Abstract
Aim: To present seven eyes of suspected donor to host transmitted Pseudomonas sp corneal graft infection after corneal and scleral graft leading to corneal melting within 24 hours, in a span of 10 months.
Methods: Case series. Seven eyes, operated for either penetrating or lamellar keratoplasty or scleral patch graft for different indications and which developed massive corneal/corneoscleral infection within 24 hours, were studied prospectively.
Results: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, resistant to almost all antibiotics except polymyxin B in all and vancomycin in two, was identified as the causative organism from all the specimens obtained from the infected graft.
Conclusion: Post-keratoplasty infection is a disaster. The source of early infection is invariably iatrogenic. Use of empirical antibiotics in the media is not always sufficient to prevent such infection. Thus, measures must be taken in the form of strict maintenance of asepsis and revision of antibiotics added to the storage medium. Further, early recognition and energetic therapy for such infection could reduce the ophthalmic morbidity.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, cornea
Graft infection after keratoplasty is a well recognised but infrequent phenomenon.1–8 Among bacterial invasions, infection by Gram positive organisms is more frequently reported than that by Gram negative bacteria. Post-transplant Pseudomonas infection is a disaster. The source of early infection is usually iatrogenic and donor to host transmission of infection is infrequent.9,10 In this report we describe seven eyes with Pseudomonas graft infection probably transmitted from contaminated donor tissue and discuss the measures taken to control the infection. Further, the emphasis is given to minimise the possible source of infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The details of seven eyes of seven patients are tabulated (table 1–3) and illustrated (figs 1–6).
Table 1.
Donor eye details
| Eye No | Age/sex | Cause of death | ETD | Tissue retrieval and, grade of donor eye | Storage medium | Duration of tissue in MK before use | Duration of tissue at room temperature before use | Size of donor button | Culture report |
| 1 | 30/M | Burn | 4 hours | Enucleation, B+ | M-K | 27 hours | Immediate | 7. 5 mm | P aeruginosa, Staph albus |
| 2 | 23 F | Hanging | 10 hours | Enucleation, B- | M-K | 19 hours | Immediate | 8.25 mm | sterile |
| 3 | 55/M | Cardiac arrest | 3 hours | Enucleation, B+ | M-K | 10 hours | Immediate | 8.0 mm | diphtheroid |
| 4A | 39/M | RTA | 16 hours | Enucleation, B+ | M-K | 24 hours | Immediate | 8.0 mm | sterile |
| 4B | 39/M | RTA | 16 hours | Enucleation, B+ | M-K | 24 hours | 1 hour | 8.0 mm | diphtheroid |
| 5A | 75/M | Cardiac arrest | 3 hours | In situ removal, B+ | M-K | 5 hours | Immediate | 8.0 mm | No growth |
| 5B | 75/M | Cardiac arrest | 3 hours | In situ removal, B+ | M-K | 6 hours | Immediate | 8.0 mm | No growth |
RTA, road traffic accident; ETD, estimated time of death.
Table 3.
