Abstract
Background: There is evidence that perfusion abnormalities of the optic nerve head are involved in the pathogenesis of glaucoma. There is therefore considerable interest in the effects of topical antiglaucoma drugs on ocular blood flow. A study was undertaken to compare the ocular haemodynamic effects of dorzolamide and timolol in patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT).
Methods: One hundred and forty patients with POAG or OHT were included in a controlled, randomised, double blind study in two parallel groups; 70 were randomised to receive timolol and 70 to receive dorzolamide for a period of 6 months. Subjects whose intraocular pressure (IOP) did not respond to either of the two drugs were switched to the alternative treatment after 2 weeks. Scanning laser Doppler flowmetry was used to measure blood flow in the temporal neuroretinal rim and the cup of the optic nerve head. Pulsatile choroidal blood flow was assessed using laser interferometric measurement of fundus pulsation amplitude.
Results: Five patients did not respond to timolol and were changed to the dorzolamide group, and 18 patients changed from dorzolamide treatment to timolol. The effects of both drugs on IOP and ocular perfusion pressure were comparable. Dorzolamide, but not timolol, increased blood flow in the temporal neuroretinal rim (8.5 (1.6)%, p<0.001 versus timolol) and the cup of the optic nerve head (13.5 (2.5)%, p<0.001 versus timolol), and fundus pulsation amplitude (8.9 (1.3)%, p<0.001 versus timolol).
Conclusions: This study indicates augmented blood flow in the optic nerve head and choroid after 6 months of treatment with dorzolamide, but not with timolol. It remains to be established whether this effect can help to reduce visual field loss in patients with glaucoma.
Keywords: dorzolamide, timolol, ocular blood flow, glaucoma, ocular hypertension
There is increasing evidence that ocular blood flow abnormalities are involved in the pathogenesis of glaucoma,1 so there is considerable interest in the potential ocular haemodynamic effects of currently available antiglaucoma drugs. A large number of clinical studies have been performed to clarify this issue using different techniques for the assessment of ocular blood flow, yielding partially contradicting results.2 However, many published studies suffer from the fact that only a small number of patients were included.
We have compared the ocular haemodynamic effects of dorzolamide and timolol in a larger number of patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension (OHT). Dorzolamide was chosen on the basis of previous evidence that this drug may increase ocular blood flow,3–9 although not all studies showed a positive outcome.10–12 Timolol was chosen as a control substance because the ocular hypotensive effect of this β-receptor antagonist is only slightly superior to that of dorzolamide13 and comparable effects on ocular perfusion pressure (OPP) can be expected.
Optic nerve head (ONH) blood flow was measured using scanning laser Doppler flowmetry (SLDF)14 and pulsatile choroidal blood flow was assessed by laser interferometric measurement of fundus pulsation amplitude (FPA).15
METHODS
Patients
After approval from the ethics committee of the Vienna University School of Medicine, 140 patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) or OHT were included. For the sample size calculation, which was based on the reproducibility data of the Heidelberg retina flowmeter (standard deviation of 32% as calculated from monthly measurements for 6 months in POAG patients, unpublished data), a repeated measures ANOVA model was used with an α level of 0.05 and a β level of 0.2. Differences of less than 10% between treatment groups were considered to be clinically irrelevant. Hence, the sample size calculation gave a total number of 127 subjects. Originally, a drop out rate of 20% was anticipated and 160 patients were scheduled accordingly. Since it turned out that the drop out rate was smaller, only 140 patients were included. The variability of topical fundus pulsation measurement is smaller and was therefore not considered in our sample size calculation.
The baseline characteristics of these patients have been reported in detail previously.16 Inclusion criteria were either POAG or OHT with an untreated intraocular pressure (IOP) of ⩾21 mm Hg in at least one eye, which had to be documented on at least three different occasions. A washout period of 2 weeks for previous antiglaucoma treatment was scheduled for all patients. Any of the following excluded a patient from participation in the trial: exfoliation glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma, history of acute angle closure, mean deviation (MD) of visual field testing (Humphrey 30-2 program) >12, intraocular surgery or argon laser trabeculoplasty within the last 6 months, ocular inflammation or infection within the last 3 months, bradycardia (heart rate <50 beats/min), second and third degree heart block, asthma bronchiale, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, congestive heart failure, severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <1.8 l/h), history of hypersensitivity to one of the study drugs or drugs with similar chemical structure, history of non-IOP responder to topical β-blockers or topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs), and pregnancy.
