Abstract
Background: Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) is a potent toxin normally present in the colonic lumen which may play a role in ulcerative colitis (UC). Two enzymes, thiol methyltransferase (TMT) and rhodanese (RHOD), are thought to be responsible for sulphide removal but supportive evidence is lacking.
Aims: To determine the distribution of TMT and RHOD in different sites throughout the gastrointestinal tract and their efficacy as detoxifiers of H2S.
Methods: Enzyme activities were measured in normal tissue resected from patients with cancer. TMT and RHOD activities were determined using their conventional substrates, 2-mercaptoethanol and sodium thiosulphate, respectively. For measurement of H2S metabolism, sodium sulphide was used in the absence of dithiothreitol. Thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT), which in common with TMT methylates sulphydryl groups but is not thought to act on H2S, was also examined.
Results: TMT, RHOD, and TPMT activities using their conventional substrates were found throughout the gastrointestinal tract with highest activity in the colonic mucosa. When H2S was given as substrate, no reaction product was found with TMT or TPMT but RHOD was extremely active (Km 8.8 mM, Vmax 14.6 nmol/mg/min). Incubation of colonic homogenates with a specific RHOD antibody prevented the metabolism of H2S, indicating that RHOD is responsible for detoxifying H2S. A purified preparation of RHOD also detoxified H2S.
Conclusions: RHOD, located in the submucosa and crypts of the colon, is the principal enzyme involved in H2S detoxication. TMT does not participate in the detoxication of H2S.
Keywords: colonic mucosa, hydrogen sulphide, ulcerative colitis, rhodanese, thiol methyltransferase, thiopurine methyltransferase
The concentration of hydrogen sulphide (H2S) in human faeces, varying between 1.0 and 2.4 mmol/kg, is well within the known toxic range.1 H2S is released in the colonic lumen by anaerobic sulphate reducing bacteria from sulphate, originating from dietary sulphur containing preservatives, mucin sulphate, and by amino acid fermenting bacteria from sulphur containing amino acids.1 H2S disrupts cellular energy synthesis by complexing with enzymes responsible for oxidative phosphorylation,2 and is known to inhibit butyrate metabolism,3 a more important source of energy than glucose in the colonic mucosa.4
The possible importance of H2S as an aetiological agent or as a cofactor in the genesis or maintenance of ulcerative colitis (UC) is suggested by evidence that counts of sulphate reducing bacteria are raised in the faeces of patients with active UC,5 that H2S concentrations are also increased,6 and that butyrate oxidation is inhibited.3 The toxic effects of H2S and its mercapto derivatives would be expected to be mitigated by effective removal mechanisms. The enzymes thiol methyltransferase (TMT) and rhodanese (RHOD) have both been suggested to be capable of removing H2S and these mercapto derivatives, but supportive evidence is lacking.7,8 If either enzyme is important in H2S detoxification, it would be expected to be detectable in high concentrations in the colonic mucosa, and the ability to remove H2S should easily be demonstrable.
We have therefore examined the activity of both enzymes throughout the gastrointestinal tract using synthetic substrates. We have also examined the distribution of another enzyme active against sulphydryl groups, thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT), but which has no recognised action on H2S.9 We have determined the relative importance of the enzymes in the detoxication of H2S.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Tissue preparation
A total of 73 samples, obtained at surgery during routine operative procedures from the oesophagus to the rectum from 40 patients (24 male, 16 female) with a mean age of 56 years (range 28–91), were analysed. Three of 11 patients who provided upper gastrointestinal tract tissue samples (oesophagus and stomach) were taking omeprazole. Two of the nine patients who provided lower gastrointestinal tract tissue samples (small intestine, right colon, left colon, and rectum) were taking prednisolone, and one of the nine was taking sulphasalazine. Normal tissue was resected from patients with cancer at a site distant from the primary carcinoma. Samples from both the muscularis propria and the mucosa (comprising both the submucosa and crypts) were analysed. The muscularis propria was stripped from the mucosal layers by blunt dissection, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −70°C.
Crypt preparation
Mucosal epithelial crypts were prepared by scraping a scalpel blade along the mucosal surface to separate the mucosa from the submucosa. Intact crypts were obtained by digestion in 0.1% collagenase (type 1, Worthington) for one hour. Cells were cultured in suspension for 24 hours in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium before harvesting by centrifugation at 1000 g for five minutes in a bench top centrifuge.