Recipient data (postoperative)
| Series No | 1st day, morning | 1st day, evening | 2nd day, morning | 2nd day, evening | 3rd day | 4th day | Subsequent follow up | At healing |
| 1 | Uneventful, 4-5 suture abscess. Betadine, cleaning, routine medication GC-4 + VA, 3/60 | Intense pain, lid oedema, profuse mucopurulent discharge, more suture abscess. Cleaning, sample for microbiology, Betadine, cautery | Worsen, hazy cornea. Standard corneal ulcer therapy | Total graft melting. Therapeutic PK planned. Poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly, neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Total therapeutic PK (figs 3, 4). Intracameral VM Slough sent for microbiology | Pseudomonas growth from graft ulcer specimen, sensitive to poly B. Resistant to all tested antibiotics .Standard therapy tapered poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly Neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Pseudomonas growth from infected button, sensitive to poly B. Resistant to all tested antibiotics. Therapy continued, gradual remission (fig 5) | Visual acuity counting fingers close to face. Leucomatous corneal opacity |
| 2 | Uneventful, 4–5 suture abscess. Betadine cleaning, routine medication GC-4 + VA-6/24P | Intense pain, lid oedema, profuse mucopurulent discharge, 2 mm graft ulcer, hypopyon (fig 6) Cleaning, sample for microbiology, Betadine, cautery, standard corneal ulcer therapy | Total graft hazy, poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly neosporin ointment 3 times daily added | Graft melting. Therapy continued | Graft removal, VM wash, slough for microbiology. Standard therapy tapered, poly B drop and neosporin ointment continued | Pseudomonas growth from graft ulcer specimen, sensitive to poly B. Resistant to all tested antibiotics, poly B drop and neosporin ointment continued | Gradual remission | Visual acuity 1/60. Leucomatous corneal opacity |
| 3 | Intense pain, lid oedema, profuse mucopurulent discharge, multiple suture abscess. Cleaning, sample for microbiology, Betadine, cautery, routine post-keratoplasty therapy | Worsen, hazy cornea, hypopyon + standard corneal ulcer therapy, poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly, neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Status quo | Status quo. Therapy continued | Partial keratectomy, Betadine cautery | Pseudomonas growth from graft ulcer specimen, sensitive to poly B, Resistant to all tested antibiotics. Standard therapy tapered poly B drop Neosporin ointment continued | Gradual remission | Visual acuity, defective PR. Leucomatous corneal opacity |
| 4 | Intense pain, lid oedema, profuse mucopurulent discharge, suture abscess cleaning, sample for microbiology, Betadine cautery. Standard therapy for corneal ulcer | Worsen, hazy cornea, hypopyon, poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly, neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Hypopyon reduced | Status quo | Graft melting. PR inaccurate | Pseudomonas growth from graft ulcer specimen, sensitive to poly B. Resistant to all tested antibiotics. Standard therapy tapered poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly. Neosporin ointment continued | Gradual remission | Visual acuity hand movement close to face. Leucomatous corneal opacity |
| 5 | Uneventful, 4–5 suture abscess. Betadine, cleaning, routine medication VA-6/12 | Intense pain, lid oedema, profuse mucopurulent discharge, more suture abscess. Cleaning, sample for microbiology, Betadine cautery | Worsen, hazy cornea. Standard corneal ulcer therapy poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly Neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Graft removal, VM wash, slough for microbiology. Standard therapy tapered, poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly, neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Remission of pain, lid oedema, discharge | Pseudomonas growth from graft ulcer specimen, sensitive to poly B. Resistant to all tested antibiotics. Standard therapy tapered poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly Neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Gradual remission | Visual acuity 6/9. Clear cornea |
| 6 | Multiple suture abscess Betadine cleaning, routine medication GC-2+VA-1/60 KP ++cells in AC+ | Intense pain, lid oedema, profuse mucopurulent discharge, more suture abscess. Cleaning, sample for microbiology, Betadine cautery | Worsen, hazy cornea. Standard corneal ulcer therapy poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly Neosporin ointment 3 times daily | KP + cells in AC occasional | Pseudomonas growth from graft ulcer specimen, sensitive to poly B. Resistant to all tested antibiotics. Standard therapy tapered poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly Neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Gradual remission | Visual acuity 1/60. Leucomatous corneal opacity | |
| 7 | Multiple suture abscess. Betadine, cleaning, routine medication GC-2 + VA-1/60 | Intense pain, lid oedema, profuse mucopurulent discharge, more suture abscess. Cleaning, sample for microbiology, Betadine cautery | Worsen, hazy cornea. Standard corneal ulcer therapy poly B drop 50 000 IU½ hourly Neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Graft melting, therapeutic PK | Pseudomonas growth from graft ulcer specimen, sensitive to poly B. Resistant to all tested antibiotics. Standard therapy tapered poly B drop 50 000 IU ½ hourly Neosporin ointment 3 times daily | Pseudomonas growth from infected button, sensitive to poly B. Resistant to all tested antibiotics. Therapy continued. Eye became phthisical | Visual acuity nil (phthisis bulbi) |
VA, visual acuity; GC, gentamicin; VM, vancomycin; KP, keratoprecipitates; AC, anterior chamber; PK, penetrating keratoplasty; poly B, polymyxin B.