The differentiation between POAG and OHT patients was based on the criteria of the Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study.17 An abnormal visual field was accordingly defined as a glaucoma hemifield test outside normal limits and/or a corrected pattern standard deviation with p<0.05.
Protocol
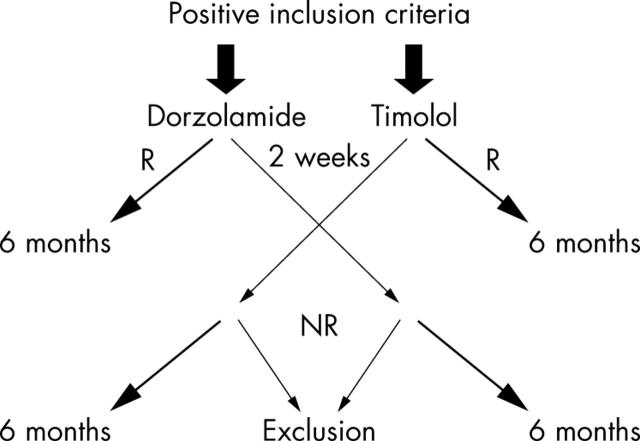
The study was performed in a randomised, double blind, parallel group design. Patients either received timolol twice daily (Timoptic, MSD) or dorzolamide three times a day for 6 weeks. To enable double blind conditions, patients in the timolol group received a placebo bottle identical in appearance for lunch time instillation. The study schedule is shown in fig 1. During the 2 weeks before the start of the study, patients were assessed for eligibility and examined as outlined above. If at least one eye was eligible for the study, a baseline visit was scheduled. If possible, both eyes were treated with the study medication. If not, the contralateral eye was treated according to the clinical requirements. At the baseline visit all outcome variables were assessed between 08.00 and 12.00 hours.
Figure 1.
Study schedule (R = IOP responders; NR = IOP non-responders).
Patients were asked to return 2 weeks after the baseline visit. During this visit they were divided into responders and non-responders. Responders were defined as patients with an IOP ⩽19 mm Hg or a decrease in IOP compared with baseline of ⩾25% in the index eye, and they continued the study as scheduled. Non-responders or patients who did not tolerate the study medication crossed over to the alternative treatment and were scheduled for a further visit 2 weeks later. At the visit 2 weeks after changing the medication these patients were again divided into responders and non-responders. Non-responders to both medications were eliminated from the study. Those patients who responded to the second antiglaucoma drug continued the study as scheduled.
Further visits were scheduled 3 months and 6 months after the baseline visit. All haemodynamic outcome variables and IOP were assessed during these visits. At the last visit a visual field test and an ophthalmic examination were performed again. A deviation of ±3 days was accepted for the 2 weeks visit and of ±1 week for the other visits.
The studies were performed at the Department of Clinical Pharmacology and the Department of Ophthalmology, Allgemeines Krankenhaus, Vienna.
Measurements
Scanning laser Doppler flowmetry (SLDF)
SLDF was performed using the Heidelberg retina flowmeter (HRF; Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany). The HRF is a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope employing the principles of SLDF. The mean red blood cell velocity, blood volume, and blood flow can be calculated in relative units for any image point.18 In the present study one 10×10 pixel area (100×100 µm) in the cup of the optic disc (CupBF) and one 20×20 pixel area (200×200 µm) at the temporal neuroretinal rim (RimBF) were chosen for calculation of haemodynamic parameters. The selection of the measurement areas was based on the method described by Nicolela et al.19 The neuroretinal rim was measured from images focused on the superficial retina and the cup from images focused on the lamina cribrosa. The measurements were performed in regions without major surface vessels.
Reproducibility is a critical issue with SLDF.20,21 At least two recordings were therefore taken and the mean of the two values from the best images obtained was calculated. Only flow readings with a coefficient of variation of less than 20% were included in the analysis.
Laser interferometric measurement of fundus pulsation
Pulse synchronous pulsations of the eye fundus were assessed by laser interferometry as described in detail by Schmetterer et al.15 The eye is illuminated by a laser beam which is reflected at both the front surface of the cornea and the fundus. The two re-emitted waves produce interference fringes from which the distance changes between the cornea and retina during a cardiac cycle can be calculated. The maximum distance change is called the fundus pulsation amplitude (FPA) and estimates the choroidal pulsatile blood flow.22,23 Again, two measurements were performed and the mean was calculated. FPA values with a coefficient of variation of more than 20% were not included in the analysis.
