Abstract
1. Adrenalectomy reduced the median antinociceptive dose (AD50) of morphine in male Sprague-Dawley rats. The antinociceptive effect was assessed by the tail-flick method of D'Amour & Smith (1941).
2. Tolerance to the antinociceptive effect of morphine developed in adrenalectomized and sham-operated rats after chronic exposure to morphine. Development of tolerance did not significantly alter the increased sensitivity of adrenalectomized rats to the antinociceptive effect of morphine.
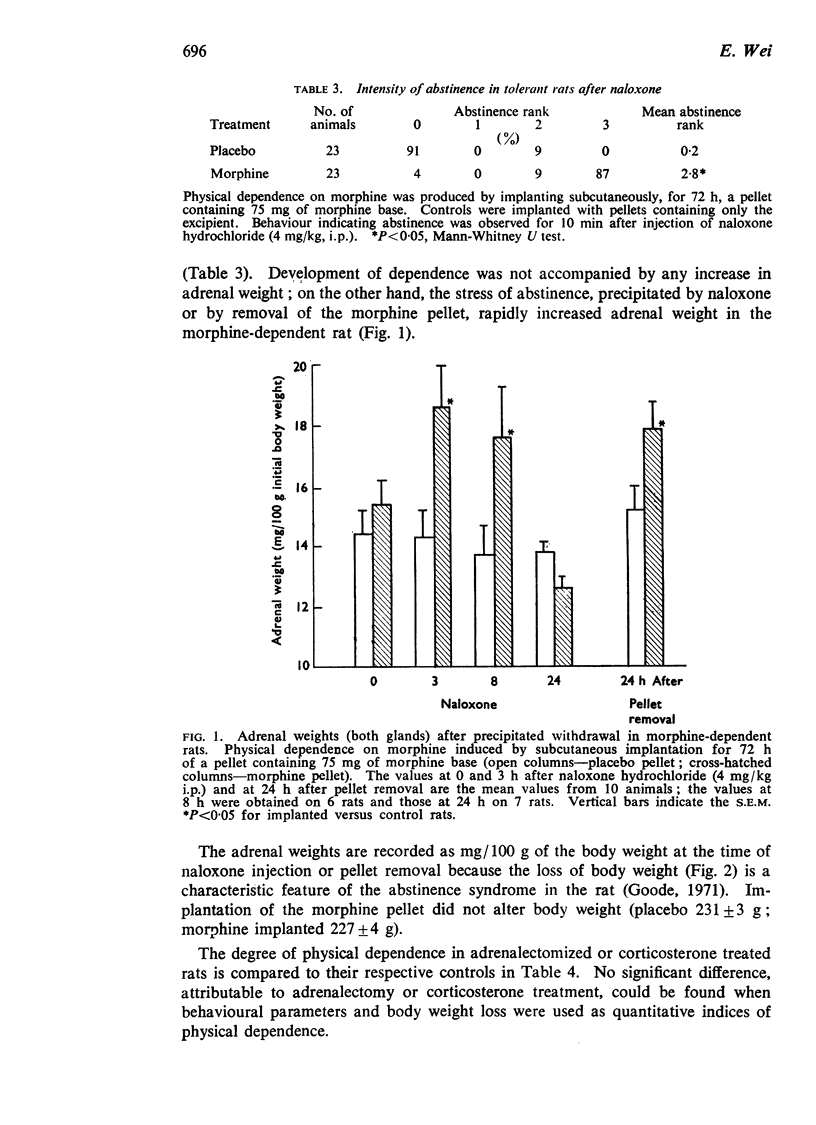
3. Adrenal weights were not increased in rats rendered physically dependent on morphine by subcutaneous implantation of a morphine pellet. Withdrawal, induced by intraperitoneal injection of naloxone hydrochloride, 4 mg/kg, or by removal of the implanted pellet, resulted in a rapid increase in adrenal weight.