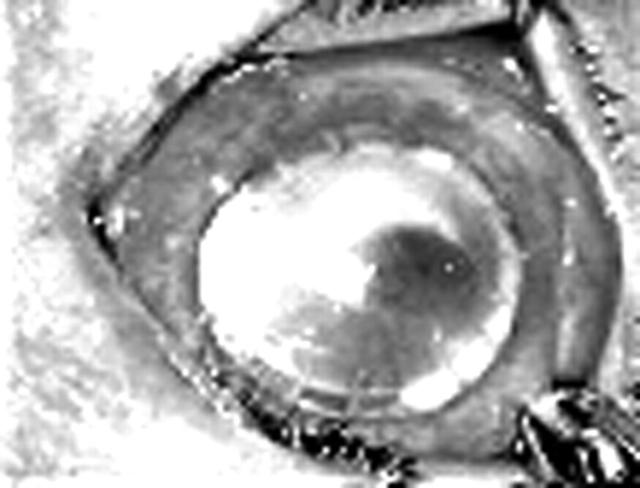
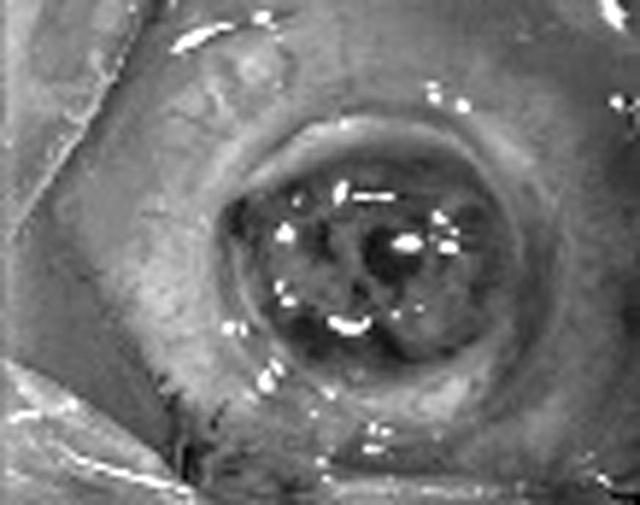
Figure 1.
Intraoperative clinical photograph of congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy showing microvitreoretinal entry.
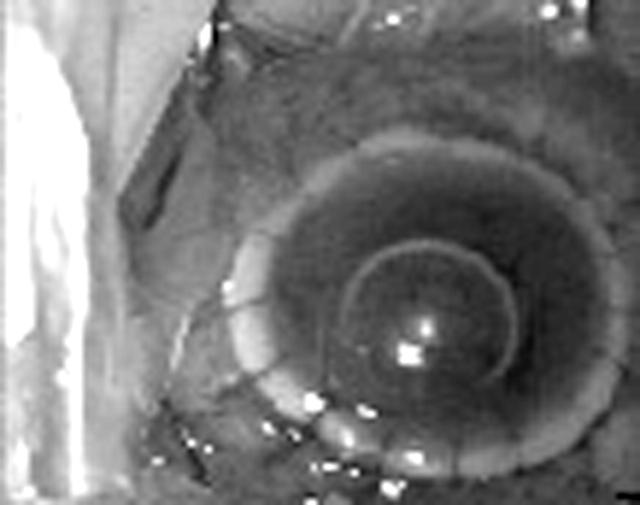
Figure 6.
Clinical photograph of case 2 showing an ulcer at the graft-host junction with hypopyon.
DISCUSSION
Donor to host transmission of graft infection was established as early as early as 25 years ago.9 A review of the literature since then confirmed isolation of Pseudomonas from both the sources in four reports.5–8 Of four, two did not mention the sensitivity of gentamicin and the other two confirmed resistance to gentamicin, which is routinely used in the storage medium. The reported cases are concurrent with the latter two studies as organisms were resistant to gentamicin and other antibiotics except polymyxin B, commonly tested for sensitivity in our laboratory. Further, as the culture from the medium used for donor eyes in our study revealed growth of the organism in two, the routine culture specimen testing from the culture medium after corneal button removal in the operating theatre should be adhered to; as well as the first specimen—that is, from the untreated donor eye, a second specimen should be tested after treating the eyeball with broad spectrum antibiotics. Further, the samples collected from the donor eye should be inoculated immediately as the first and second samples from five of the donor eyes obtained in our series were sent for microbiological evaluation after a lapse of some hours. This may help in early diagnosis of graft infection and modulate postoperative therapy. Thus, it also calls for addition of an extra broad spectrum antibiotic to the storage medium.