Visual field testing
Visual field testing was performed with the Humphrey Field analyser (Full Threshold Program 30-2). All patients were experienced in visual field testing having performed at least three tests in total and one test during the 3 months before the beginning of the study. All measurements were supervised by an experienced technician. Visual field eligibility criteria were less than 33% false positives, less than 33% false negatives, and less than 33% fixation losses.
Non-invasive measurement of systemic haemodynamics
Systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP, DBP) were measured on the upper arm by an automated oscillometric device; mean arterial pressure (MAP) was calculated as 1/3 SBP + 2/3 DBP. Pulse rate was automatically recorded from a finger pulse oximetric device (HP-CMS patient monitor, Hewlett Packard, Palo Alto, CA, USA). Ocular perfusion pressure (OPP) was calculated as 2/3 * MAP − IOP.
Analysis of data
A two way repeated measures ANOVA model was used to compare the effects of dorzolamide and timolol. Patients who only appeared at the baseline visit were not included in the analysis. In all patients who did not complete the study but who attended at least the 2 week visit, the last observation was carried forward. The data from the last visit that actually took place were therefore used for all further missing entries. In patients who did not respond to the medication at randomisation and switched over to the alternative treatment, the pretreatment values were taken as baseline. In these cases the values assessed at the 2 week visit were not included in the analysis. In addition, a multiple regression analysis model was performed using stepwise inclusion of predicting variables (for order of inclusion see table 3) to characterise potential determinants of dorzolamide and timolol induced changes in blood flow parameters versus baseline. Data are presented as mean (SD) values. The level of significance was set at p = 0.05.
Table 3.
Multiple regression analysis between dorzolamide induced changes in ocular haemodynamic parameters and the other assessed parameters (p values are shown)
| RimBF | CupBF | FPA | |
| POAG/hypertension | 0.52 | 0.60 | 0.59 |
| % change in OPP (after 6 months) | 0.28 | 0.40 | 0.25 |
| % change in IOP (after 6 months) | 0.20 | 0.60 | 0.23 |
| OPP | 0.67 | 0.56 | 0.69 |
| Intraocular pressure | 0.61 | 0.78 | 0.33 |
| Mean deviation | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.71 |
| Age | 0.42 | 0.49 | 0.64 |
| SBP | 0.66 | 0.56 | 0.73 |
| DBP | 0.82 | 0.72 | 0.84 |
| Pulse rate | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.76 |
RimBF, rim blood flow; CupBF, cup blood flow; FPA, fundus pulsation amplitude; OPP, ocular perfusion pressure; IOP, intraocular pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.
RESULTS
The baseline characteristics of the study population have been presented in a previous report16 and are summarised in table 1.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the study population
| POAG(n = 49) | OHT(n = 91) | |
| Age (years) | 63.0 (13.5) | 61.2 (13.3) |
| Sex (M/F) | 19/30 | 48/43 |
| IOP (mm Hg) | 22.6 (2.9) | 23.2 (3.8) |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 141.0 (15.8) | 142.8 (17.8) |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 75.7 (10.1) | 74.8 (11.9) |
| OPP (mm Hg) | 39.0 (7.2) | 40.6 (9.0) |
| Pulse rate (/min) | 78.1 (12.5) | 78.0 (11.6) |
| Mean deviation | −1.58 (−11.09–+2.83) | −0.16 (−5.35–+4.10) |
| Vertical C/D ratio | 0.75 (0.11) | 0.59 (0.12) |
| Horizontal C/D ratio | 0.77 (0.11) | 0.62 (0.11) |
| Optic disc area | 1.58 (0.37) | 1.46 (0.34) |
| RimBF (au) | 287 (51) | 333 (111) |
| CupBF (au) | 192 (71) | 212 (101) |
| FPA (μm) | 3.0 (0.8) | 3.3 (0.9) |
IOP, intraocular pressure; SBP, systolic pressure; DBP, diastolic pressure; OPP, ocular perfusion pressure; C/D ratio, cup to disc ratio; RimBF, rim blood flow; CupBF, cup blood flow; FPA, fundus pulsation amplitude.