TMT assay
The activity of TMT was measured using a method based on that of Pacifici and colleagues9 and Weinshilboum and colleagues10 with 2-mercaptoethanol as substrate. Tissue homogenate was incubated with 100 mM (low affinity enzyme reaction) or 30 μM (high affinity enzyme reaction) 2-mercaptoethanol and 100 μM 3H-S-adenosyl methionine (500 mCi/mmol; Amersham, UK) in 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer with 1 mM EDTA and 0.5% Triton-X-100 (pH 7.9) at 37°C for 10 minutes in a final volume of 25 μl. Reactions were terminated on ice by the addition of an equal volume of 1 M hydrochloric acid. Radiolabelled product was extracted into 10 volumes of toluene. Each sample was assayed in triplicate together with a heated enzyme (100°C, 10 minutes) and a no enzyme control.
RHOD assay
RHOD activity was measured using sodium thiosulphate as substrate, as described by Aminlari and Gilanpour,11 based on the work of Sorbo.12 Tissue homogenate was incubated with 50 mM sodium thiosulphate, 50 mM potassium cyanide, and 40 mM sodium glycine buffer (pH 9.2) at 20°C for 10 minutes in a final volume of 200 μl. Reactions were terminated on ice by the addition of 37% formaldehyde. The reaction product, thiocyanate, forms a red precipitate on mixing with an equal volume of 0.025 M ferric nitrate and was detected at 460 nm with a Pharmacia LKB-Ultrospec III spectrophotometer. Each sample was assayed in triplicate together with a formaldehyde inactivated enzyme control.
TPMT assay
The activity of TPMT was measured using 6-mercaptopurine as substrate, as described by Pacifici and colleagues9 and Weinshilboum and colleagues.13 Tissue homogenate was incubated with 4 mM 6-mercaptopurine added in 2.5 μl dimethyl sulphoxide together with 50 μM allopurinol, 5 mM dithiothreitol, and 25 μM 3H-S-adenosyl methionine (500 mCi/mmol; Amersham) in 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer containing 0.5% Triton-X-100 (pH 6.7) at 37°C for 60 minutes in a total volume of 25 μl. Reactions were terminated on ice by addition of an equal volume of 0.5 M sodium borate, pH 9.5. Radiolabelled product was extracted into 10 volumes of 10% isoamyl alcohol in toluene. Each sample was assayed in triplicate with controls of heated enzyme (100°C, 10 minutes) and no enzyme.
Thiocyanate levels in plasma
Plasma was prepared from freshly obtained whole blood in EDTA by centrifugation at 2000 g. Plasma was removed from the pelleted whole cells and no haemolysis was evident. An equal volume of ferric nitrate was added to aliquots of plasma and product measured as described for the RHOD assay.
Protein determination
Protein concentration was calculated by the Bradford method14 using an equal volume of tissue homogenate buffer as the control for background absorbance.
Immunoprecipitation of RHOD
RHOD was immunoprecipitated by overnight incubation at 4°C with a rabbit antirhodanese polyclonal antiserum15 using normal rabbit serum as a control. Complexed rabbit 7 antirhodanese antibody was immunoprecipitated using formalin fixed staphylococcus protein A (Sigma, St Louis, Missouri, USA). The precipitate was removed by centrifugation. The supernatant was assayed for RHOD, TMT, and TPMT activity using the standard methods described above. Background levels of product were measured with no substrate, no enzyme, and heated enzyme controls.