Factors responsible for the early graft infection as reported are
recurrence of host infection such as preoperative herpetic keratitis and/or other infective keratitis
intraoperative contamination
use of contaminated donor buttons.
In the present series the first and second factors are ruled out as there was no evidence of any clinical or subclinical preoperative infection and the subsequent surgeries contemplated in the same operating theatre by same surgical team did not reveal any abnormality. The third factor, use of contaminated donor buttons, is more likely to have had a role as all the samples from graft infection and three donor tissues showed the isolation of the same organism. Further, use of cooled donor endothelium on the recipient bed could be another factor.
The analysis of the data for the donor eye used for our patients revealed that eyes were enucleated in the mortuary and processed in the eye bank in a routine environment. Thus, the role of environmental contamination, aseptic surgical process, and endothelial side contamination cannot be ruled out.
Lack of a constant electric supply is also a major factor as the majority of the eye bank refrigerators do not have the provision of a constant electric supply, despite the emphasis given to this issue by the “eye bank standard.”11
Insler et al in 19852 reported the possibility of donor to host contamination following keratoplasty as:
a large potential inoculum due to (a) increased length of storage, (b) possibility of tissue culture fluid which encourages growth of micro-organisms
contamination of endothelial surface of the donor cornea
the emergence of more antibiotic resistant micro-organisms in antibiotic supplemented media.
To this we add another four factors which are also pertinent as a source of infection that includes:
the environment and quality of surgical preparation at the site of removal of donor corneal rim during processing
inconsistent electric supply for the refrigerator where the donor eyes were stored
immediate use of donor eye after removal from storage at 4°C, as warming the donor tissue to room temperature before use is not strictly adhered to by most surgeons
insufficient antibiotics in storage medium which is emphasised time and again in the literature but cannot be overemphasised. However, the aspect of “insufficient antibiotics” is not certain in this study, but it is high time to evaluate the storage media experimentally.
In the literature, two aspects have been emphasised for management of donor to host bacterial contamination: (1) parenteral antibiotics for 72 hours postoperatively until the culture report is available; and (2) routine culture of donor rim at the time of surgery.
The first factor appears to be impractical for all patients but the second factor is quite justified and should be adhered to routinely. On the basis of our data and data reported in literature, we think the presumptive factors as suggested by us are more meaningful for our set-up and therefore should be looked into.
Persistence of a white spot on a grafted cornea should arouse the suspicion of the post-keratoplasty infection and broad spectrum antibiotics should be started immediately after specimen collection for smear and culture sensitivity. However, occasionally this conventional therapy also fails to prevent/control graft infection as has happened here. Therefore, it is essential to consider antibiotic resistance and use of specific antibiotics against Pseudomonas spp such as polymyxin B, which should be added immediately to the treatment regimen if there is progressive graft infection despite appropriate medical therapy against Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria.
On the basis of present series a few important facts are drawn:
Though Pseudomonas infection in a graft is infrequent it is an emergency and requires immediate attention when it occurs.
Donor predisposing factors such as patients on a ventilator before death, prolonged death enucleation time, and use of compromised cornea may not always be responsible for immediate development of an ulcer as all the donor corneas were obtained from donors ranging in age from 23–75 years; none of them were on a ventilator, and the scheduled death enucleation time and removal utilisation time were within normal limit in most of the eyes.
Strict asepsis of corneoscleral tissue removal in an eye bank is mandatory as all the infected donor corneas in the present series underwent corneoscleral tissue removal in a routine environment.
Graft infection does not necessarily require a recipient eye with ocular surface disorder and compromised cornea as none of the patients had ocular surface disorder.
Considering a large number of reports that are available on gentamicin resistant organisms and as gentamicin is the only antibiotic commonly used in M-K medium, antibiotic efficacy in M-K medium should be evaluated experimentally.
Finally, the aspect of warming the donor tissue to room temperature before use, which is not practised most of the time, should be adhered to.
