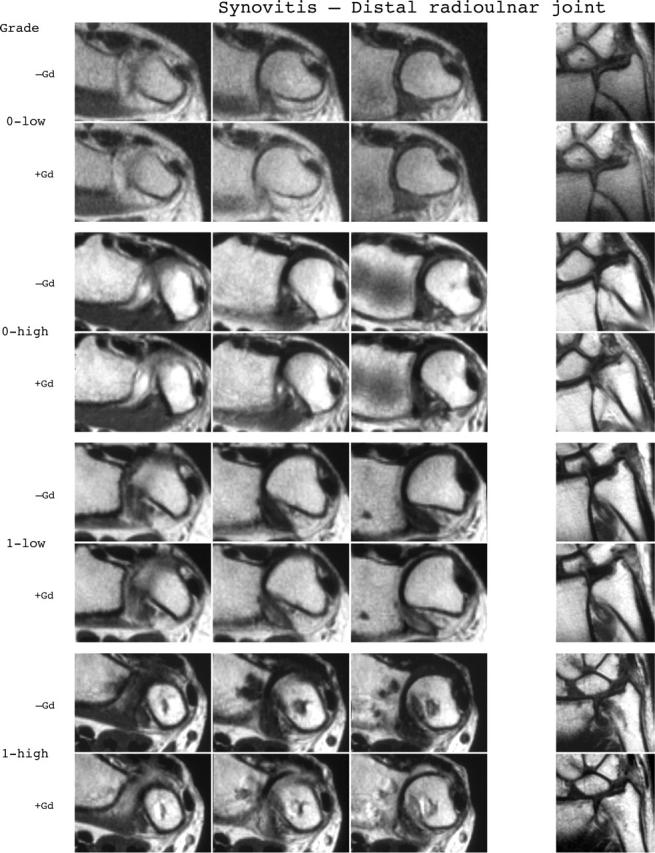
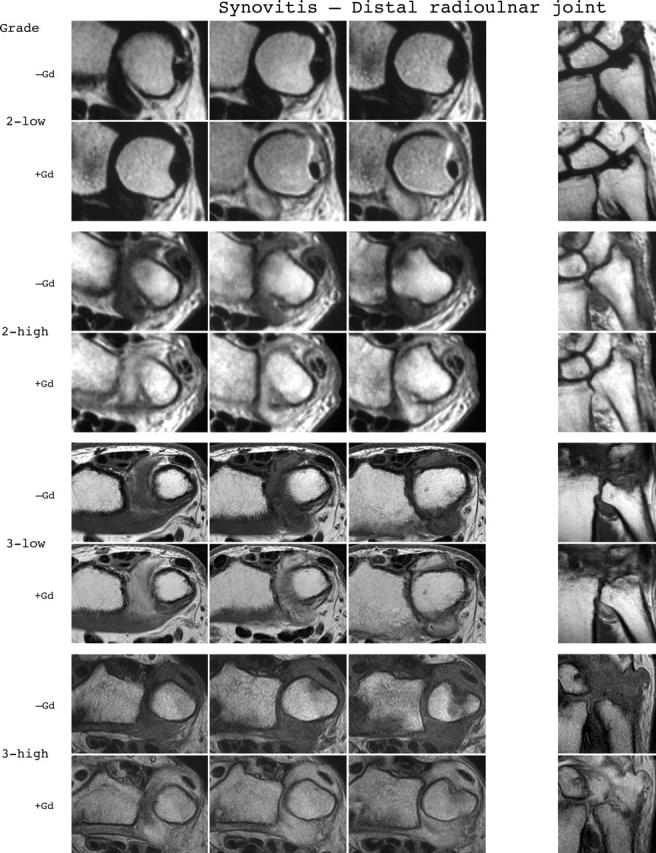
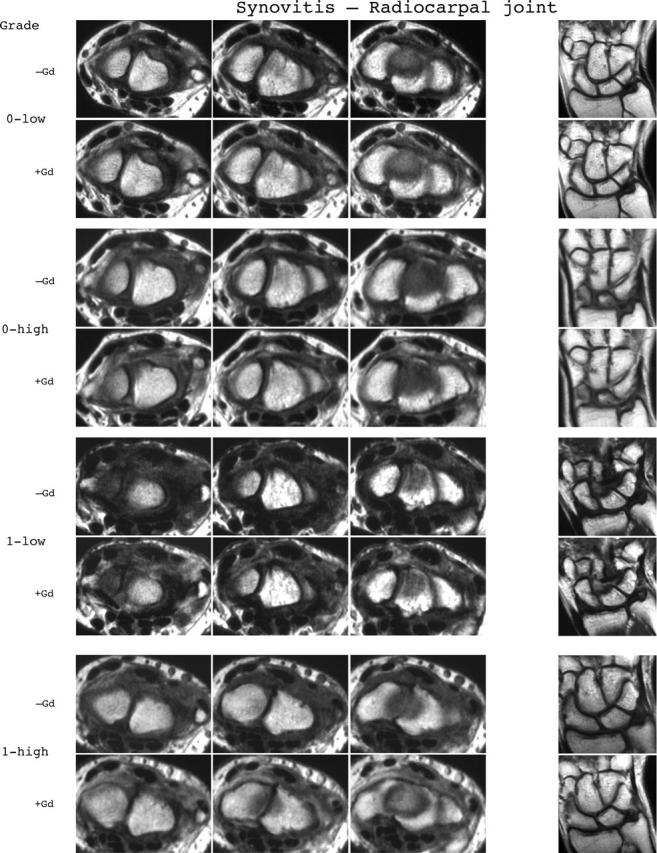
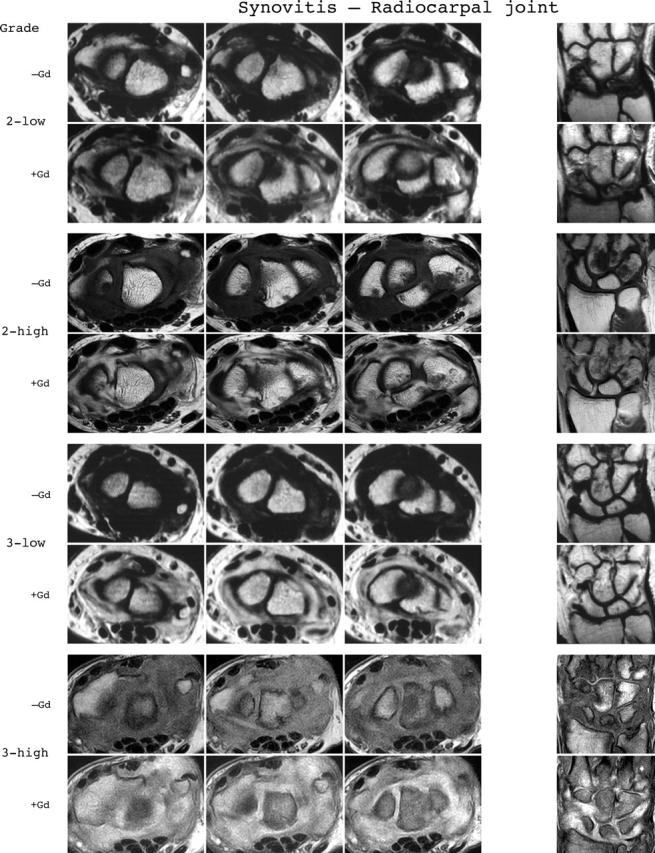
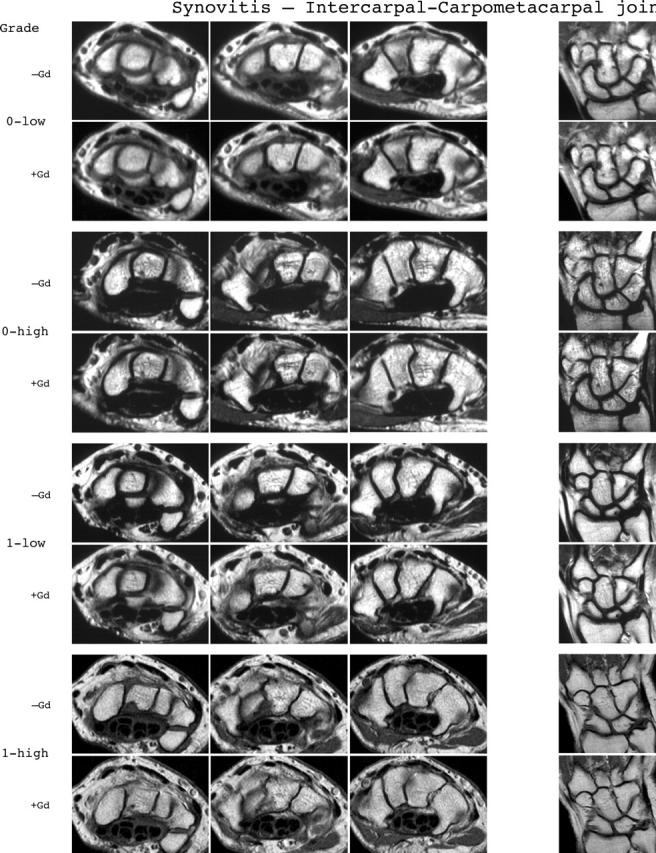
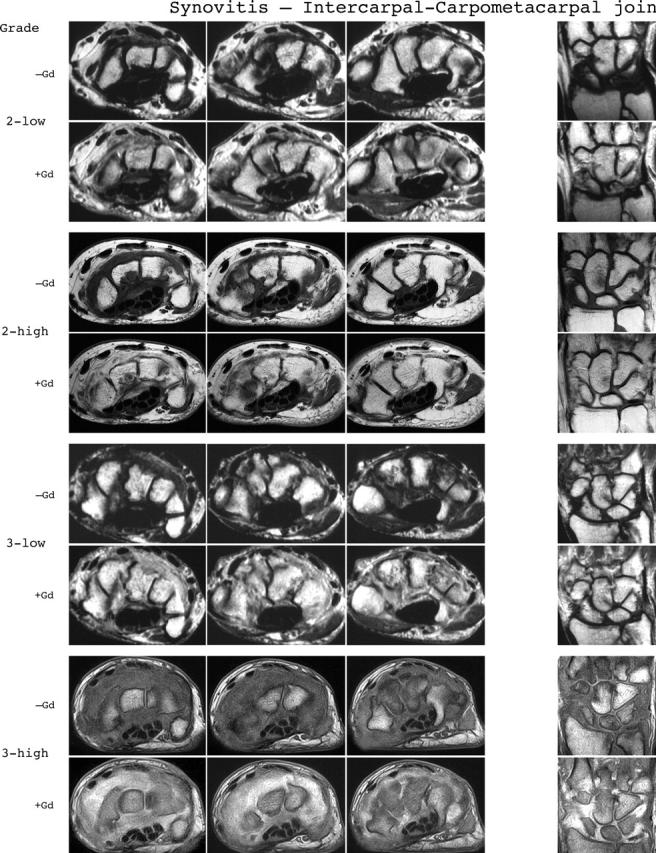
Synovitis reference image sheets (pages i24–i29, total 6). Reference image sheets for synovitis in the distal radioulnar joint, the radiocarpal joint, and the intercarpal-carpometacarpophalangeal joints are illustrated on two single-page sheets each. Examples are provided from the low end and high end of each grade (0–3). Synovitis is graded 0–3 (normal, mild, moderate, severe) as estimated by thirds of the presumed maximum volume of enhancing tissue as described in the OMERACT RAMRIS (see table 1, reference 11). The MRI set to be assessed should be compared with the axial precontrast and postcontrast T1 weighted reference images and the joint assigned the score of the best possible match. The first carpometacarpal joint should not be scored. All axial slices covering the joint should be taken into account. A total score (range 0–9) can be calculated. The diagram above describes the positions and types of images included.
Figure 2.


