Abstract
Background: A raised intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) count with normal villous architecture is a recognised finding in latent coeliac disease. Little information is available in cases without gluten sensitive enteropathy in adults.
Aims: To assess the frequency of such a finding in routine practice and to determine whether it is clinically relevant.
Methods: Patients with subjectively increased IELs as the only abnormality were identified prospectively from a routine duodenal biopsy series over a 12 month period. The biopsy specimens in these index cases were re-examined together with two controls with normal histology for each case, and three counts of IEL/100 epithelial cells were made in all samples. The index cases were then contacted and interviewed to obtain clinical information, approximately 12 months from the initial biopsy. Further data were obtained from their clinical records.
Results: Fourteen of 626 (2.2%) patients who had duodenal biopsies over the 12 month period had a subjective increase in IELs with normal villous architecture. Fifteen patients with newly diagnosed gluten sensitive enteropathy were also identified during the study period. Formal counting of the index cases and controls revealed a significant difference in IELs/100 epithelial cell counts between the two (mean, 38 (SD, 6.2) v 12.4 (4.6); p < 0.0001). Three of the 14 index cases tested had a positive coeliac antibody test compared with 12 of 15 newly diagnosed patients with coeliac disease and 10 of 93 patients with normal histology. The major clinical diagnostic categories in raised IEL cases were those with positive coeliac serology (n = 3), unexplained anaemia (n = 3), and chronic liver disease (n = 3). Six of 10 patients who were interviewed had ongoing gastrointestinal symptoms one year later. Three patients had had follow up duodenal biopsies, at the discretion of their responsible clinicians, with no change in IEL counts despite the commencement of a gluten free diet in two patients.
Conclusion: A raised IEL count with normal villous architecture is not uncommon. Six of the 14 patients may have had latent coeliac disease. The cause in at least half of cases is not obvious at present. The finding of a raised IEL count with normal villous architecture is of sufficient clinical importance to be highlighted in routine duodenal biopsy reports.
Keywords: intraepithelial lymphocytes, duodenum, villous architecture, coeliac disease
Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) belong to a unique T cell population interspersed between epithelial cells of both the small and large intestine. They have been proposed to have a wide variety of immunological roles, particularly in response to antigen(s) in the gut lumen.1 The presence of increased IELs with villous atrophy and crypt hyperplasia is a classic feature of gluten sensitive enteropathy.2 However, in the presence of a normal villous height and villus/crypt ratio, the finding of raised IELs alone has been recognised as a latent manifestation of coeliac disease.3,4 In particular, IELs with the γ/δ T cell receptor have been shown to have a higher predictive value for gluten enteropathy.5–7 An increased IEL count with normal villous architecture has also been described in first degree relatives of patients with coeliac disease,8 especially in the presence of positive coeliac serology.9 A recent study has suggested that gluten challenge can be used to uncover latent coeliac disease in such cases.10
“The presence of increased intraepithelial lymphocytes with villous atrophy and crypt hyperplasia is a classic feature of gluten sensitive enteropathy”
Increased IEL counts have also been described in patients without gluten sensitive enteropathy, such as in cases of cow's milk protein intolerance,11 giardiasis,12 IgA deficiency,13 tropical sprue,14 hypogammaglobulinaemia,14 post infective malabsorption,14 blind loop syndrome,14 and unexplained diarrhoea with failure to thrive.15 However, all of these cases had some form of villous morphological abnormality. Furthermore, most of these reports refer to findings in children. There is very little information on the prevalence and the clinical relevance of an increased IEL count with normal duodenal villous architecture in adults without gluten sensitive enteropathy. The only publication of this finding in recent times described patients with primary glomerulonephritis.16
The aim of our study was twofold, namely: (1) to examine the frequency of increased IELs with an otherwise normal duodenal biopsy in routine practice; and (2) to review these patients' clinical and serological data to determine whether this finding is clinically relevant.
