Abstract
This paper reviews the existing evidence regarding the use of superagonistic anti-CD28 antibodies (CD28 superagonists) for therapeutic manipulation of regulatory T cells (Treg cells). The molecular properties of superagonistic anti-CD28 antibodies allow the generation of a strong activating signal in mature T cells, including Treg cells, without additional stimulation of the T cell receptor complex. CD28 superagonist administration in vivo leads to the preferential expansion and strong activation of naturally occurring CD4+CD25+CTLA-4+FoxP3+ Treg cells over conventional T cells. In animal models, both prophylactic and therapeutic administration of a CD28 superagonist prevented or at least greatly mitigated clinical symptoms and induced remission. Adoptive transfer experiments have further shown that CD28 superagonists mediate protection by expansion and activation of CD4+CD25+ Treg cells. Therefore, superagonistic anti-CD28 antibodies offer a promising novel treatment option for human autoimmune diseases and the first clinical trials are eagerly awaited.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (189.9 KB).
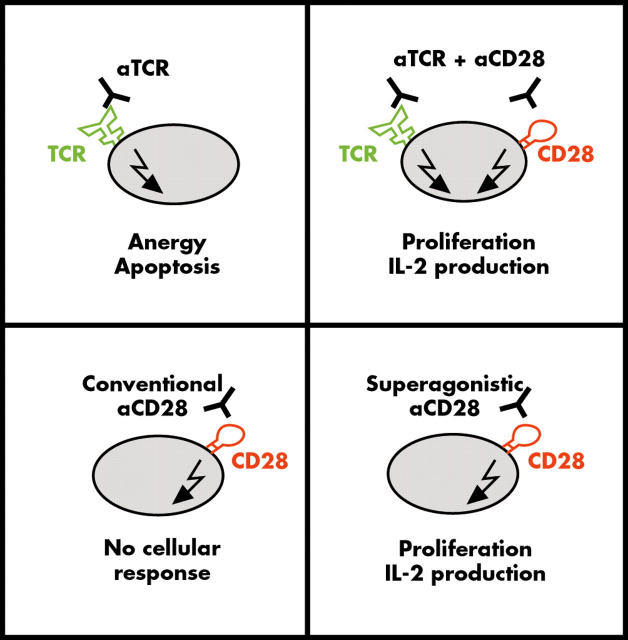
Figure 1.
Two classes of CD28 specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs): "conventional" and "superagonistic". Conventional anti-CD28 mAbs are, only in the context of costimulation, capable of driving interleukin (IL)-2 production and T cell proliferation. In contrast, superagonistic anti-CD28 antibodies do not depend on exogenous T cell receptor (TCR) triggering for full T cell activation.
Figure 2.
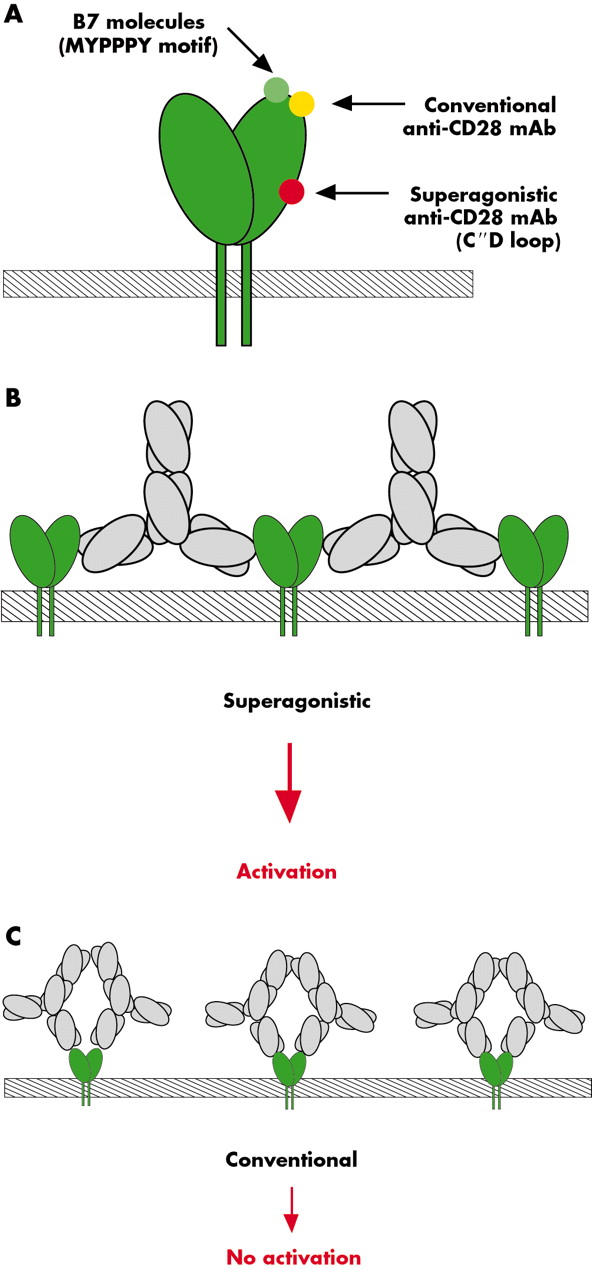
Bivalent linear complex formation could be the molecular clue to superagonistic CD28 stimulation. Only CD28 superagonists (red), but not conventional anti-CD28 antibodies (yellow) or B7 molecules (green), bind to a lateral motif of the CD28 molecule (A).4 Therefore, only CD28 superagonists are capable of forming linear complexes with CD28 molecules (B, C). In these complexes activating signalling components, presumably, get aggregated, which is sufficient to surpass the threshold for T cell activation.