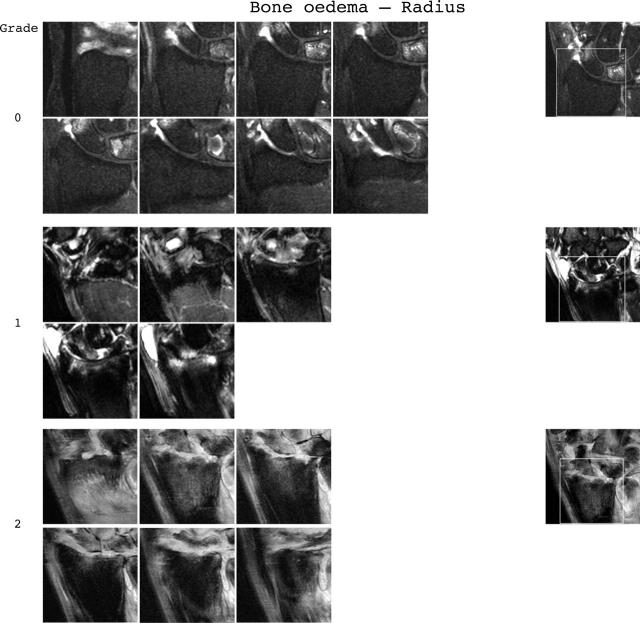
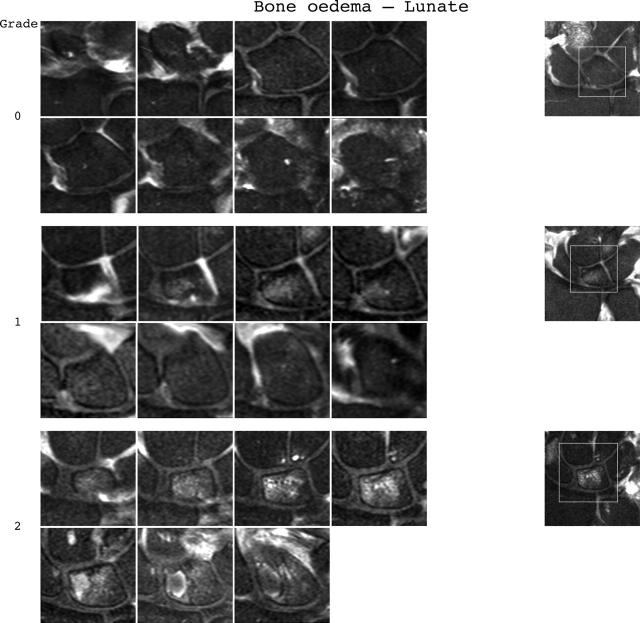
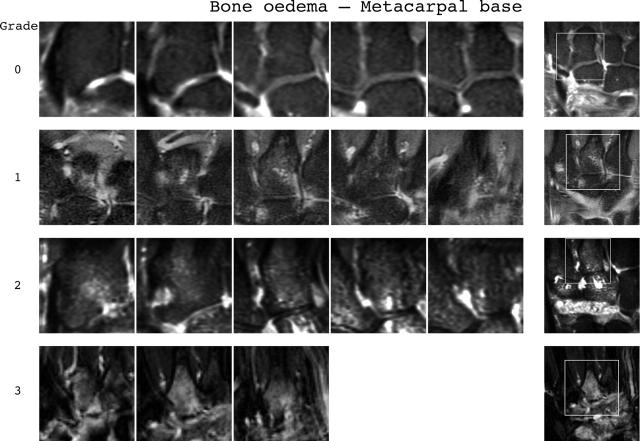
Bone oedema reference image sheets (pages i30–i34, total 5). Bone oedema in the radius, scaphoid, lunate, capitate, and a metacarpal base is illustrated on a single-page sheet each. All grades (0–3) are presented except when appropriate examples could not be found. Bone oedema is graded by percentage volume (0–3, by 33% volume increments) of the assessed bone as described in the OMERACT RAMRIS (see table 1, reference 17). For long bones (radius, ulna, metacarpal bases), the "assessed bone volume" is from the articular surface (or its best estimated position if absent) to a depth of 1 cm, and in carpal bones it is the whole bone. If erosion and oedema are concurrently present, oedema is scored as the proportion of the original bone. All coronal slices (T2 weighted fat saturated or short tau inversion recovery (STIR)) covering the bone need to be assessed to estimate the percentage of the total volume occupied by the oedema. The atlas reference images can be used for guidance and calibration. Each bone of the wrist should be scored separately. A total score (range 0–45) can be calculated. The diagram above describes the positions and types of images included. The varying number of coronal slices needed to cover the bone reflects varying bone sizes and varying slice thickness (2–3 mm).