METHODS
Our study design consisted of both an initial laboratory and subsequent clinical component. Approval was obtained from the local research ethics committee to obtain the clinical data.
Histology
During the 12 month study period, August 1998 to July 1999, duodenal biopsies sent to our department from adult patients were routinely reported by one pathologist (JIW). All biopsy specimens were routinely fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin wax, and 3 μm sections were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Those biopsies showing a subjective increase in IELs present throughout the duodenal biopsy but with no abnormality of villous architecture were identified at the time of reporting and coded as “lymphocytic inflammation”. Biopsies with only a focal increase in IELs, or where there was partial villous atrophy with an increase in lamina propria cellularity, were coded as “normal” or “chronic inflammation”, respectively. These were studied no further. Biopsies showing subtotal villous atrophy, an increase in IELs and increased lamina propria mononuclear cells were coded as “histology suggesting coeliac disease”.
At the end of the study period, the biopsies coded as “lymphocytic inflammation” were retrieved, together with two control biopsies for each case that had been obtained on the same day and had a coded diagnosis of normal histology (fig 1). These slides were anonymised and randomly assessed. The number of IELs in each 100 epithelial cells was counted on the H&E sections in three well orientated, randomly selected areas of the biopsy for each case by the same pathologist, blinded to the original diagnosis. The value for the number of IELs in each 100 epithelial cells was taken as the average of the three counts.
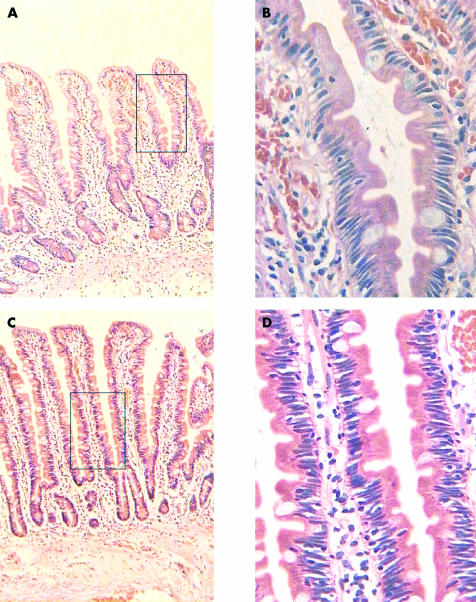
Figure 1.
(A,B) Low and high power views of normal control biopsy; the intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) count in this case was 12/1000 epithelial cells. (C,D) Low and high power views of an index case with raised IEL count (35/100 epithelial cells) and a normal villous architecture.
Clinical data
Patients identified from the duodenal biopsy series with increased IELs but an otherwise normal morphology were contacted and interviewed between 12 and 15 months after their duodenal biopsies had been taken. Specific questions were asked regarding gastrointestinal symptoms, history of dietary sensitivities/allergies, and family history of gastrointestinal disease (including gluten sensitive enteropathy).
Their case notes were also reviewed to examine the clinical indications for duodenal biopsy, the results of coeliac serology (anti-endomysial and antigliadin antibodies; see below), and the current working clinical diagnosis. These data were then compared with those from the patients in the same cohort who had definite histological features of coeliac disease and with those from the patients whose biopsies were reported to be histologically normal. Repeat duodenal biopsies (with or without an empirical gluten free diet) had been performed at the discretion of the clinicians responsible for the patient and not as part of our study.
Coeliac serology
In our hospital, IgA anti-endomysial antibodies were detected by indirect immunofluorescence on monkey oesophagus slides (Binding Site, Birmingham, UK). In active coeliac disease, these are stated to have a sensitivity and specificity of 99%. IgA and IgG antigliadin antibodies were detected by an in house enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (Sigma, Poole, Dorset, UK). IgA antigliadin antibodies tested in this manner have a sensitivity of 80–90% in active coeliac disease.
Statistics
The Mann Whitney U test was used to compare the IELs/100 epithelial cells between cases and controls and the χ2 test for the comparison of clinical symptoms.