RESULTS
Enzyme distribution in the gastrointestinal tract
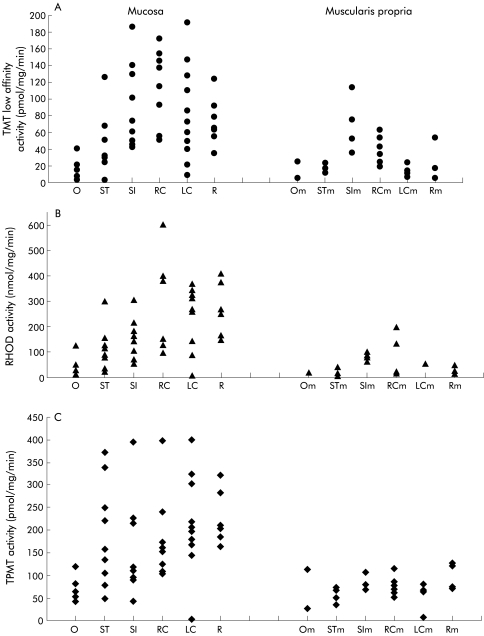
The distribution of TMT, RHOD, and TPMT throughout the gastrointestinal tract is shown in fig 1A ▶–C, respectively, for the mucosa and the muscularis propria. Table 1 ▶ shows the mean (SEM) data for mucosal activity of all three enzymes throughout the gastrointestinal tract. The distribution of all three enzymes was similar with activity highest in the large bowel mucosa (right colon, left colon, and rectum) and lowest in the oesophagus. TMT activity in the large bowel was similar to that in the small intestine but was significantly higher than that in the oesophagus and stomach mucosa (p=0.04, Mann Whitney U test) (fig 1A ▶). Activity within the large bowel (right colon, left colon, and rectum) did not differ significantly. Activity of low affinity TMT was closely correlated with high affinity TMT (correlation coefficient 0.80, data not shown). Similar to TMT, RHOD mucosal activity (fig 1B ▶) was significantly lower in the oesophagus, increasing threefold in the stomach (p=0.026, Mann Whitney U test). Activity continued to rise throughout the gastrointestinal tract and in the left colon and rectum was significantly greater than in the stomach (p=0.04, p=0.008, respectively, Mann Whitney U test) (fig 1B ▶). TPMT activity (fig 1C ▶) was also lower in the oesophagus compared with the stomach (p=0.017, Mann Whitney U test). Although the trend was upward towards the rectum, there was no significant difference between the small intestine or stomach and the large bowel.
Figure 1.
Distribution of (A) thiol methyltransferase (TMT), (B) rhodanese (RHOD), and (C) thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) throughout the gastrointestinal tract for the mucosa and the muscularis propria. O, oesophagus; ST, stomach; SI, small intestine; RC, right colon; LC, left colon; R, rectum.
Table 1.
Mucosal thiol methyltransferase (TMT), rhodanese (RHOD), and thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) activity at each site throughout the gastrointestinal tract
| TMT activity (pmol/mg/min) | RHOD activity (nmol/mg/min) | TPMT activity (pmol/mg/min) | |
| Oesophagus | 17.6 (5.4) (n=6) | 46.7 (18.1) (n=6) | 66.8 (12.2) (n=6) |
| Stomach | 51.5 (11.9) (n=9) | 127.6 (26.1) (n=9) | 189.2 (37.9) (n=9) |
| Small intestine | 91.7 (16.7) (n=9) | 157.6 (26.0) (n=9) | 156.4 (35.8) (n=9) |
| Right colon | 114.4 (15.9) (n=8) | 292.4 (80.9) (n=6) | 182.5 (34.2) (n=8) |
| Left colon | 82.4 (16.8) (n=11) | 245.6 (38.9) (n=10) | 209.5 (31.5) (n=11) |
| Rectum | 72.4 (10.7) (n=7) | 253.9 (39.4) (n=7) | 223.3 (21.1) (n=7) |
| Values are mean (SEM). | |||
Activity was approximately 50% higher in the mucosa compared with the muscularis propria (fig 1A ▶–C), which mirrored the distribution found in the mucosa. Enzyme activity within the mucosa was further studied by assaying activity within epithelial crypt pellets. Activity of TMT in crypts was 669.9 (SEM 115.7) pmol/mg/min (n=13) compared with 89.5 (9.4) pmol/mg/min (n=26) in the large bowel mucosa, indicating that TMT activity is predominantly localised within the crypts in the mucosa. RHOD activity was similar in both preparations (190.8 (89.9) nmol/mg/min (n=13) in crypts compared with 260.3 (28.3) nmol/mg/min (n=23) in large bowel mucosa) indicating that RHOD activity is not confined to crypts. TPMT activity was 22.6 (3.5) pmol/mg/min (n=13) in crypts compared with 204.9 (17.5) pmol/mg/min (n=26) in the underlying mucosa, indicating that in contrast, TPMT activity is not localised in crypts.