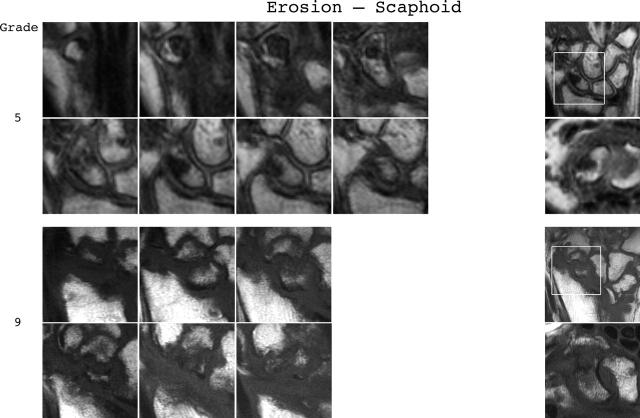
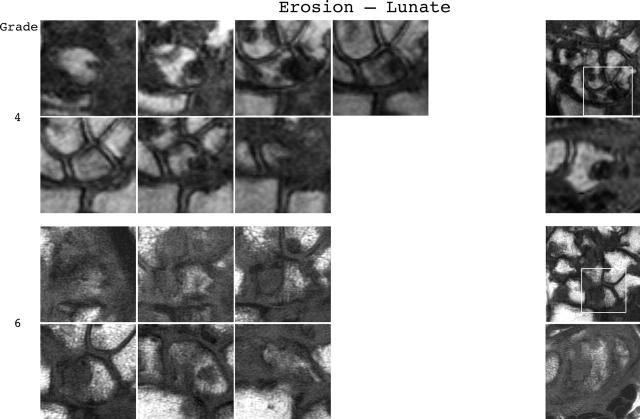
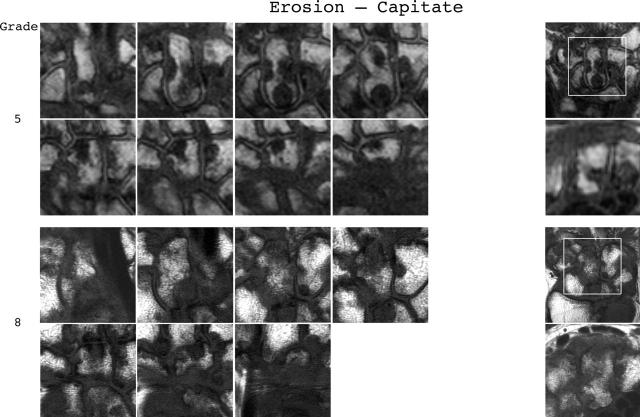
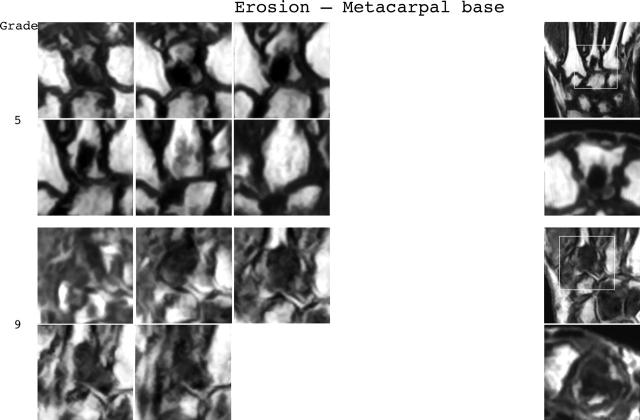
Figure 3.