RESULTS
Six hundred and twenty six patients had had a duodenal biopsy reported by a single pathologist (JIW) over the 12 month period. This represented an unselected 80% of all adult patients undergoing duodenal biopsy at our hospital during that time. Table 1 shows the histological diagnoses that were present in this group. Fourteen (2.2%) patients were identified who had increased IELs and normal villous architecture. The proportion of patients with newly diagnosed coeliac disease was 2.4%. The mean age of patients with raised IELs alone was 47.7 years (range, 19–84). There were eight men and six women. The control group (for histological counting) of patients with a normal duodenal biopsy had a mean age of 60.1 years (range, 28–88) and a male to female ratio of 2 : 1.
Table 1.
Diagnoses in duodenal biopsy series
| Diagnoses | n (%) |
| Normal | 502 (80.2) |
| Raised IEL count alone | 14 (2.2) |
| Coeliac disease (newly diagnosed) | 15 (2.4) |
| Treated coeliac disease (follow up) | 23 (3.7) |
| Peptic duodenitis/ulcer | 55 (8.8) |
| Giardia | 3 (0.5) |
| Candida | 4 (0.6) |
| Crohn's disease | 1 (0.16) |
| Eosinophilic infiltration | 1 (0.16) |
| Lymphoma | 1 (0.16) |
| Metastatic cancer | 1 (0.16) |
| Graft versus host disease + CMV | 1 (0.16) |
| Lipoma | 1 (0.16) |
| Gastric heterotropia | 4 (0.6) |
| Total | 626 (100) |
CMV, cytomegalovirus; IEL, intraepithelial lymphocytes.
Histology
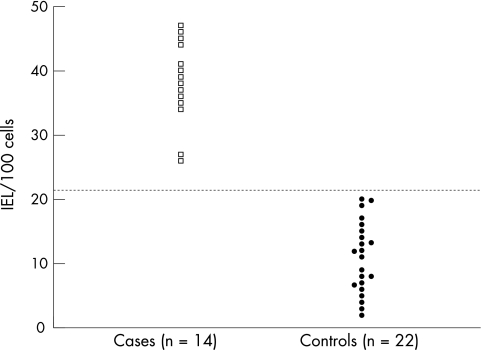
The formal counting of IELs/100 epithelial cells in index cases and controls confirmed the initial subjective impression of increased IELs in these patients. The index cases had average counts over three areas ranging from 27 to 46 IELs/100 epithelial cells with a mean (SD) of 38 (6.2) IELs/100 epithelial cells. This was significantly higher than the controls, who had a range of 2 to 20 IELs/100 epithelial cells with a mean (SD) count of 12.4 (4.6) IELs/100 epithelial cells (p < 0.0001; fig 2). In our cohort of patients, we derived an upper limit of normal as 22 IELs/100 epithelial cells, based on the mean +2SD in the control group.
Figure 2.
Intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs)/100 epithelial cells in cases and controls. The dotted horizontal line represents the upper limit of normal (control mean +2SD).
Clinical indications for biopsy
The indications for duodenal biopsy in the 14 patients with increased IELs with normal villi were anaemia (n = 6), weight loss (n = 4), diarrhoea (n = 2), duodenal polyps seen at endoscopy (n = 1), and a routine biopsy to exclude coexisting coeliac disease in a patient with primary biliary cirrhosis (n = 1). When the major clinical indications (anaemia, weight loss, and gastrointestinal symptoms) of these patients were compared with those with normal histology or with newly diagnosed coeliac disease there was no significant difference (p = 0.4; table 2).
Table 2.
Diagnoses in duodenal biopsy series
| Normal histology n (%) | Coeliac disease n (%) | Raised IEL cases n (%) | |
| Anaemia | 261 (52) | 9 (60) | 6 (42) |
| Weight loss | 55 (11) | 3 (20) | 4 (28) |
| GI symptoms | 60 (12) | 3 (20) | 2 (14) |
GI, gastointestinal; IEL, intraepithelial lymphocytes.
