Infective endocarditis is a rare but severe disease, the incidence of which seems to have been stable over the past decades. Streptococci are the most frequent causative organisms. In France, infective endocarditis ranges from 25–30 cases/million inhabitants/year (about 1500 cases/year). The profile of patients presenting with infective endocarditis, though, is changing, with an increased proportion of elderly patients and a decrease of endocarditis due to oral streptococci. Valve surgery for endocarditis is performed in about one patient in two with a perioperative mortality that remains high.
Since 1992, the date of the French consensus conference on the prophylaxis of infective endocarditis, new data have been published, requiring an update of its conclusions. These new data feature the following points:
Endocarditis remains a severe disease
Bacteraemia causing infective endocarditis is probably more often related to a daily transfer of bacteria from mouth to blood than to occasional oral or dental procedures
There is no scientific proof of the efficacy, or non-efficacy, of antibiotic prophylaxis
In France, antibiotic prophylaxis is given to less than one patient in two at risk before oral or dental procedures
A broad use of antibiotic prophylaxis, supposing that it is totally efficacious, would prevent only a small number of cases in France
A worrying increase of bacteria with decreased sensitivity to antibiotics has been reported in France.
Consequently the working group suggests:
to maintain the principle of antibiotic prophylaxis when performing procedures at risk in patients with cardiac conditions at risk, but
to limit its indications to cases that have the highest ratio of individual benefit to individual and collective risk.
This is the executive summary of the full recommendations, which are available at www.infectiologie.com.
These recommendations, however, cannot substitute for the physician’s evaluation of the individual risk in a given patient.
RECOMMENDATION 1: DEFINITION OF GROUPS AT RISK
Two groups of patients are defined: group A, high risk, for whom the incidence but also the morbidity and mortality of infective endocarditis are high; and group B, with a lower risk (lower incidence and severity) (table 1).
Table 1.
Cardiac conditions conferring risk of infective endocarditis (IE)
| Group A: cardiac conditions conferring high risk of IE | Group B: cardiac conditions conferring lower risk of IE |
| • Valvar prostheses (mechanical, homograft, or bioprostheses) • Non-operated cyanotic congenital heart disease and pulmonary–systemic shunts | • Valvar diseases: aortic insufficiency, mitral insufficiency, aortic stenosis |
| • Mitral valve prolapse with mitral insufficiency or valve thickening | |
| • History of IE | • Bicuspid aortic valve |
| • Congenital non-cyanotic heart diseases except for atrial septal defect (cardiac condition without risk) | |
| • Obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (with murmur on auscultation) |
Beside groups A and B, there are many cardiac conditions for which there is no increased risk of infective endocarditis compared with the global population (see full text).
RECOMMENDATION 2: IMPORTANCE OF HYGIENE MEASURES
General hygiene measures are the most important. They aim at decreasing the risk of bacteraemia. They include oral, dental, and skin hygiene to prevent any rupture of the skin or mucosal barriers, disinfection of wounds, curative antibiotic treatment of infection, and strict compliance with asepsis when performing procedures at risk of infection. A systematic surveillance of the oral and dental state is mandatory at least twice a year for patients with heart diseases.
Any procedure leading to a mucosal or skin wound must be avoided. Thus, skin piercing is strictly contraindicated for patients with cardiac conditions that confer risk. Acupuncture should be avoided. Infusion catheters should be used only when mandatory, especially in patients at risk, with peripheral rather than central catheters and systematic replacement of peripheral catheters every three or four days.
RECOMMENDATION 3: ORAL AND DENTAL CARE
In group A and B patients, it is recommended that local chlorhexidine based antiseptics be used as mouthwash for 30 seconds before dental procedures and that dental care be provided in as few sessions as possible. If several sessions are required, and if the practitioner uses antibiotic prophylaxis, the sessions must be scheduled at least 10 days apart if possible.
Indications for systemic antibiotic prophylaxis
Group A patients
Using antibiotic prophylaxis according to the rules described below is recommended for non-contraindicated invasive oral or dental procedures (table 2).
Table 2.