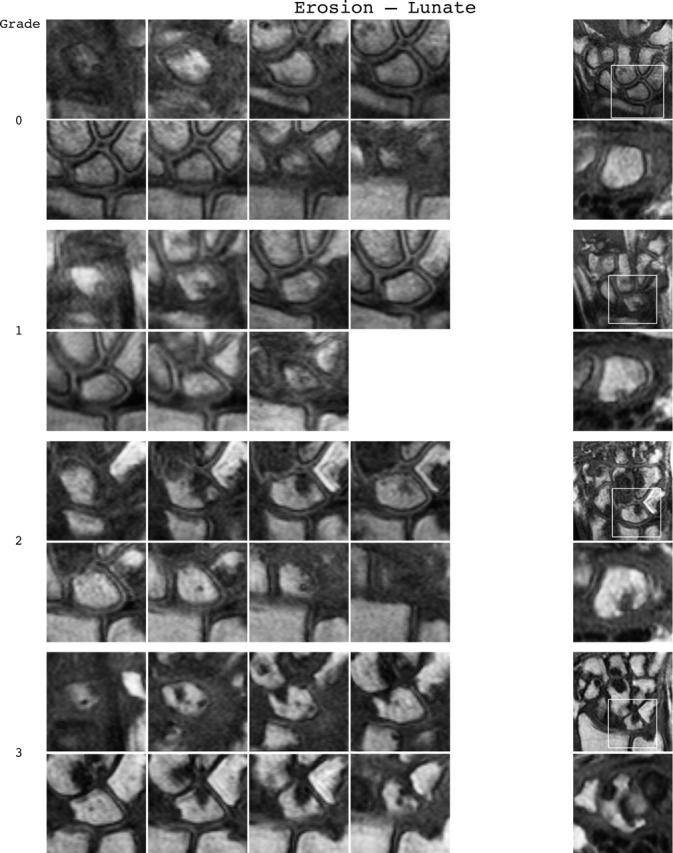
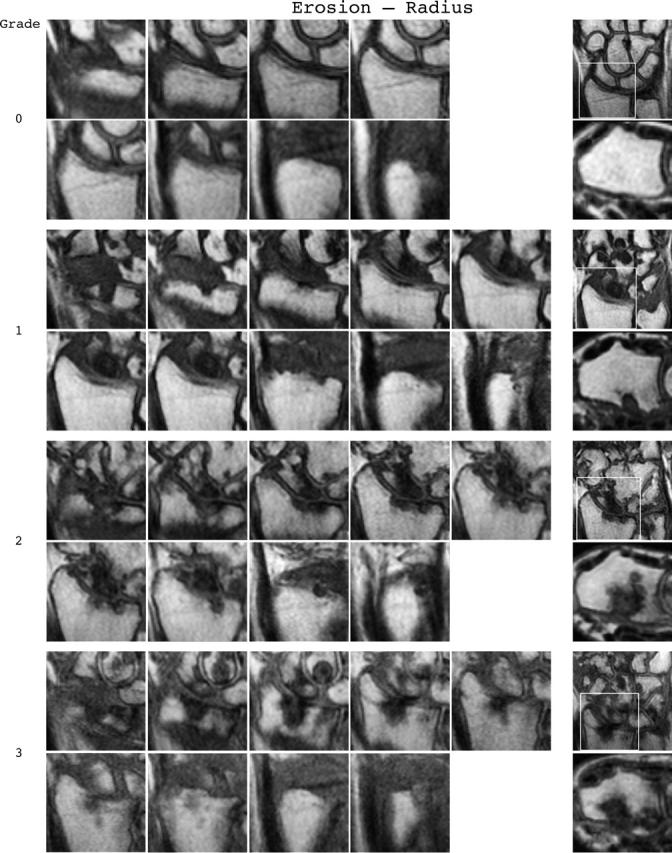
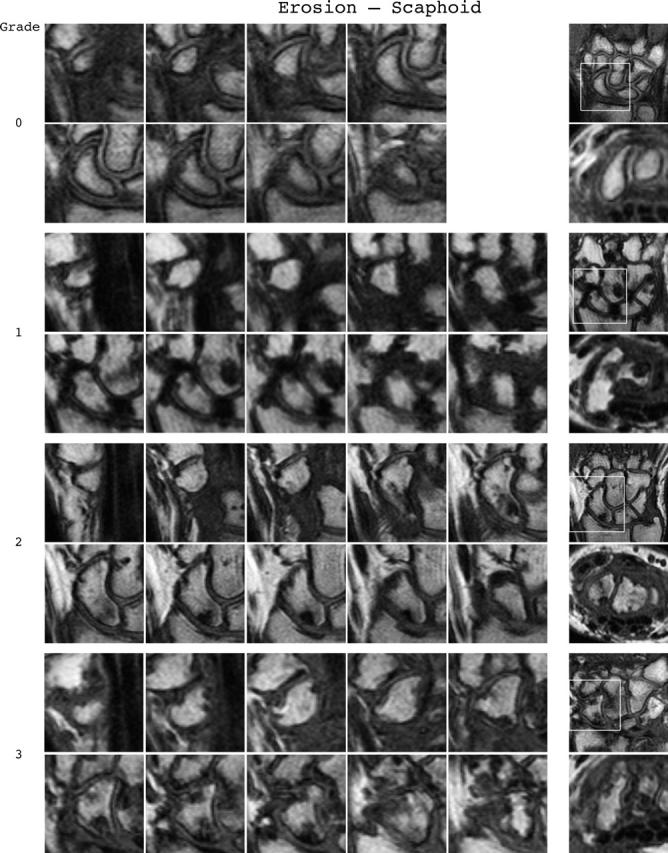


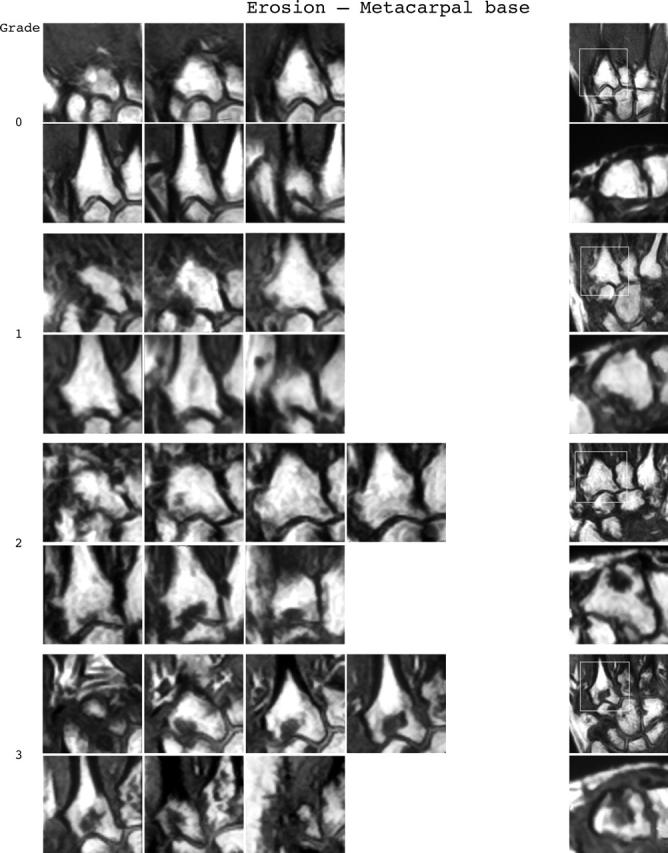
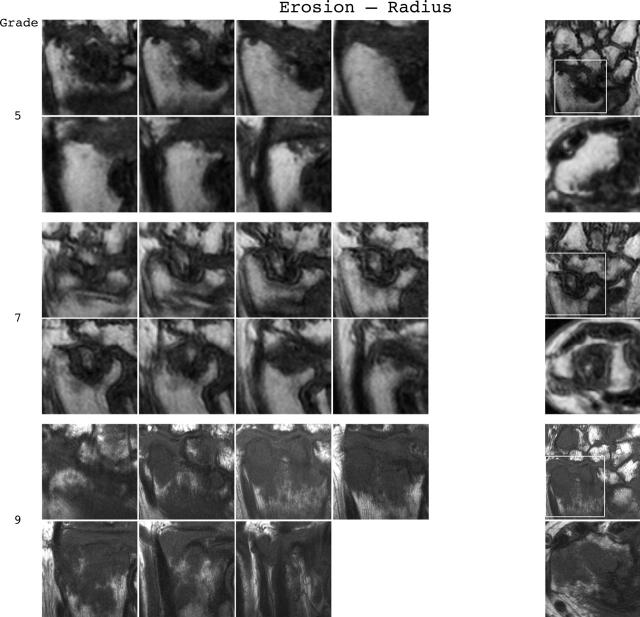
Bone erosion reference image sheets (pages i36–i45, total 10). Bone erosion in the radius, scaphoid, lunate, capitate and a metacarpal base is illustrated on two single-page sheets each. Grades 0–3 supplemented with examples of three higher grades are provided. Bone erosion is graded by assessing percentage volume (1–10, by 10% volume increments) of the assessed bone volume as described in the OMERACT RAMRIS (see table 1, reference 17). The "assessed bone volume" is defined as described above. It should be emphasised that all coronal slices covering the bone should be assessed to estimate the percentage of the total volume occupied by the erosion. The atlas reference images can be used for guidance and calibration. Each bone of the wrist should be scored separately. A total score (range 0–150) can be calculated. The drawing above explains the types and positions of images presented. The varying number of coronal slices needed to cover the bone reflects varying bone sizes and varying slice thickness (2–3 mm).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird P., Conaghan P., Ejbjerg B., McQueen F., Lassere M., Peterfy C., Edmonds J., Shnier R., O'Connor P., Haavardsholm E. The development of the EULAR-OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Feb;64 (Suppl 1):i8–10. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.031807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird Paul, Lassere Marissa, Shnier Ron, Edmonds John. Computerized measurement of magnetic resonance imaging erosion volumes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with existing magnetic resonance imaging scoring systems and standard clinical outcome measures. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Mar;48(3):614–624. doi: 10.1002/art.10820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaghan Philip, Lassere Marissa, Østergaard Mikkel, Peterfy Charles, McQueen Fiona, O'Connor Philip, Bird Paul, Ejbjerg Bo, Klarlund Mette, Shnier Ron. OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Exercise 4: an international multicenter longitudinal study using the RA-MRI Score. J Rheumatol. 2003 Jun;30(6):1376–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felson D. T., Anderson J. J., Boers M., Bombardier C., Chernoff M., Fried B., Furst D., Goldsmith C., Kieszak S., Lightfoot R. The American College of Rheumatology preliminary core set of disease activity measures for rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The Committee on Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Jun;36(6):729–740. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming A., Benn R. T., Corbett M., Wood P. H. Early rheumatoid disease. II. Patterns of joint involvement. Ann Rheum Dis. 1976 Aug;35(4):361–364. doi: 10.1136/ard.35.4.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassere Marissa, McQueen Fiona, Østergaard Mikkel, Conaghan Philip, Shnier Ron, Peterfy Charles, Klarlund Mette, Bird Paul, O'Connor Philip, Stewart Neal. OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Exercise 3: an international multicenter reliability study using the RA-MRI Score. J Rheumatol. 2003 Jun;30(6):1366–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen F. M., Stewart N., Crabbe J., Robinson E., Yeoman S., Tan P. L., McLean L. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals progression of erosions despite clinical improvement. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Mar;58(3):156–163. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.3.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen Fiona M., Benton Nick, Perry David, Crabbe Jeff, Robinson Elizabeth, Yeoman Sue, McLean Lachy, Stewart Neal. Bone edema scored on magnetic resonance imaging scans of the dominant carpus at presentation predicts radiographic joint damage of the hands and feet six years later