Enzyme affinity constants for TMT, RHOD, and TPMT were calculated from dose-response curves using the methods of Eadie-Hoffstee and Hanes.16 The calculated Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) for TMT (low affinity) using 2-mercaptoethanol as substrate was 5.2 mM and the high affinity Km was 0.01 mM. The Km for RHOD using thiosulphate as substrate was 1.1 mM and that for TPMT using 6-mercaptopurine as substrate 0.26 mM.
TMT action on H2S
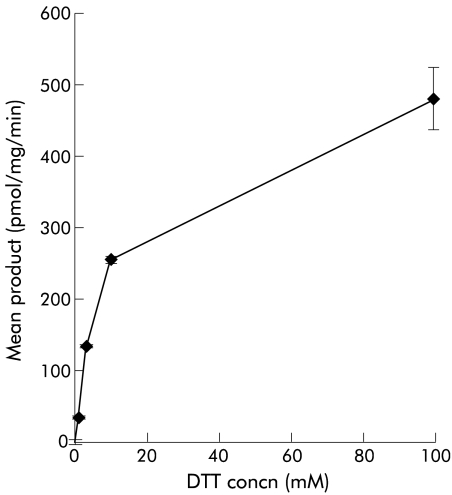
In an earlier report examining the effect of TMT on H2S, dithiothreitol (DTT) was included as a reducing agent7 and an apparent Km for H2S of 8 mM was found. We found however that DTT is itself a substrate for TMT, as shown in fig 2 ▶, with a Km of 11.5 mM and a maximal velocity (Vmax) of 527.4 pmol/mg/min. Incubation of enzyme with a wide range of H2S concentrations (nM to M) in the presence of 0.2 mM DTT had no additive effect, confirming that DTT, and not H2S, is metabolised by TMT (data not shown). Experiments examining the effect of TMT on H2S were therefore performed in the absence of DTT. No enzyme activity was seen when H2S (supplied as sodium sulphide) was used as substrate (n=8) (fig 3 ▶). To check for functional enzyme activity, parallel experiments using 2-mercaptoethanol as substrate continued to show enzyme activity consistent with functioning enzyme. As no toluene extractable reaction product was formed with 3H-S-adenosyl methionine, these data contradict the earlier report7 and show that TMT is unable to detoxify H2S.
Figure 2.
Effect of thiol methyltransferase (TMT) on dithiothreitol (DTT). DTT is itself a substrate for TMT, with a Km of 11.5 mM and a maximal velocity of 527.4 pmol/mg/min.
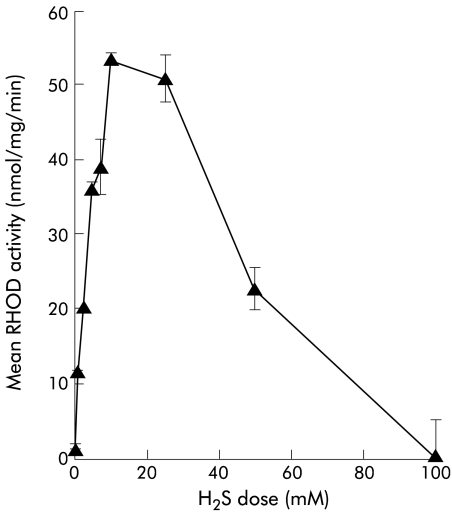
Figure 3.
Effect of rhodanese (RHOD) on hydrogen sulphide (H2S) (supplied as sodium sulphide). High levels of enzyme activity were found with a maximal velocity of 14.6 nmol/mg/min. The calculated Km was 8.8 mM.
RHOD action on H2S
RHOD action on H2S (supplied as sodium sulphide) was determined with 50 mM cyanide as cosubstrate in place of thiosulphate. High levels of enzyme activity were found, as shown in fig 3 ▶. Vmax was 14.6 nmol/mg/min, and at a physiological concentration of 1 mM activity was 6.7 nmol/mg/min. The calculated Km was 8.8 mM. At very high concentrations of H2S (>30 mM) there was inhibition of enzyme action.
Thiocyanate levels in plasma
Thiocyanate levels in plasma from controls and smokers were measured at 0.19 (0.01) mM (n=42) and 0.32 (0.04) mM (n=16), respectively.
Effect of antibody to RHOD on H2S detoxification in colonic homogenates
RHOD assays in colonic homogenates and using thiosulphate or H2S as substrate in the presence or absence of polyclonal antibody to RHOD were performed. Addition of antibody inhibited enzyme activity greatly when either thiosulphate (92% reduction) or H2S (86% reduction) was used as substrate. No effect was seen on enzyme activity when similar volumes of normal rabbit serum were added. Polyclonal antibody to RHOD had no effect on the activity of TMT or TPMT (data not shown).