Data are presented as mean (SD) except for mean deviation which is shown as median (range).
Three patients appeared at the baseline visit only and were not included in the analysis. Five patients did not respond to timolol and changed to the dorzolamide group after the first 2 weeks of treatment. Eighteen patients did not show an adequate IOP response to dorzolamide or did not tolerate the treatment and changed to the timolol group. The failure rate due to inadequate IOP control or adverse reactions was significantly higher in the dorzolamide group than in the timolol group (p<0.001). After switching to the alternative treatment, all patients showed satisfactory IOP control and no subject had to be excluded at this stage of the study.
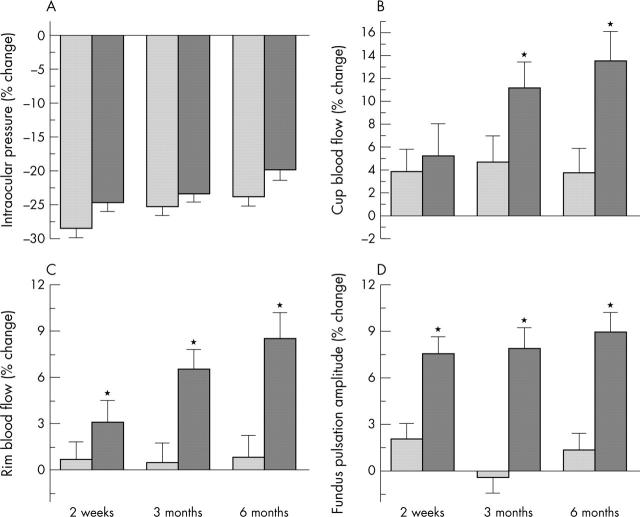
After the 2 week and 3 month visits, seven and five patients respectively were lost to follow up. The data on these 12 subjects were carried forward. The study drugs had no influence on blood pressure or pulse rate (SBP: p = 0.823 between groups; DBP: p = 0.644 between groups; pulse rate: p = 0.511 between groups; table 2). Baseline IOP was similar in both treatment groups (timolol: 23.0 (3.1) mm Hg; dorzolamide: 22.8 (3.3) mm Hg). The reduction in IOP was similar in the two groups (p = 0.32, fig 2). At the 6 month visit the reduction in IOP was 23.8 (1.4)% with timolol treatment and 19.9 (1.6)% with dorzolamide. Accordingly, the OPP tended to be increased in both groups to a similar degree (p = 0.912 between groups; table 2). All ocular haemodynamic variables increased during treatment with dorzolamide but did not change during timolol treatment (fig 2). This difference was significant for CupBF (p<0.001), RimBF (p<0.001), and FPA (p<0.001). After 6 months of treatment CupBF increased by 13.5 (2.5)%, RimBF by 8.5 (1.6)%, and FPA by 8.9 (1.3)% after treatment with dorzolamide; no effect was seen with timolol.
Table 2.
Effects of dorzolamide and timolol on blood pressure and pulse rate
| Baseline | 2 weeks | 3 months | 6 months | |
| Timolol | ||||
| SBP (mm Hg) | 142.1 (16.5) | 140.7 (19.2) | 137.4 (20.7) | 134.3 (24.1) |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 75.3 (9.5) | 73.6 (9.9) | 73.0 (10.3) | 75.6 (11.7) |
| OPP (mm Hg) | 39.3 (7.4) | 41.3 (7.6) | 40.0 (6.3) | 41.0 (8.3) |
| Pulse rate (/min) | 76.8 (12.0) | 75.9 (12.0) | 73.4 (11.8) | 73.4 (11.7) |
| Dorzolamide | ||||
| SBP (mm Hg) | 142.3 (18.1) | 140.7 (21.4) | 136.8 (19.5) | 138.1 (17.9) |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 75.0 (13.7) | 75.6 (12.4) | 72.8 (11.6) | 71.4 (11.8) |
| OPP (mm Hg) | 39.0 (8.3) | 41.8 (9.3) | 40.6 (8.4) | 39.4 (8.3) |
| Pulse rate (/min) | 79.9 (12.0) | 82.1 (13.3) | 81.2 (12.9) | 79.2 (13.4) |
SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; OPP, ocular perfusion pressure.
Data are presented as mean (SD).