in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Jul;48(7):1814–1827. doi: 10.1002/art.11162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Hansen M., Stoltenberg M., Gideon P., Klarlund M., Jensen K. E., Lorenzen I. Magnetic resonance imaging-determined synovial membrane volume as a marker of disease activity and a predictor of progressive joint destruction in the wrists of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 May;42(5):918–929. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199905)42:5<918::AID-ANR10>3.0.CO;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Klarlund M., Lassere M., Conaghan P., Peterfy C., McQueen F., O'Connor P., Shnier R., Stewart N., McGonagle D. Interreader agreement in the assessment of magnetic resonance images of rheumatoid arthritis wrist and finger joints--an international multicenter study. J Rheumatol. 2001 May;28(5):1143–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M. Plain X-rays in rheumatoid arthritis: overview of scoring methods, their reliability and applicability. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1996 Aug;10(3):435–453. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(96)80043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Østergaard M., Edmonds J., McQueen F., Peterfy C., Lassere M., Ejbjerg B., Bird P., Emery P., Genant H., Conaghan P. An introduction to the EULAR-OMERACT rheumatoid arthritis MRI reference image atlas. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Feb;64 (Suppl 1):i3–i7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.031773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Østergaard Mikkel, Hansen Michael, Stoltenberg Michael, Jensen Karl Erik, Szkudlarek Marcin, Pedersen-Zbinden Brigitta, Lorenzen Ib. New radiographic bone erosions in the wrists of patients with rheumatoid arthritis are detectable with magnetic resonance imaging a median of two years earlier. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Aug;48(8):2128–2131. doi: 10.1002/art.11076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]