Coeliac serology
Eleven of the 14 index cases had been serologically tested for coeliac disease at the time of initial investigation. Serum sampling in the remaining three was not possible retrospectively as a result of death or moving away from the region. Three of 11 patients had positive coeliac serology with positive anti-endomysial antibodies in all three cases, two also being positive for IgA antigliadin and one for IgG antigliadin antibodies. Among the patients with newly diagnosed coeliac disease in our cohort, 12 of the 15 had positive serology; of these 12 patients, eight had anti-endomysial antibodies but four had antigliadin antibodies only. Ninety three patients in the histologically normal group had been tested serologically for coeliac disease; there were 10 positive cases but these were all IgG antigliadin antibodies and none in this group had anti-endomysial antibodies. Table 3 provides the details of the coeliac serology in those patients who were tested.
Table 3.
Details of antibodies in patients who were tested for coeliac serology
| Endomysial positive | IgA gliadin positive | IgG gliadin positive | Antibody negative | |
| Raised IEL alone (n=11) | 3 | 2 | 1 | 8 |
| Newly diagnosed coeliac disease (n=15) | 8 | 4 | 7 | 3 |
| Normal histology (n=93) | − | − | 10 | 83 |
IEL, intraepithelial lymphocytes; n, number of patients tested.
Clinical summary and follow up
Table 4 shows the various clinical diagnostic categories in the 14 index cases. At least six of the 14 patients had either anti-endomysial antibodies or unexplained anaemia. IEL counts did not correlate with the diagnostic categories and the three patients with positive anti-endomysial antibodies had counts of 27, 35, and 39 IELs/100 epithelial cells. None of these patients had been diagnosed as having giardiasis, IgA deficiency, hypogammaglobulinaemia, cow's milk intolerance, tropical sprue, or post infective malabsorption in the course of their investigation.
Table 4.
Diagnostic categories in patients with raised intraepithelial lymphocytes
| Categories | n |
| Positive coeliac antibodies | 3 |
| Unexplained anaemia | 3 |
| Chronic liver disease | 3 |
| Colonic polyps | 2 (1 benign, 1 malignant) |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | 2 |
| Chronic pancreatitis | 1 |
Ten patients were interviewed during the study period. One further patient declined to be interviewed and the remaining three had either died or moved out of the region. Of the 10 patients, six had non-specific gastrointestinal symptoms: two patients had diarrhoea, abdominal bloating, pain, and mild weight loss (one case each from the positive anti-endomysial antibody and unexplained anaemia category), two had diarrhoea with abdominal pain (one case each from the irritable bowel syndrome and colonic polyps category), one had diarrhoea only (colonic polyps), and one had constipation with mild weight loss (chronic pancreatitis). There was no specific history of dietary sensitivities/allergies, particularly no intolerances to gluten or wheat containing products. None of the patients had a family history of gluten sensitive enteropathy; however, both patients with colonic tumours and one patient with unexplained anaemia had a history of colorectal carcinoma in the family.
Follow up duodenal biopsies were performed in three patients (two anti-endomysial antibody positive and one irritable bowel syndrome). In the first patient with positive anti-endomysial antibodies, repeat duodenal biopsies two months after starting a gluten free diet showed persistently raised IEL counts, despite an improvement in her symptoms. No histological change was noted in the repeat duodenal biopsy of the second patient, taken five months after the initial sample. He had not been started on a gluten free diet. In the third patient, with irritable bowel syndrome, two further series of duodenal biopsies were taken over a 12 month period from the initial sample, while on a gluten free diet. Again, the IEL counts were persistently raised without change in villous architecture, but there was a pronounced improvement in his symptoms. A fourth patient, with colonic polyps, had had duodenal biopsies taken 12 months before our study, which showed increased IELs. She had not been started on a gluten free diet before her second set of duodenal biopsies, which were included in our study.