Action of purified bovine RHOD on H2S
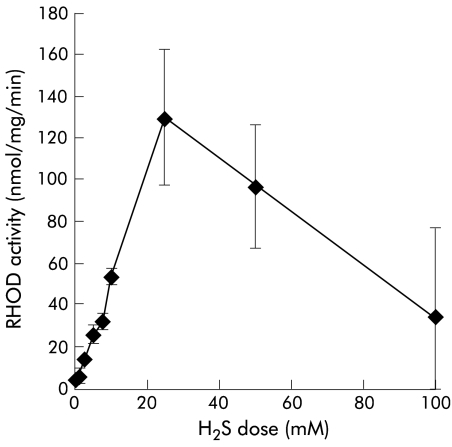
Purified bovine liver RHOD (Sigma) action on H2S was determined with 50 mM cyanide as cosubstrate, as shown in fig 4 ▶, and illustrated a similar dose-response to that produced by colonic mucosal RHOD. At concentrations of >30 mM, H2S inhibited enzyme activity, as found in the colonic homogenate. Antibody to RHOD was also effective when used with bovine RHOD. When incubated with the antibody, purified bovine RHOD activity on H2S was lost (100%).
Figure 4.
Effect of purified bovine liver rhodanese (RHOD) on hydrogen sulphide (H2S). A similar dose-response to that produced by colonic mucosal RHOD was illustrated.
DISCUSSION
We have found that the activities of all three enzymes studied were highest in the large bowel and lowest in the oesophagus, with results consistently higher in the mucosa than in the muscularis propria of the submucosa. Although the findings for TMT distribution and for the chosen control, TPMT, agree with previous results,9,17 those for RHOD are new. When comparing activities in the crypts and the mucosa (comprising crypts and submucosa), total TMT activity was accounted for in the crypt cells, RHOD was in both crypts and the submucosa, whereas TPMT was principally in the submucosa.
When sodium sulphide was used as a direct source of H2S, high levels of RHOD activity were found in the presence of cyanide as cosubstrate, with a Vmax of 14.6 nmol/mg/min and a Km of 8.8 mM. In contrast, TMT (in the absence of DTT) did not remove H2S generated from sodium sulphide. This finding disagrees with the results of others7 but activity noted in the past may have reflected the presence of DTT in the reaction mix as we have shown that DTT is a good substrate for TMT. That RHOD was the responsible enzyme for sulphide removal in our studies was confirmed by the loss of activity with a polyclonal antibody to RHOD. Separate experiments showed that purified bovine liver RHOD has a similar ability to detoxify H2S and that RHOD antibody also blocked enzyme activity. In vivo clearance of H2S in rat colon has recently been estimated to be 20 nmol/mg/min.18 We found that in human colonic homogenates, a similar level of RHOD enzyme activity exists at physiological concentrations of H2S (1–2 mM), substantiating the claim that this enzyme may be the in vivo detoxifier of H2S.18
Levitt and colleagues18 have demonstrated radiolabelled H2S removal in rat caecal blood and have shown that the TMT transmethylation reaction is not involved, in contrast with data recently reported using 2-mercaptoethanol as substrate.19 Our studies indicate that RHOD is likely to be the responsible enzyme for detoxification of H2S. In vivo, data to date have focused on the role of RHOD as a detoxifier of cyanide and not on the role proposed here, as a detoxifier of H2S. The source of the cyanide cosubstrate is unknown but we found that prevailing levels of thiocyanate are high in plasma (0.19 mM in non-smokers and 0.32 mM in smokers), indicating that there is an ample source of cyanide available to act as cosubstrate in the proposed reaction.
