Abstract
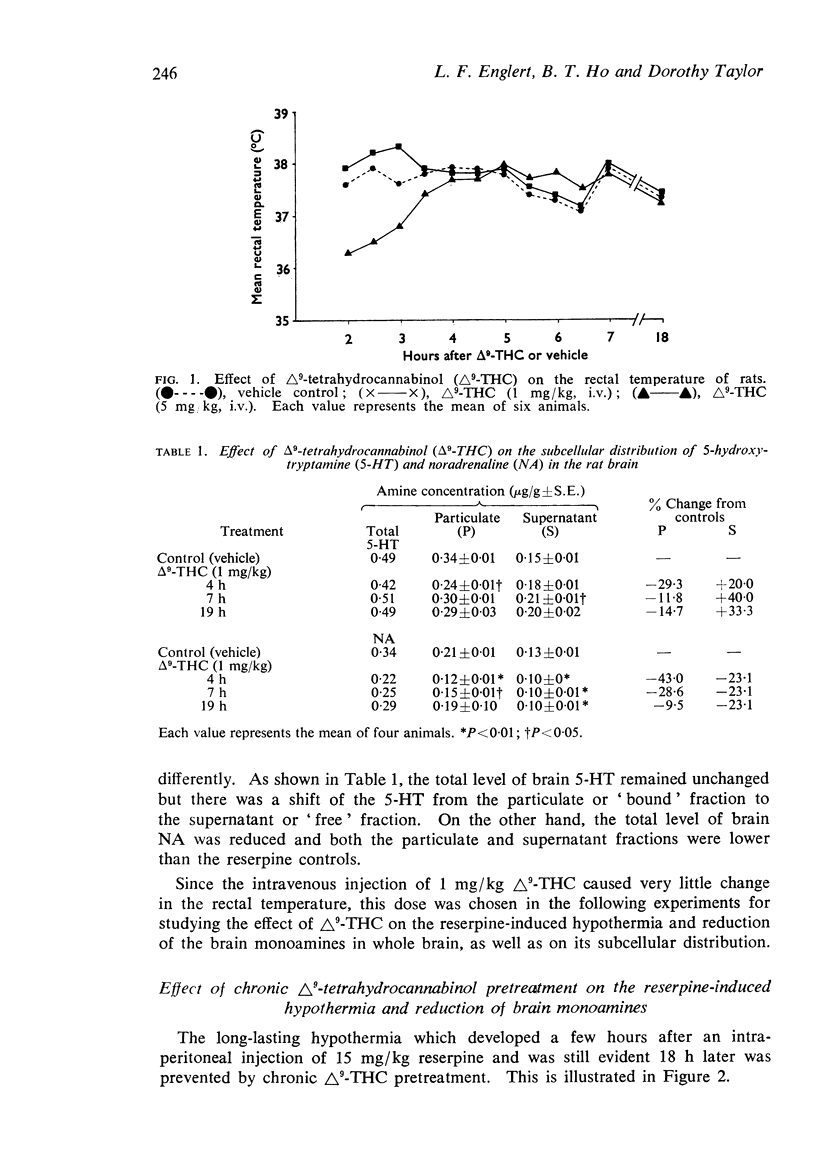
1. An intravenous injection into rats of 1 mg/kg (-)-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol Δ9-THC) had no effect on rectal temperature and produced in the subcellular fractions of the brain a shift of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) from the particulate or `bound' 5-HT to the supernatant or `free' fraction, whereas the noradrenaline (NA) decreased in both fractions.