Figure 2.
Effects of dorzolamide (darker bars) and timolol (lighter bars) on (A) intraocular pressure, (B) cup blood flow, (C) rim blood flow, and (D) fundus pulsation amplitude. Data are presented as mean (SD). Asterisks indicate significant effects of dorzolamide compared with timolol.
The results of the multiple regression analysis are shown in table 3. The increase in ocular haemodynamic parameters during dorzolamide treatment was independent of the decrease in IOP and independent of baseline IOP. In addition, the increase was comparable in POAG and OHT patients and was not influenced by any other measured variable. After 6 months of treatment with timolol or dorzolamide, visual field parameters remained unchanged (data not shown).
DISCUSSION
This study indicates that 6 months of treatment with dorzolamide, but not with timolol, is associated with an increase in ocular blood flow. This was shown using two independent methods for the assessment of ocular haemodynamic parameters. Several arguments indicate that this result is caused by a direct vasodilator effect of dorzolamide and not secondary to a decrease in IOP. On the one hand, dorzolamide and timolol induced a comparable decrease in IOP and a comparable increase in OPP, whereas ocular haemodynamic effects were only observed with dorzolamide. On the other hand, the results of our multiple regression analysis indicate that the increase in OPP is independent of the IOP lowering effects.
The relevance of our results for the treatment of glaucoma is critically dependent on whether reduced ONH blood flow contributes to retinal ganglion cell loss in glaucoma. Many studies have shown that blood flow in the ONH is reduced in patients with glaucoma,19,24–27 but cross sectional studies do not provide a link between reduced perfusion and progression of the disease. In recent years, however, there is increasing evidence that reduced ocular blood flow is directly associated with visual field loss. In a longitudinal study in patients with normal tension glaucoma, decreased blood flow velocities in retrobulbar vessels were associated with progression of visual field loss.28 This is in keeping with a more recent retrospective study in which the rate of progression of visual field damage was related to reduced retrobulbar blood flow velocities independently of the pre-existing visual field damage and the IOP.29 A significant correlation between ONH blood volume, as assessed by SLDF, and visual field loss in POAG was recently reported in a longitudinal study with a mean follow up of 33 months.30 In addition, numerous studies indicate that glaucoma is not only related to reduced ONH blood flow but also to abnormal ocular blood flow regulation; this is not easy to explain by a secondary reduction in blood flow. Analysis of baseline blood flow in the present study showed that there is an abnormal association between RimBF, CupBF and FPA and systemic blood pressure which is not seen in age matched healthy control subjects.16 While these trials do not establish direct evidence for a beneficial treatment effect of enhancing ONH blood flow in patients with POAG, they provide a strong rationale for characterising antiglaucoma drugs with ocular hypotensive as well as ocular vasodilator properties.
The exact mechanism underlying the vasodilator effects of CAIs in ocular vessels is unclear. In rat retinal organ culture CAIs decreased pH in the extracellular space and increased pH in the intracellular space, related to an increase in retinal capillary diameters and retinal pericyte relaxation.31 Intravenously administered dorzolamide induces acidosis of arterial blood32 and of the extracellular space over the ONH.33 On the other hand, experiments in isolated precontracted bovine retinal arteries indicate that the vasodilator effects of dorzolamide are independent of changes in pH because dorzolamide induced dilatation is also seen when pH is kept constant.34 Activation of nitric oxide does not appear to play a major role in CAI induced vasodilation in the eye,35 and further studies are required to understand the mechanisms underlying the vascular effects of CAIs.
An interesting observation from the present study is that all ocular haemodynamic parameters were virtually unchanged after treatment with timolol. Previous reports on the ocular haemodynamic effects of timolol are contradictory, which may be related to different treatment regimens, method related problems, and a lack of adequate study design.36–41 Our results do, however, indicate that long term topical administration of timolol is not associated with relevant ocular haemodynamic effects.