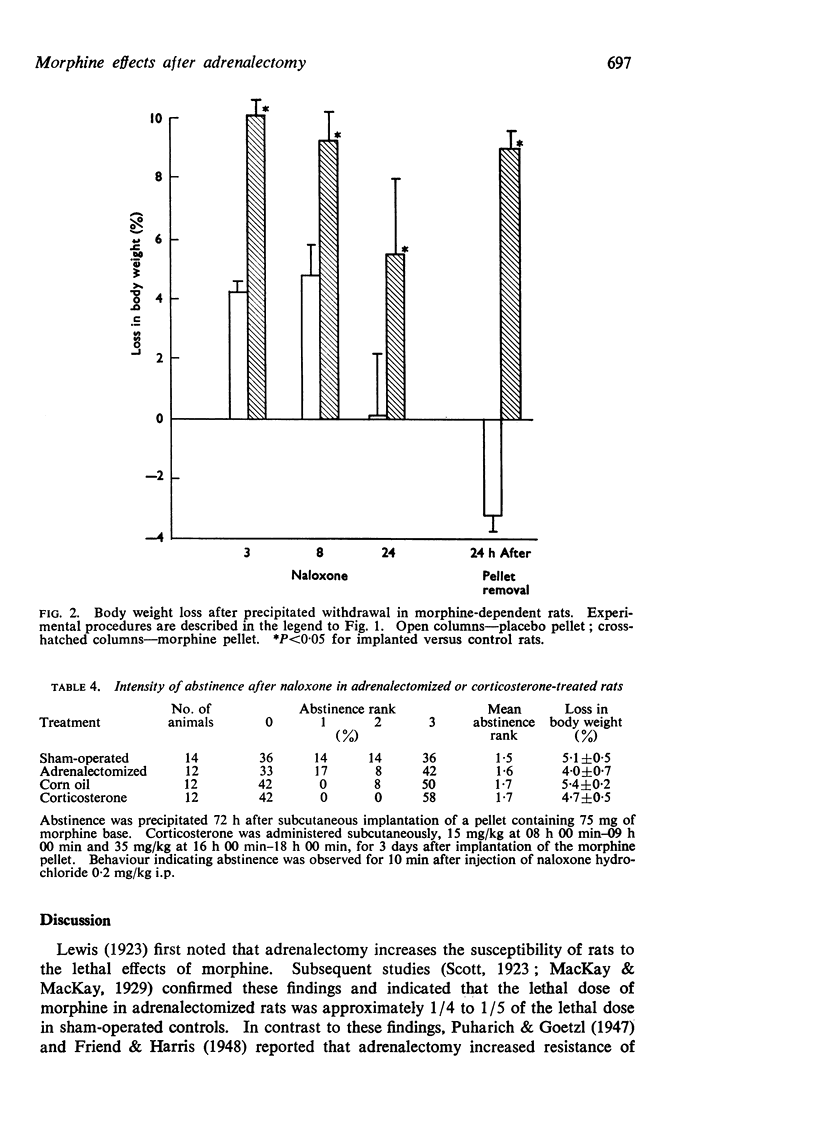
4. In morphine-dependent animals, the incidence of abstinence signs and body weight loss during precipitated withdrawal did not appear to be significantly influenced by adrenalectomy or by corticosterone-pretreatment.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akera T., Brody T. M. The addiction cycle to narcotics in the rat and its relation to catecholamines. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 May;17(5):675–688. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENMAN A. J., FRASER H. F., BROOKS J. W. Urinary excretion and plasma levels of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids during a cycle of addiction to morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 May;132:226–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhart G. F., Mitchell C. L. The effect of adrenalectomy on morphine analgesia and tolerance development in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;18(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. D., Tingstad J. E. Formulation of a morphine implantation pellet suitable for tolerance-physical dependence studies in mice. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Mar;59(3):426–427. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goode P. G. An implanted reservoir of morphine solution for rapid induction of physical dependence in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;41(3):558–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb08054.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz A., Albus K., Metys J., Schubert P., Teschemacher H. On the central sites for the antinociceptive action of morphine and fentanyl. Neuropharmacology. 1970 Nov;9(6):539–551. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(70)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayan S., Woods L. A., Mitchell C. L. Experience as a factor in the development of tolerance to the analgesic effect of morphine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969;6(3):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER J. W., GEORGE R., ELLIOTT H. W., SUNG C. Y., WAY E. L. The influence of the adrenal medulla in morphine analgesia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 May;114(1):43–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAROLI E., MELCHIORRI P. Urinary excretion of hydroxysteroids, 17-ketosteroids and aldosterone in rats during a cycle of treatment with morphine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Apr;6:1–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paré W. P. The effect of adrenalectomy, adrenal demedullation, and adrenalin on the aversive threshold in the rat. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Jul 30;159(3):869–879. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb12985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radzialowski F. M., Bousquet W. F. Daily rhythmic variation in hepatic drug metabolism in the rat and mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Sep;163(1):229–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUNG C. Y., WAY E. L., SCOTT K. G. Studies on the relationship of metabolic fate and hormonal effects of D, L-methadone to the development of drug tolerance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Jan;107(1):12–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANABE T., CAFRUNY E. J. Adrenal hypertrophy in rats treated chronically with morphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Jan;122(1):148–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSOU K., JANG C. S. STUDIES ON THE SITE OF ANALGESIC ACTION OF MORPHINE BY INTRACEREBRAL MICRO-INJECTION. Sci Sin. 1964 Jul;13:1099–1109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. A., FLATAKER L. The effect of cortisone, desoxycorticosterone, and adrenocorticotrophic hormone upon the responses of animals to analgesic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1951 Sep;103(1):93–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei E., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Quantitative aspects of precipitated abstinence in morphine-dependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Feb;184(2):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei E., Wilson J. T. Stress-mediated decrease in liver hexobarbital metabolism: the role of corticosterone and somatotropin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):227–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