Molecular data have introduced a second closely related enzyme with a possible role in the detoxication of H2S, namely mercaptopyruvate sulphur transferase (MST). MST has 60% homology to RHOD20 and can perform the same reaction as RHOD but is thought to primarily catalyse the production of thiosulphate from mercaptopyruvate and a sulphydryl group donor. Similarly, RHOD will catalyse the formation of thiosulphate although it primarily transfers sulphydryl groups to cyanide, forming thiocyanate and sulphate.20 In common with RHOD, MST is found in mitochondria but is also found in the cytosol.12 The balance of expression of RHOD and MST in various tissues is not known or whether both enzymes are required for effective detoxication of H2S. Finally, our data offer an explanation for the reduced incidence of UC in smokers. Cyanide and sulphide react together to form thiocyanate under the influence of RHOD which may explain why smokers have raised levels of thiocyanate as shown here, consequent on cyanide removal from inhaled tobacco smoke.21 Cyanide may conceivably act as a protective agent in these circumstances.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Wellcome Trust.
Abbreviations
H2S, hydrogen sulphide
DTT, dithiothreitol
Vmax, maximal velocity
MST, mercaptopyruvate sulphur transferase
Km, Michaelis-Menten constant
RHOD, rhodanese
TMT, thiol methyltransferase
TPMT, thiopurine methyltransferase
UC, ulcerative colitis
The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not to be construed as opinions of the Department of Defense or the Department of the Army
REFERENCES
- 1.MacFarlane GT, Gibson GR, Cummings JH. Comparison of fermentation reactions in different regions of the human colon. J Appl Bacteriol 1992:72:57–64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Khan AA, Schuler MM, Prior MG, et al. Effects of hydrogen sulfide exposure on lung mitochondrial respiratory chain enzymes in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1990;103:482–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Moore JWE, Babidge W, Millard S, et al. Effect of sulphide on short chain acyl-CoA metabolism in rat colonocytes. Gut 1997;41:77–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roediger WEW. Utilization of nutrients by isolated epithelial cells of the rat colon. Gastroenterology 1982;83:424–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pitcher MCL, Beatty ER, Cummings JH. The contribution of sulphate reducing bacteria and 5-aminosalicylic acid to faecal sulphide in patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut 2000;46:64–72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Roediger WEW. The colonic epithelium in ulcerative colitis: an energy-deficiency disease? Lancet 1980;2:712–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Weisiger RA, Pinkus LM, Jakoby WB. Thiol S-methyltransferase: suggested role in detoxication of intestinal hydrogen sulfide. Biochem Pharmacol 1980:29:2885–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Huxtable RJ. Biochemistry of sulphur. New York: Plenum, 1986:124–9.
- 9.Pacifici GM, Romiti P, Santerini S, et al. S-methyltransferases in human intestine: differential distribution of the microsomal thiol methyltransferase and cytosolic thiopurine methyltransferase along the human bowel. Xenobiotica 1993:23:671–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Weinshilboum RM, Sladek S, Klumpp S. Human erythrocyte thiol methyltransferase: radiochemical microassay and biochemical properties. Clin Chim Acta 1979;97:59–71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Aminlari M, Gilanpour H. Comparative studies on the distribution of rhodanese in different tissues of domestic animals. Comp Biochem Physiol-B: Comp Biochem 1991;99:673–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sorbo BH. Thiosulfate sulfurtransferase and mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase. In: Greenberg DM, ed. Metabolic pathways. Academic Press: New York 1975; 7:433–56.
- 13.Weinshilboum RM, Raymond FA, Pazmino PA. Human erythrocyte thiopurine methyltransferase: radiochemical microassay and biochemical properties. Clin Chim Acta 1978;85:323–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bradford M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 1976;72:248–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Merrill GA, Butler M, Horowitz PM. Limited tryptic digestion near the amino terminus of bovine liver rhodanese produces active electrophoretic variants with altered refolding. J Biol Chem 1993;268:15611–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Whitehead EP. Co-operativity and the methods of plotting binding and steady-state kinetic data. Biochem J 1978;171:501–4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weisiger RA, Jakoby WB. Thiol s-methyltransferase from rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys 1979;196:631–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Levitt MD, Furne JK, Springfield J, et al. Detoxification of hydrogen sulfide and methanethiol in the cecal mucosa. J Clin Invest 1999;104:1107–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Roediger WEW, Babidge WJ. Thiol methyltransferase activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2000;47:206–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nagahara N, Okazaki T, Nishino T. Cytosolic mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase is evolutionarily related to mitochondrial rhodanese. J Biol Chem 1995;270:16230–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wilson J, Matthews DM. Metabolic inter-relationships between cyanide, thiocyanate and vitamin B12 in smokers and non-smokers. Clin Sci 1966;31:1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]