DISCUSSION
Our study was performed to determine whether the observation of increased IELs in patients with normal villous architecture should be specified in the histology report, or considered as part of the normal spectrum of duodenal histology. We have found a frequency of 2.2% of increased IELs with normal villous architecture in our routine duodenal biopsy series, which was similar to the frequency of histologically newly diagnosed coeliac disease.
The upper limit of normal in this series, 22 IEL/100 epithelial cells, was similar to a recent independent study from Leeds.17 Conventionally quoted data in the literature have referred to a normal range of 6–40 IELs/100 epithelial cells in the small intestine. These have been based on studies in the 1970s where jejunal capsule biopsies were routinely used.11,14,18,19 It is possible that there are normally fewer IELs in the proximal duodenum than in the jejunum, although we know of no studies that have investigated that point. Alternatively, technical variations such as thickness of histological sections may account for the difference.
Six of 14 patients with raised IEL counts but an otherwise normal duodenal biopsy had positive anti-endomysial antibodies and/or unexplained anaemia. We suggest that these patients may have latent coeliac disease. This is particularly so for the three patients with positive serology, whose coeliac antibody pattern matched those with newly diagnosed gluten sensitive enteropathy in our series compared with those with a normal histological diagnosis. IgA anti-endomysial antibodies have been shown to have a sensitivity of 97–100% and specificity of 98–99 % for coeliac disease.20 None of the patients in our study with a histologically normal duodenal biopsy had positive endomysial antibodies, confirming the accuracy of this screening test. Wahab et al have recently shown that 12 of 38 patients with raised IELs alone will develop more typical coeliac-type histology when challenged with extra dietary gluten.10 We suggest that this may be required to prove gluten sensitivity in the six patients in our study.
The fact that the IEL counts did not decrease with a gluten free diet in two of the patients over a short space of time does not exclude latent coeliac disease. It is well recognised that IEL counts in patients with confirmed gluten sensitive enteropathy do lag behind villous architectural improvement when gluten is withdrawn from the diet.19 However, in the remaining eight patients with raised IELs in our study, a definite cause remains uncertain. This was also the case in study of Wahab et al,10 where 68% of patients could not be strictly classified as being gluten sensitive. A common hypothesis for the presence of increased intestinal IELs is their immunological function against antigens in the bowel lumen.1 In line with their immunological function, it has been postulated that IELs have a role in the breakdown of “oral tolerance”, which may play a part in generalised and even organ specific autoimmune diseases.16,21 This hypothesis may explain the finding of increased IELs in the two patients with primary biliary cirrhosis or idiopathic pancreatitis.
“It is well recognised that intraepithelial lymphocyte counts in patients with confirmed gluten sensitive enteropathy do lag behind villous architectural improvement when gluten is withdrawn from the diet”
The presence of gastrointestinal symptoms in the group of index cases did not differentiate them from the patients with entirely normal histology or with coeliac disease (table 2). Because approximately 15% of the normal population and up to 50% of those referred to a gastroenterological clinic have symptoms of functional bowel disease,22 this is not unexpected.
In conclusion, the finding of a raised IEL count with normal villous architecture is not uncommon. Three of the 14 patients in our study had positive anti-endomysial antibodies and a further three had otherwise unexplained anaemia. These patients may have latent coeliac disease but longterm follow up or a gluten challenge would be required to determine the real clinical relevance of this finding. Nevertheless, we consider the finding of increased IELs with normal villous architecture to be one of potential clinical importance, which should be highlighted in routine histological reports of duodenal biopsies. We recognise that further studies and follow up of these patients, particularly those presumed not to have gluten sensitivity, is needed.
Take home messages.