Both techniques used for the assessment of ocular haemodynamics have limitations. With the HRF the sampling depth within ONH tissue is not known. In addition, reproducibility is a problem with this technique19,20 and is more severe in patients with glaucoma than in healthy control subjects, leading to comparatively high sample sizes. With FPA measurement it is obvious that only the pulsatile portion of choroidal blood flow is measured. Accordingly, any conclusion on the pharmacodynamic effects with this technique is critically dependent on the assumption that the ratio of pulsatile to non-pulsatile blood flow is constant. In the present study consistent results were observed with both techniques, indicating that the observed effects are not influenced to a significant degree by the limitations of the techniques.42
In conclusion, the data presented here indicate that dorzolamide, but not timolol, increases ONH and choroidal blood flow in patients with POAG or OHT. It remains to be seen whether this effect is associated with a preservation of visual fields in patients with glaucoma.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the following ophthalmologists for sending their patients to our unit for inclusion in the present study: Dr Elisabeth Arocker-Mettinger, Dr Helga Azem, Dr Alexandra Crammer, Dr Paul Drobec, Dr Marcela Hakl, Dr Christine Hönigsmann, Dr Hans Kössler, Dr Eva Krammer, Dr Constanze Merenda, Dr Maria Reichel, Dr Günther Reichelt, Dr Karin Schmetterer, Dr Herbert Schuster, Dr Naresh Sheetal, Dr Elisabeth Sienko, Dr Eva Weingessl.
Abbreviations
FPA, fundus pulsation amplitude
HRF, Heidelberg retina flowmeter
IOP, intraocular pressure
OHT, ocular hypertension
ONH, optic nerve head
OPP, ocular perfusion pressure
POAG, primary open angle glaucoma
SLDF, scanning laser Doppler flowmetry
Financial support from an unrestricted grant from Merck, Sharpe and Dohme is acknowledged.
REFERENCES
- 1.Flammer J, Orgul S, Costa VP, et al. The impact of ocular blood flow in glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res 2002;21:359–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Harris A, Jonescu-Cuypers CP. The impact of glaucoma medication on parameters of ocular perfusion. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2001;12:131–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Harris A, Arend O, Arend S, et al. Effects of topical dorzolamide on retinal and retrobulbar hemodynamics. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 1996;74:569–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Martinez A, Gonzalez F, Capeans C, et al. Dorzolamide effect on ocular blood flow. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999;40:1270–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Harris A, Arend O, Kagemann L, et al. Dorzolamide, visual function and ocular hemodynamics in normal-tension glaucoma. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther 1999;15:189–97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Harris A, Arend O, Chung HS, et al. A comparative study of betaxolol and dorzolamide effect on ocular circulation in normal-tension glaucoma patients. Ophthalmology 2000;107:430–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Harris A, Jonescu-Cuypers CP, Kagemann L, et al. Effect of dorzolamide timolol combination versus timolol 0.5% on ocular blood flow in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 2001;132:490–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Avunduk AM, Sari A, Akyol N, et al. The one-month effects of topical betaxolol, dorzolamide and aprachlonidine on ocular blood flow velocities in patients with newly diagnosed primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmologica 2001;215:361–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bernd AS, Pillunat LE, Bohm AG, et al. Okuläre Hämodynamik und Gesichtsfeld beim Glaukom unter Dorzolamid-Therapie. Ophthalmologe 2001;98:451–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Grunwald JE, Mathur S, DuPont J. Effects of dorzolamide hydrochloride 2% on the retinal circulation. Acta Ophthalmol 1997;75:236–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pillunat LE, Bohm AG, Koller AU, et al. Effect of topical dorzolamide on optic nerve head blood flow. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1999;237:495–500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bergstrand IC, Heijl A, Harris A. Dorzolamide and ocular blood flow in previously untreated glaucoma patients: a controlled double-masked study. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2002;80:176–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Balfour JA, Wilde MI. Dorzolamide. A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic potential in the management of glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Drugs Aging 1997;10:384–403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Michelson G, Schmauss B, Langhans MJ, et al. Principle, validity, and reliability of scanning laser Doppler flowmetry. J Glaucoma 1996;5:99–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schmetterer L, Lexer F, Unfried C, et al. Topical measurement of fundus pulsations. Opt Eng 1995;34:711–6. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fuchsjäger-Mayrl G, Wally B, Georgopoulos M, et al. Ocular blood flow and systemic blood pressure in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004;45:834–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Keltner JL, Johnson CA, Cello KF, et al. Classification of visual field abnormalities in the ocular hypertension treatment study. Arch Ophthalmol 2003;121:643–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bonner R, Nossal R. Principles of laser-Doppler flowmetry in laser-Doppler blood flowmetry. In: Shepard AP, Öberg AP, eds. Developments in cardiovascular medicine. Volume 107. Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1990:17–45.