Figure 2.
Clinical photograph after completion of keratoplasty.
Figure 3.
Clinical photograph showing sloughing of the graft and host cornea.
Figure 4.
Clinical photograph at the completion of therapeutic keratoplasty for the sloughing cornea.
Figure 5.
Clinical photograph on the 10th postoperative day after therapeutic keratoplasty showing an apparently quiet eye.
Table 2.
Recipient data (preoperative and intraoperative)
| Series No | Age | Diagnosis | Date of surgery | Preoperative medication | Donor eye No | Type of surgery | Course of surgery | Type and No of suture | Subcutaneous injection | Culture from media in OT |
| 1 | 5/F | CHED | 28.6.03 | 0.3% ciprofloxacin four times daily | 1 | Optical PK (figs 1, 2) | Uneventful | 10.0 MFN 16, interrupted | Dexamethasone and gentamicin | Pseudomonas sensitive to poly B |
| 2 | 17/F | Keratoconus | 30.8.03 | 0.3% ciprofloxacin four times daily | 2 | DLK | Uneventful | 10.0 MFN 16, interrupted | Dexamethasone and gentamicin | Not sent |
| 3 | 46/M | Leucomatous corneal opacity | 7.11.03 | 0.3% ciprofloxacin four times daily | 3 | Optical PK | Uneventful | 10.0 MFN 16, interrupted | Dexamethasone and gentamicin | Not sent |
| 4 | 65/F | Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy | 7.4.04 | 0.3% ciprofloxacin four times daily | 4* | Triple procedure | Uneventful | 10.0 MFN 16, interrupted | Dexamethasone and gentamicin | Pseudomonas sensitive to poly B |
| 5 | 39/F | Post-pterygium surgery, scleral melting | 7.4.04 | 0.3% ciprofloxacin four times daily | 4* | Scleral patch graft | Uneventful | 10.0 MFN interrupted 5, 8-0 Vicryl scleral suture 6 | Dexamethasone and gentamicin | Pseudomonas sensitive to poly B |
| 6 | 50/M | Leucomatous corneal opacity | 21.4.04 | 0.3% ciprofloxacin four times daily | 5A | Triple procedure | Uneventful | 10-0 MFN 16 interrupted | Dexamethasone and gentamicin | Not sent |
| 7 | 55/M | Leucomatous corneal opacity | 21.4.04 | 0.3% ciprofloxacin four times daily | 5B | Optical PK | Uneventful | 10.0 MFN 16, interrupted | Dexamethasone and gentamicin | Not sent |
CHED, congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy; PK, penetrating keratoplasty; OT, operating theatre; poly B, polymyxin B.
REFERENCES
- 1.Leveille AS, Mc Mullan FD, Cavanagh HD. Endophthalmitis following penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 1983;90:38–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Insler MS, Cavanagh HD, Wilson LA. Gentamicin resistant pseudomonas endophthalmitis after penetrating keratoplasty. Br J Ophthalmol 1985;69:189–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Selwa AF, AL-Hazzaa, Tabbara Khalid F. Bacterial keratitis after penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 1988;95:1504–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bates AK, Kirkness CM, Ficker LA, et al. Microbial keratitis after penetrating keratoplasty. Eye 1990;4:74–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kloess PM, Stulting RD, Waring GO III, et al. Bacterial and fungal endophthalmitis after penetrating keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol 1993;115:309–16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Panda A, Puskar N, Nainiwal S, et al. Rhodotorula sp infection in corneal interface following lamellar keratoplasty. Acta Ophthalmol 1999;77:227–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Panda A, Puskar N. Acanthamoeba keratitis following penetrating keratoplasty. Eye 1999;13:588–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tuberville AW, Wood TO. Corneal ulcers in corneal transplants. Curr Eye Res 2002;1:479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Khodadus AA, Franklin RM. Transfer of bacterial infection from donor cornea in penetrating keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol 1979;87:130–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sutphin JE, Pfaller MA, Tollis RJ, et al. Donor to host trransmission of Candida albicans after corneal transplant. Am J Ophthalmol 2002;134:120–1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Panda A . Eye bank standard. Essential of eye banking. India: CBS publisher, 2003:41–9.