It is not uncommon to find a raised intraepithelial lymphocyte (IEL) count with normal villous architecture in the duodenum
Six of the 14 patients with such a finding may have had latent coeliac disease (three had positive anti-endomysial antibodies and three had otherwise unexplained anaemia), although longterm follow up or a gluten challenge would be needed to determine the clinical relevance of this finding
The cause in at least half of cases is not obvious at present
The finding of a raised IEL count with normal villous architecture is of sufficient clinical importance to be highlighted in routine duodenal biopsy reports
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr J Gooi for his assistance with the information on coeliac serology testing in this hospital.
Abbreviations
H&E, haematoxylin and eosin
IEL, intraepithelial lymphocyte
REFERENCES
- 1.Ferguson A. Intraepithelial lymphocytes. Gut 1977;18:921–37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Maki M, Collin P. Coeliac disease. Lancet 1997;349:1755–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Maki M, Holm K, Collin P, et al. Increase in γ/δ T cell receptor bearing lymphocytes in normal small bowel mucosa in latent celiac disease. Gut 1991;32:1412–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arranz E, Ferguson A. Intestinal antibody pattern of celiac disease: occurrence in patients with normal jejunal biopsy histology. Gastroenterology 1993;104:1263–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Holm K, Maki M, Savilahti E, et al. Intraepithelial γδ T-cell receptor lymphocytes and genetic susceptibility to celiac disease. Lancet 1992;339:1500–3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Arranz E, Bode J, Kingstone K, et al. Intestinal antibody pattern of celiac disease: association with γ/δ T cell receptor expression by intraepithelial lymphocytes, and other indices of potential celiac disease. Gut 1994;35:476–82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kankinen K, Markku M, Partanen J, et al. Coeliac disease without villous atrophy. Dig Dis Sci 2001;46:879–87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Marsh MN, Bjarnason I, Shaw J, et al. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. XIV-HLA status, mucosal morphology, permeability and epithelial lymphocyte populations in first degree relatives of patients with celiac disease. Gut 1990;31:32–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vazquez H, Cabanne A, Sugai E, et al. Serological markers identify histologically in latent celiac disease among first-degree relatives. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1996;8:15–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wahab PJ, Crusius BA, Meijer JWR, et al. Gluten challenge in borderline gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:1464–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mavromichalis J, Brueton MJ, McNeish AS, et al. Evaluation of the intraepithelial lymphocyte count in the jejunum in childhood enteropathies. Gut 1976;17:600–3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Taylor CJ. Predictive value of intraepithelial lymphocyte counts in childhood celiac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1988;7:532–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Klemola T. Immunohistochemical findings in the intestine of IgA-deficient persons: number of intraepithelial T lymphocytes is increased. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1988;7:537–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Montgomery RD, Shearer AC. The cell population of the upper jejunal mucosa in tropical sprue and post infective malabsorption. Gut 1974;15:387–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ferguson A, McCLure JP, Townley RRW. Intraepithelial lymphocyte count in small intestine biopsies from children with diarrhoea. Acta Paediatr Scand 1976;65:541–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rostoker G, Delchier JC, Chaumette MT. Increased intestinal intra-epithelial T lymphocytes in primary glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2001;16:513–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hayat M, Cairns A, O'Mahony S, et al. Quantitation of intra-epithelial lymphocytes in duodenal mucosa: what is normal [abstract]? Gut 2000;46(suppl I):A90. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fry L, Sheah PP, Harper PG, et al. The small intestine in dermatitis herpetiformis. J Clin Pathol 1974;27:817–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ferguson A, Murray D. Quantitation of intraepithelial lymphocytes in human jejunum. Gut 1971;12:988–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ferreira M, Lloyd Davies S, Butler M, et al. Endomysial antibody: is it the best screening test for coeliac disease? Gut 1992;33:1633–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Miller M, Cowdery J, Laskin C, et al. Heterogeneity of oral tolerance defects in autoimmune mice. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 1984;31:231–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Thompson WG, Creed F, Drossman D, et al. Functional bowel disease and functional abdominal pain. Gastroenterology International 1992;5:75–91. [Google Scholar]