- 19.Nicolela MT, Hnik P, Drance SM. Scanning laser Doppler flowmetry study on retinal and optic disc blood flow in glaucomatous patients. Am J Ophthalmol 1996;122:775–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Strenn K, Menapace R, Rainer G, et al. Reproducibility and sensitivity of scanning laser Doppler flowmetry during graded changes in pO2. Br J Ophthalmol 1997;81:360–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Nicolela MT, Hnik P, Schulzer M, et al. Reproducibility of retinal and optic nerve head blood flow measurements with laser Doppler flowmetry. J Glaucoma 1997;6:157–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schmetterer L, Dallinger S, Findl O, et al. A comparison between laser interferometric measurement of fundus pulsation and pneumotonometric measurement of pulsatile ocular blood flow. 1. Baseline considerations. Eye 2000;14:39–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schmetterer L, Dallinger S, Findl O, et al. A comparison between laser interferometric measurement of fundus pulsation and pneumotonometric measurement of pulsatile ocular blood flow. 2. Effects of changes in pCO2 and pO2 and of isoproterenol. Eye 2000;14:46–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Grunwald JE, Piltz J, Hariprasad SM, et al. Optic nerve and choroidal circulation in glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998;39:2329–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kerr J, Nelson P, O’Brien C. A comparison of ocular blood flow in untreated primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Am J Ophthalmol 1998;126:42–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Michelson G, Langhans MJ, Groh MJ. Perfusion of the juxtapapillary retina and the neuroretinal rim area in primary open angle glaucoma. J Glaucoma 1996;5:91–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Findl O, Rainer G, Dallinger S, et al. Assessment of optic disc blood flow in patients with open angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 2000;130:589–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yamaaki Y, Drance SM. The relationship between progression of visual field defects and retrobulbar circulation in patients with glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 1997;124:287–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Saltimis M, Orgul S, Doubler B, et al. Rate of progression of glaucoma correlates with retrobulbar circulation and intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol 2003;135:664–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zink JM, Grunwald JE, Piltz-Seymour J, et al. Association between lower optic nerve laser Doppler blood volume measurements and glaucomatous visual field progression. Br J Ophthalmol 2003;87:487–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Reber F, Gersch U, Funk RW. Blockers of carbonic anhydrase can cause increase of retinal capillary diameter, decrease of extracellular and increase of intracellular pH in rat retinal organ culture. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2003;241:140–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stefansson E, Jensen PK, Eysteinsson T, et al. Optic nerve oxygen tension in pigs and the effect of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1999;40:2756–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pedersen DB, Eysteinsson T, Kiilgaard JF, et al. The effect of intravenous administration of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and NH4Cl on pre-optic pH. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42: ARVO abstract, 4449.
- 34.Josefsson A, Sigurdsson SB, Bang K, et al. Dorzolamide induces vasodilatation in isolated pre-contracted bovine retina arteries. Exp Eye Res 2004;78:215–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kiss B, Dallinger S, Findl O, et al. Acetazolamide-induced cerebral and ocular vasodilation in man is independent of nitric oxide. Am J Physiol 1999;276:R1661–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Grunwald JE. Effect of topical timolol on the human retinal circulation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1986;27:1713–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Boles Carenini B, Brogliatti B, Boles Carenini A. Pulsatile ocular blood flow and antiglaucomatous drugs. New Trends Ophthalmol 1992;7:195–200. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Boles Carenini A, Sibour G, Boles Carenini B. Differences in long term effect of timolol and betaxolol on the pulsatile ocular blood flow. Surv Ophthalmol 1994;38 (Suppl) :S118–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yoshida A, Feke GT, Ogasawara H, et al. Effect of timolol on human retinal, choroidal and optic nerve head circulation. Ophthalmic Res 1991;23:162–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Harris A, Spaeth GL, Sergott RC, et al. Retrobulbar arterial hemodynamic effects of betaxolol and timolol in normal-tension glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 1995;20:168–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schmetterer L, Strenn K, Findl O, et al. Effects of antiglaucoma drugs on ocular hemodynamics in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1997;61:583–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Polska E, Polak K, Luksch A, et al. Twelve hour reproducibility of choroidal blood flow parameters in healthy subjects. Br J Ophthalmol 2004;88:533–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]