Indications for infective endocarditis antibiotic prophylaxis in patients undergoing oral or dental procedures according to the group of cardiac conditions at risk
| Oral or dental procedural risk | Group A: cardiac conditions conferring high risk of IE | Group B: Cardiac conditions conferring lower risk of IE |
| With risk | Recommended | Optional |
| Without risk | Not recommended | Not recommended |
Some procedures are contraindicated, such as prostheses on teeth to be pulpectomised, inserting implants, and periodontal surgery. Pulp diseases, periodontal diseases, and trauma require extraction. Other procedures are described in the full text.
Group B patients
Antibiotic prophylaxis is optional.
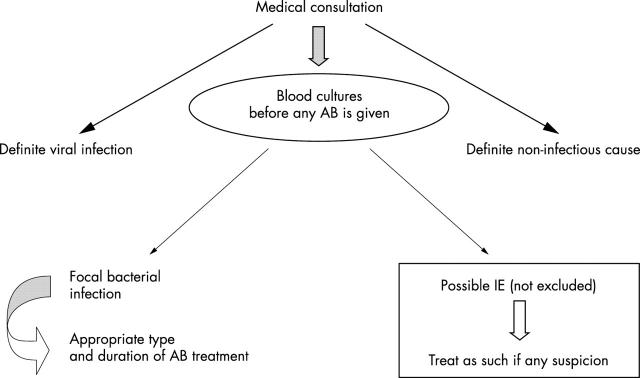
Antibiotic prophylaxis must be chosen by health care professionals, taking into account the nature of the procedures and the patient’s general condition. Table 3 lists factors that can influence this choice. Whatever the choice, it must be made after informing the patient and obtaining his or her consent to the proposed strategy. Each patient should be given a follow up leaflet where the proposed strategy has to be reported. Patients should know that in case of fever or symptoms, especially in the month following dental procedures, they must consult a physician as soon as possible before starting any drug and inform the physician of their dental history so that blood cultures can be made before initiating any antibiotic (fig 1).
Table 3.
Factors that may help in choosing whether antibiotic prophylaxis will be prescribed when prophylaxis is optional
| Arguments for prescription |
| Age >65 years |
| Associated conditions |
| Cardiac, renal, respiratory, and hepatic insufficiency |
| Diabetes mellitus |
| Acquired, constitutional or therapeutic (corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents) immunodepression |
| Oral or dental condition |
| Inadequate oral or especially dental hygiene |
| Procedure |
| Important bleeding (intensity, duration) |
| Technically difficult procedure (prolonged procedure) |
| Patient’s opinion after receiving information |
| Arguments against prescription |
| Allergy to several antibiotics |
| Patient’s opinion after receiving information |
Figure 1.
Treatment procedure for febrile patients with a cardiac condition conferring a lower risk of infective endocarditis (IE) (group B) < 3 months after a risky procedure, particularly if no antibiotic prophylaxis was used. AB, antibiotic.
Root treatment may be undertaken only under specific conditions. Implants, periodontal procedures, and some other procedures are contraindicated (see full text).
For other cardiac conditions
For other cardiac conditions, antibiotic prophylaxis is not recommended.
Before valve surgery, antibiotic prophylaxis is indicated as for group A patients. A complete radiological dental assessment must be made; only pulped teeth or teeth that have had a perfect endodontic treatment (more than a year before) without periodontal enlargement and with a healthy periodontium are kept. Pulpectomised teeth with incomplete endodontic treatment and teeth presenting with periodontal lesions and persisting roots and apex are extracted at least 15 days before cardiac surgery. In case of emergency surgery, dental care is given as soon as possible according to the context.
Indications according to the kind of procedure are described in addendum 2 of the full text.
RECOMMENDATION 4: OTHER PROCEDURES AT RISK
These recommendations are based on professional consensus, in the absence of scientific data, and cannot replace the clinician’s best judgment (table 4). They should not override recommendations concerning preoperative antibiotic prophylaxis of surgical procedures.
Table 4.
Indications for antibiotic prophylaxis in patients with other than oral or dental procedures
| Procedural risk | Group A: conditions conferring high risk of IE | Group B: conditions conferring lower risk of IE |
| Very high | Recommended | Recommended |
| High | Recommended | Optional |
| Low | Optional | Not recommended |
| Negligible | Not recommended | Not recommended |
For details, see full text and addenda.