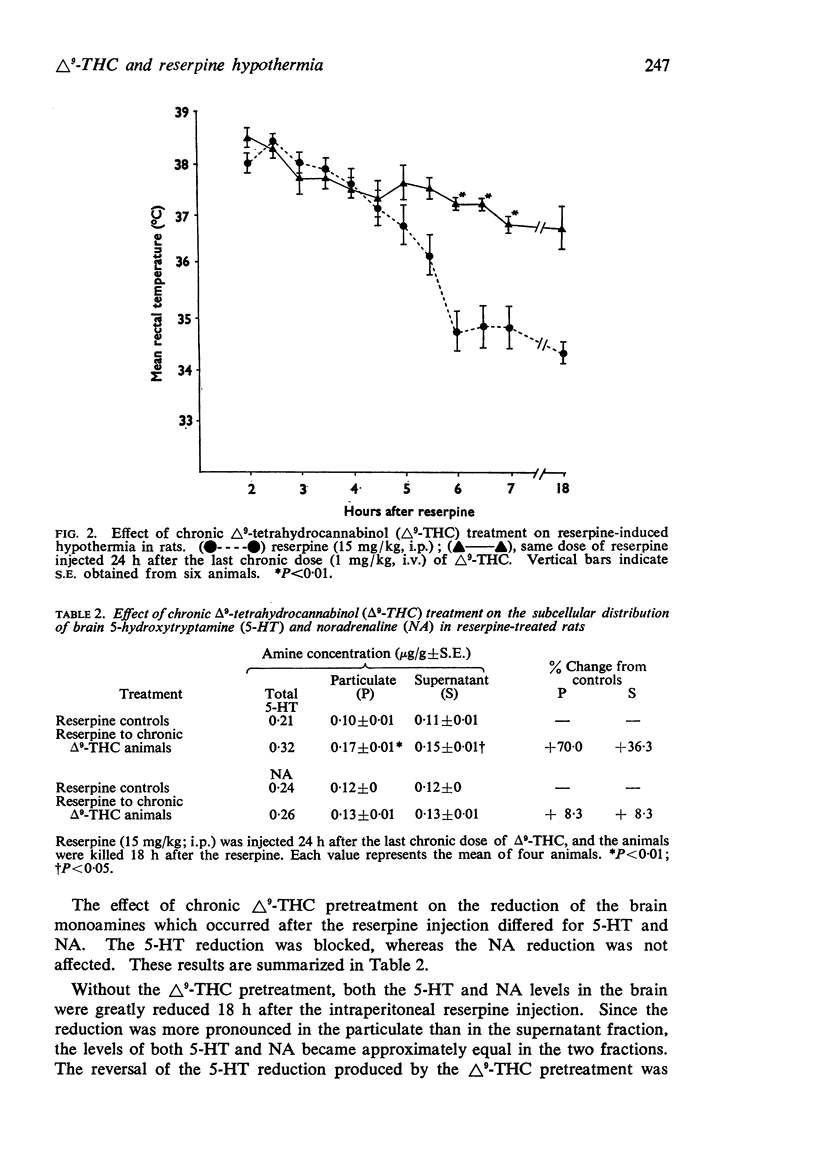
2. Pretreatment of rats by an intravenous injection of 1 mg/kg Δ9-THC three times a week for four weeks, prevented the hypothermia and the reduction in brain 5-HT produced by an intraperitoneal injection of 15 mg/kg reserpine given 24 h after the last Δ9-THC injection.
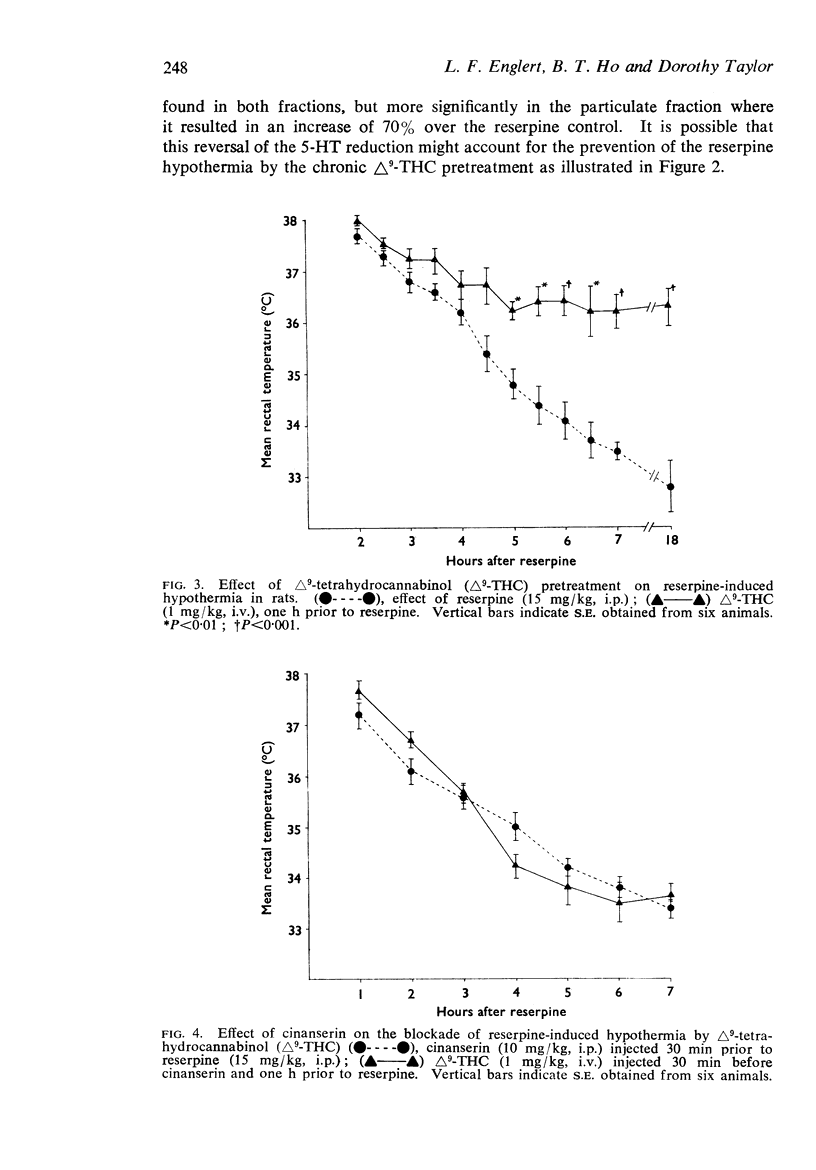
3. Pretreatment of rats by a single intravenous injection of 1 mg/kg Δ9-THC prevented the hypothermia and reduction in brain 5-HT produced by an intraperitoneal injection of reserpine given 1 h before. The reduction in brain NA was not prevented except at the 18 h time interval.
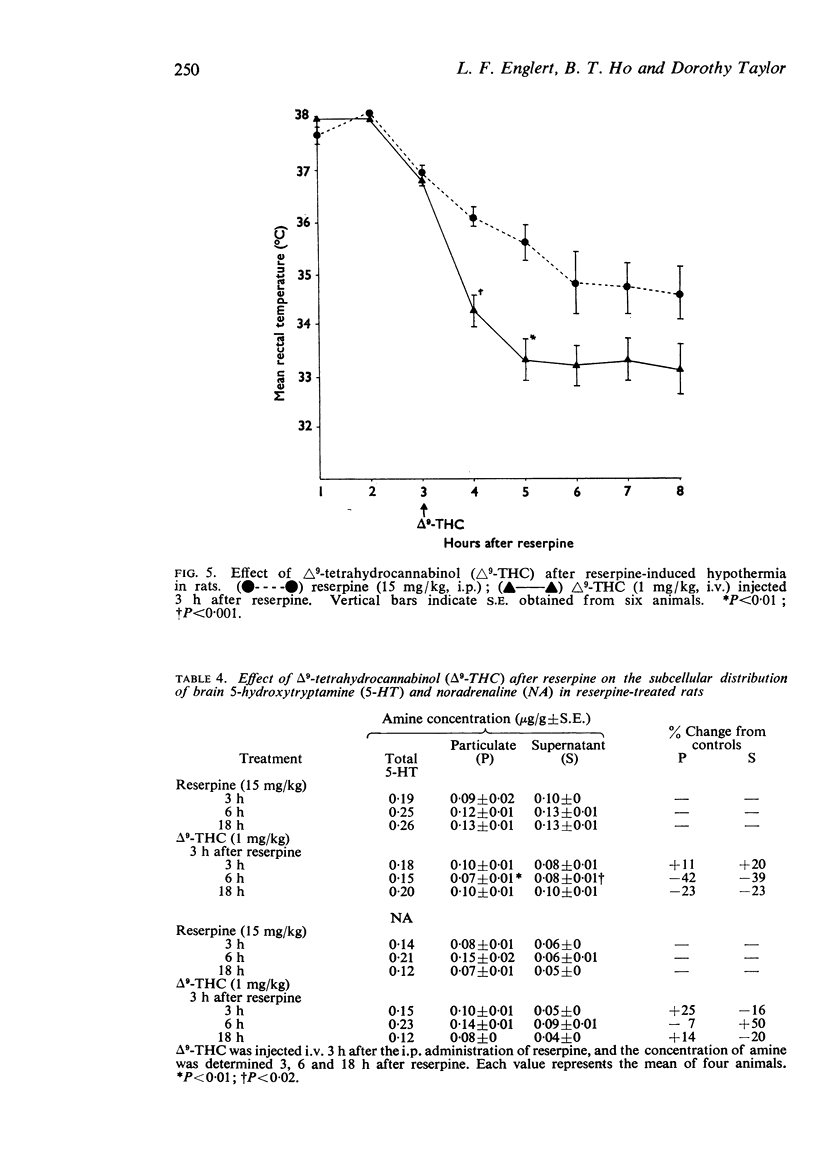
4. An injection of 1 mg/kg Δ9-THC intravenously into rats 3 h after an intraperitoneal injection of reserpine accentuated the reserpine hypothermia as well as the reduction of 5-HT but not of NA in the brain.
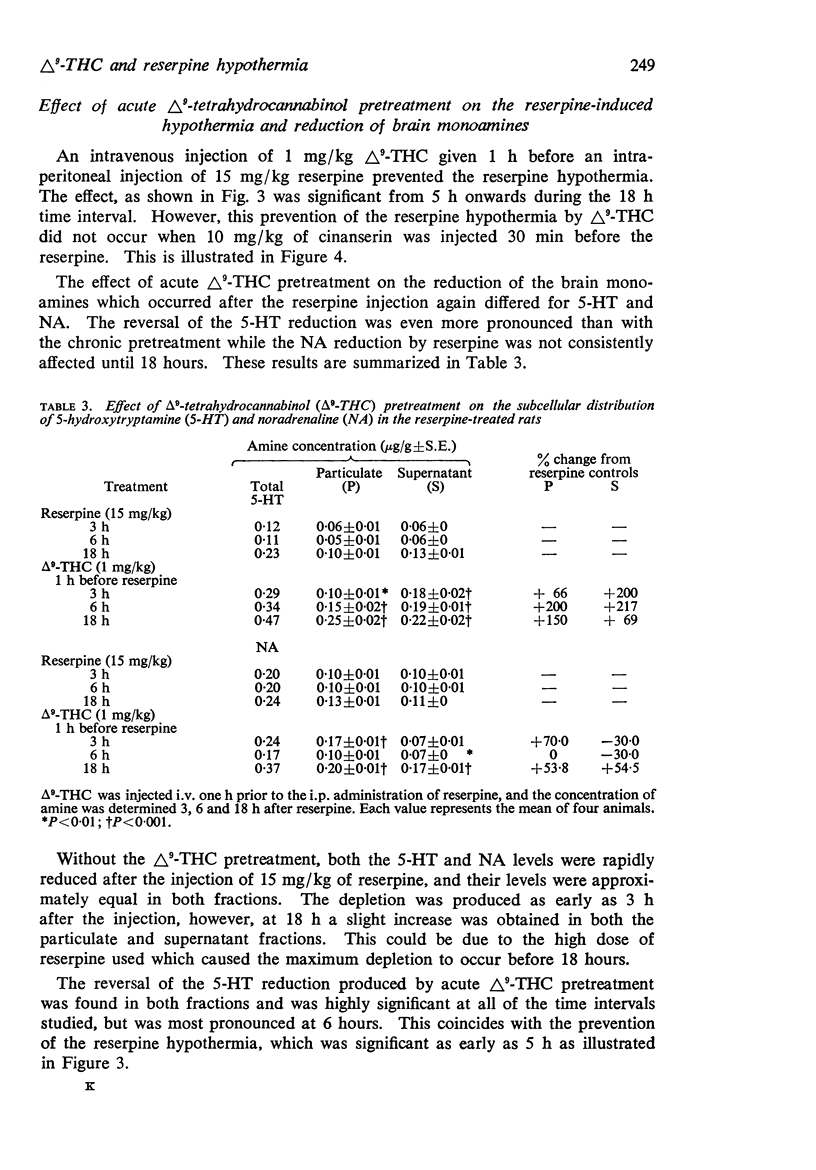
5. The reserpine hypothermia was not prevented by a single intravenous injection of 1 mg/kg Δ9-THC when cinanserin, a 5-HT inhibitor, was injected 30 min before the reserpine.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASKEW B. M. A SIMPLE SCREENING PROCEDURE FOR IMIPRAMINE-LIKE ANTIDEPRESSANT AGENTS. Life Sci. 1963 Oct;10:725–730. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(63)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie B. B., Comer M. S., Costa E., Dlabac A. The role of brain serotonin in the mechanism of the central action of reserpine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 May;152(2):340–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTA E., GARATTINI S., VALZELLI L. Interactions between reserpine, chlorpromazine, and imipramine. Experientia. 1960 Oct 15;16:461–463. doi: 10.1007/BF02171155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Green A. R. Rapid method for the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in small regions of rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;39(3):653–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MYERS R. D. A NEW CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE REGULATION BY AMINES IN THE HYPOTHALAMUS. Nature. 1963 Dec 28;200:1325–1325. doi: 10.1038/2001325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MYERS R. D. CHANGES IN TEMPERATURE PRODUCED BY MICRO-INJECTIONS OF AMINES INTO THE ANTERIOR HYPOTHALAMUS OF CATS. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:239–245. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MYERS R. D. EFFECTS ON TEMPERATURE OF AMINES INJECTED INTO THE CEREBRAL VENTRICLES. A NEW CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE REGULATION. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:226–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARATTINI S., GIACHETTI A., JORI A., PIERI L., VALZELLI L. Effect of imipramine, amitriptyline and their monomethyl derivatives on reserpine activity. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1962 Aug;14:509–514. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1962.tb11130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho B. T., Fritchie G. E., Englert L. F., McIsaac W. M., Idänpän-Heikkilä J. E. Marihuana: importance of the route of administration. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Apr;23(4):309–310. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08666.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idänpän-Heikkilä J., Fritchie G. E., Englert L. F., Ho B. T., McIsaac W. M. Placental transfer of tritiated-1-delta-9-tetrhydrocannabinol. N Engl J Med. 1969 Aug 7;281(6):330–330. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196908072810620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jori A., Garattini S. Interaction between imipramine-like agents and catecholamine-induced hyperthemia. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1965 Aug;17(8):480–488. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1965.tb07708.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverty R., Taylor K. M. The fluorometric assay of catecholamines and related compounds: improvements and extensions to the hydroxyindole technique. Anal Biochem. 1968 Feb;22(2):269–279. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90316-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN B., PIALA J. J., BURKE J. C., CRAVER B. N. A NEW, POTENT AND SPECIFIC SEROTONIN INHIBITOR, (SQ 10,643) 2'-(3-DIMETHYLAMINOPROPYLTHIO) CINNAMANILIDE HYDROCHLORIDE: ANTISEROTONIN ACTIVITY ON UTERUS AND ON GASTROINTESTINAL, VASCULAR, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS OF ANIMALS. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Nov 1;152:132–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A. Effect of environmental temperature on the turnover of 5-hydroxytryptamine in various areas of rat brain. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):93–108. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A., Uretsky N. J. Central effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on the body temperature of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;40(4):630–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofia R. D., Dixit B. N., Barry H., 3rd The effect of delta-1-tetrahydrocannabinol on serotonin metabolism in the rat brain. Life Sci I. 1971 Apr 15;10(8):425–436. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90107-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson T. H., Waldeck B. On the significance of central noradrenaline for motor activity: experiments with a new dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;7(3):278–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(69)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