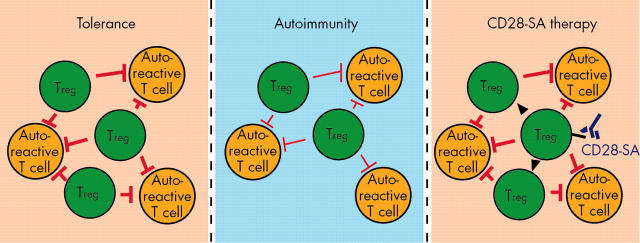
Figure 3.
A numerical and/or functional imbalance between autoreactive effector T cells and regulatory T cells (Treg cells) contributes to the induction and maintenance of autoimmunity. CD28 superagonists are capable of re-establishing peripheral tolerance via the activation and expansion of regulatory T cells.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acuto Oreste, Michel Frédérique. CD28-mediated co-stimulation: a quantitative support for TCR signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003 Dec;3(12):939–951. doi: 10.1038/nri1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apostolou Irina, Sarukhan Adelaida, Klein Ludger, von Boehmer Harald. Origin of regulatory T cells with known specificity for antigen. Nat Immunol. 2002 Jul 1;3(8):756–763. doi: 10.1038/ni816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthlott Thomas, Moncrieffe Halima, Veldhoen Marc, Atkins Christopher J., Christensen Jillian, O'Garra Anne, Stockinger Brigitta. CD25+ CD4+ T cells compete with naive CD4+ T cells for IL-2 and exploit it for the induction of IL-10 production. Int Immunol. 2005 Jan 31;17(3):279–288. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein Michael R., Evans Jamie G., Singh Animesh, Moore Samantha, Warnes Gary, Isenberg David A., Mauri Claudia. Compromised function of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis and reversal by anti-TNFalpha therapy. J Exp Med. 2004 Jul 26;200(3):277–285. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans Edward J., Esnouf Robert M., Manso-Sancho Raquel, Gilbert Robert J. C., James John R., Yu Chao, Fennelly Janet A., Vowles Cheryl, Hanke Thomas, Walse Björn. Crystal structure of a soluble CD28-Fab complex. Nat Immunol. 2005 Feb 6;6(3):271–279. doi: 10.1038/ni1170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontenot Jason D., Gavin Marc A., Rudensky Alexander Y. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003 Mar 3;4(4):330–336. doi: 10.1038/ni904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontenot Jason D., Rasmussen Jeffrey P., Williams Luke M., Dooley James L., Farr Andrew G., Rudensky Alexander Y. Regulatory T cell lineage specification by the forkhead transcription factor foxp3. Immunity. 2005 Mar;22(3):329–341. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2005.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori Shohei, Nomura Takashi, Sakaguchi Shimon. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science. 2003 Jan 9;299(5609):1057–1061. doi: 10.1126/science.1079490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh Chyi-Song, Liang Yuqiong, Tyznik Aaron J., Self Steven G., Liggitt Denny, Rudensky Alexander Y. Recognition of the peripheral self by naturally arising CD25+ CD4+ T cell receptors. Immunity. 2004 Aug;21(2):267–277. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2004.07.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan M. S., Boesteanu A., Reed A. J., Petrone A. L., Holenbeck A. E., Lerman M. A., Naji A., Caton A. J. Thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells induced by an agonist self-peptide. Nat Immunol. 2001 Apr;2(4):301–306. doi: 10.1038/86302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerstan Andreas, Hünig Thomas. Cutting edge: distinct TCR- and CD28-derived signals regulate CD95L, Bcl-xL, and the survival of primary T cells. J Immunol. 2004 Feb 1;172(3):1341–1345. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.3.1341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khattri Roli, Cox Tom, Yasayko Sue-Ann, Ramsdell Fred. An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat Immunol. 2003 Mar 3;4(4):337–342. doi: 10.1038/ni909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Cunningham A. J. A new analysis of allogeneic interactions. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1975 Feb;53(1):27–42. doi: 10.1038/icb.1975.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Chia-Huey, Hünig Thomas. Efficient expansion of regulatory T cells in vitro and in vivo with a CD28 superagonist. Eur J Immunol. 2003 Mar;33(3):626–638. doi: 10.1002/eji.200323570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lühder Fred, Huang Yun, Dennehy Kevin M., Guntermann Christine, Müller Ingrid, Winkler Erna, Kerkau Thomas, Ikemizu Shinji, Davis Simon J., Hanke Thomas. Topological requirements and signaling properties of T cell-activating, anti-CD28 antibody superagonists. J Exp Med. 2003 Apr 21;197(8):955–966. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek Thomas R., Bayer Allison L. Tolerance, not immunity, crucially depends on IL-2. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Sep;4(9):665–674. doi: 10.1038/nri1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Palmero M., Hara T., Thumbs A., Hünig T. Triggering of T cell proliferation through CD28 induces GATA-3 and promotes T helper type 2 differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Immunol. 1999 Dec;29(12):3914–3924. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199912)29:12<3914::AID-IMMU3914>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi Shimon. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol. 2005 Apr;6(4):345–352. doi: 10.1038/ni1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon B., Lenschow D. J., Rhee L., Ashourian N., Singh B., Sharpe A., Bluestone J. A. B7/CD28 costimulation is essential for the homeostasis of the CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells that control autoimmune diabetes. Immunity. 2000 Apr;12(4):431–440. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80195-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt Jens, Elflein Karin, Stienekemeier Martina, Rodriguez-Palmero Marta, Schneider Christiane, Toyka Klaus V., Gold Ralf, Hünig Thomas. Treatment and prevention of experimental autoimmune neuritis with superagonistic CD28-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Neuroimmunol. 2003 Jul;140(1-2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(03)00182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoguchi Ruka, Hori Shohei, Takahashi Takeshi, Sakaguchi Shimon. Homeostatic maintenance of natural Foxp3(+) CD25(+) CD4(+) regulatory T cells by interleukin (IL)-2 and induction of autoimmune disease by IL-2 neutralization. J Exp Med. 2005 Mar 7;201(5):723–735. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacke M., Hanke G., Hanke T., Hünig T. CD28-mediated induction of proliferation in resting T cells in vitro and in vivo without engagement of the T cell receptor: evidence for functionally distinct forms of CD28. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Jan;27(1):239–247. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai Xuguang, Cowan Michelle, Feigenbaum Lionel, Singer Alfred. CD28 costimulation of developing thymocytes induces Foxp3 expression and regulatory T cell differentiation independently of interleukin 2. Nat Immunol. 2005 Jan 9;6(2):152–162. doi: 10.1038/ni1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Qizhi, Henriksen Kammi J., Bi Mingying, Finger Erik B., Szot Greg, Ye Jianqin, Masteller Emma L., McDevitt Hugh, Bonyhadi Mark, Bluestone Jeffrey A. In vitro-expanded antigen-specific regulatory T cells suppress autoimmune diabetes. J Exp Med. 2004 Jun 7;199(11):1455–1465. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Qizhi, Henriksen Kammi J., Boden Elisa K., Tooley Aaron J., Ye Jianqin, Subudhi Sumit K., Zheng Xin X., Strom Terry B., Bluestone Jeffrey A. Cutting edge: CD28 controls peripheral homeostasis of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2003 Oct 1;171(7):3348–3352. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.7.3348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarbell Kristin V., Yamazaki Sayuri, Olson Kara, Toy Priscilla, Steinman Ralph M. CD25+ CD4+ T cells, expanded with dendritic cells presenting a single autoantigenic peptide, suppress autoimmune diabetes. J Exp Med. 2004 Jun 7;199(11):1467–1477. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton A. M., Shevach E. M. CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med. 1998 Jul 20;188(2):287–296. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viglietta Vissia, Baecher-Allan Clare, Weiner Howard L., Hafler David A. Loss of functional suppression by CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 2004 Apr 5;199(7):971–979. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Xue-Zhong, Albert Michael H., Martin Paul J., Anasetti Claudio. CD28 ligation induces transplantation tolerance by IFN-gamma-dependent depletion of T cells that recognize alloantigens. J Clin Invest. 2004 Jun;113(11):1624–1630. doi: 10.1172/JCI20940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Rosa Maurus, Rutz Sascha, Dorninger Heike, Scheffold Alexander. Interleukin-2 is essential for CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cell function. Eur J Immunol. 2004 Sep;34(9):2480–2488. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]