RECOMMENDATION 5: ANTIBIOTIC PROPHYLAXIS PRESCRIPTION
The working group considers that the evolution of the epidemiology of infective endocarditis in France is an argument to maintain the current mode of antibiotic prophylaxis administration.
General modes of antibiotic prophylaxis administration
Generally, antibiotic prophylaxis is initiated in the hour before the procedure according to the mode described below (tables 5 and 6). Nevertheless, if problems possibly leading to a specific infectious risk arise during or immediately after a procedure without prior antibiotic prophylaxis (abundant bleeding, long and difficult procedures, etc), initiating antibiotic prophylaxis as soon as possible after the procedure may be indicated. This decision is to be taken by the professional in charge.
Table 5.
Antibiotic prophylaxis for IE in dental care and upper respiratory tract procedures: administration of antibiotics respecting contraindications and usual conditions of use and surveillance
| Antibiotic | Dosage and route of administration | ||
| Ambulatory care* | Single dose in the hour before the procedure | ||
| No allergy to β lactams | Amoxicillin | 3 g orally† | |
| Allergy to β lactams | Pristinamycin‡ or | 1 g orally | |
| clindamycin‡ | 600 mg orally | ||
| General anaesthesia§ | Before (in the hour before the procedure) | After (6 hours later) | |
| No allergy to β lactams | Amoxicillin | 2 g iv (infusion 30 min) | 1 g orally |
| Allergy to β lactams | Vancomycin or | 1 g iv (infusion ⩾60 min) | No second dose |
| teicoplanin | 400 mg iv (bolus) | ||
*Oral paediatric dosages: amoxicillin 75 mg/kg; clindamycin 15 mg/kg; pristinamycin 25 mg/kg; †2 g orally if the patient’s weight is <60 kg; ‡the respective percentage of streptococci strains with a decreased susceptibility to these two antibiotics must be taken into account for the choice; §paediatric dosages: amoxicillin 50 mg/kg intravenously (iv) before, 25 mg/kg orally 6 hours later; vancomycin 20 mg/kg (maximum 1 g); teicoplanin: no official approval for antibiotic prophylaxis in children.
Table 6.
Antibiotic prophylaxis for IE during urological and digestive procedures: Administration of antibiotics respecting contraindications and usual conditions of use and surveillance
| Antibiotic | Dosage and route of administration | ||
| Before (in the hour before the procedure) | After (6 h hours later) | ||
| No allergy to β lactams | Amoxicillin then | 2 g iv (infusion 30 min) | 1 g orally |
| gentamicin | 1.5 mg/kg iv (infusion 30 min) or im | No second dose | |
| Allergy to β lactams | Vancomycin or | 1 g iv (infusion ⩾60 min) | No second dose |
| teicoplanin then | 400 mg iv (bolus) | ||
| gentamicin | 1.5 mg/kg iv (infusion 30 min) or im | ||
Paediatric dosage: amoxicillin 50 mg/kg iv before, 25 mg/kg orally 6 hours later; gentamicin 2 mg/kg (maximum 80 mg); vancomycin 20 mg/kg (maximum 1 g); teicoplanin: no official approval for antibiotic prophylaxis in children.
im, intramuscularly.
If antibiotic prophylaxis concerns a procedure for which the microorganism is a staphylococcus, pristinamycin should be used unless contraindicated.
The modes of antibiotic prophylaxis administration do not apply if curative antibiotic treatment is indicated.
PROPOSITIONS
The working group makes the propositions listed in table 7 regarding the screening, follow up, and information of patients with cardiac conditions that confer risk.
Table 7.
Propositions for the assessment and diffusion of recommendations
| 1. Identify the risk level related to a valve disease (specify group A or B) in the: |
| - echocardiography report |
| - clinical file |
| - IE prevention card |
| 2. Provide a heart disease health care leaflet for patients with a cardiac condition conferring risk in groups A and B |
| 3. Set up a cohort registry of patients with a cardiac condition at risk undergoing dental procedures |
| 4. Establish a national registry of IE, recording risky procedures and antibiotic use before the current episode |