Abstract
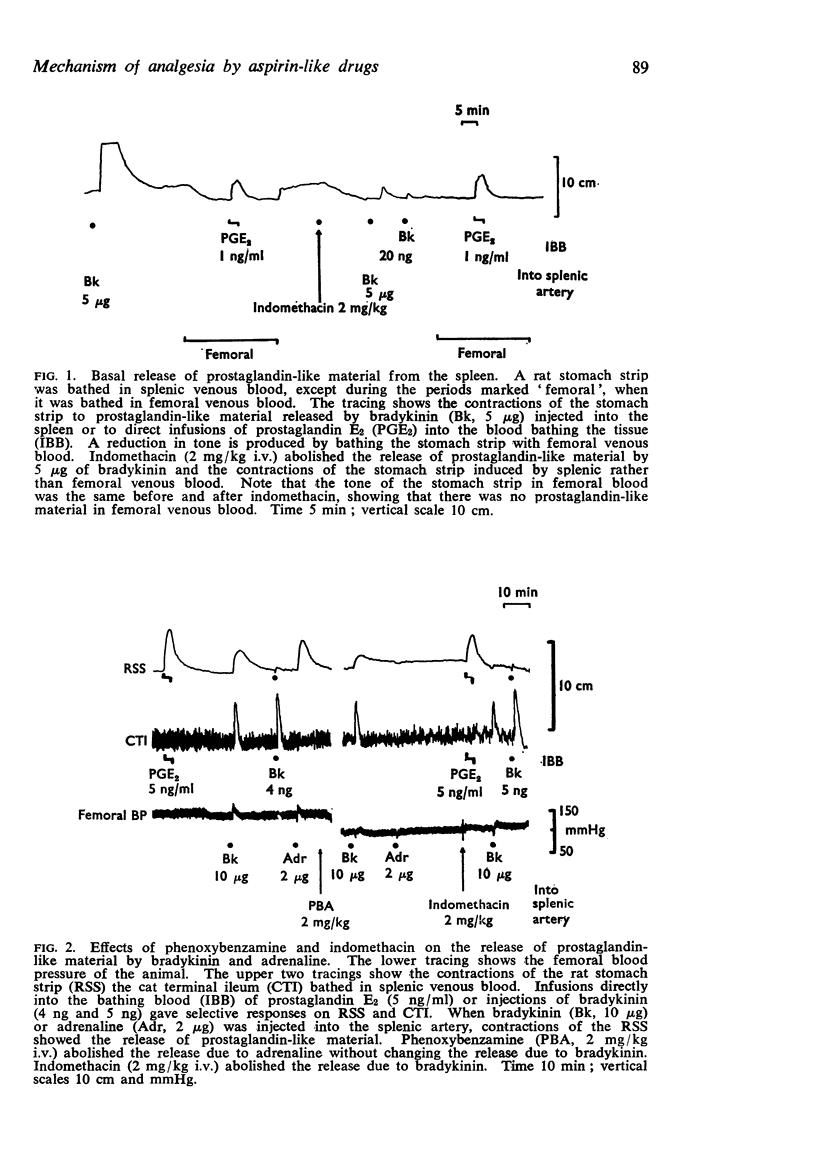
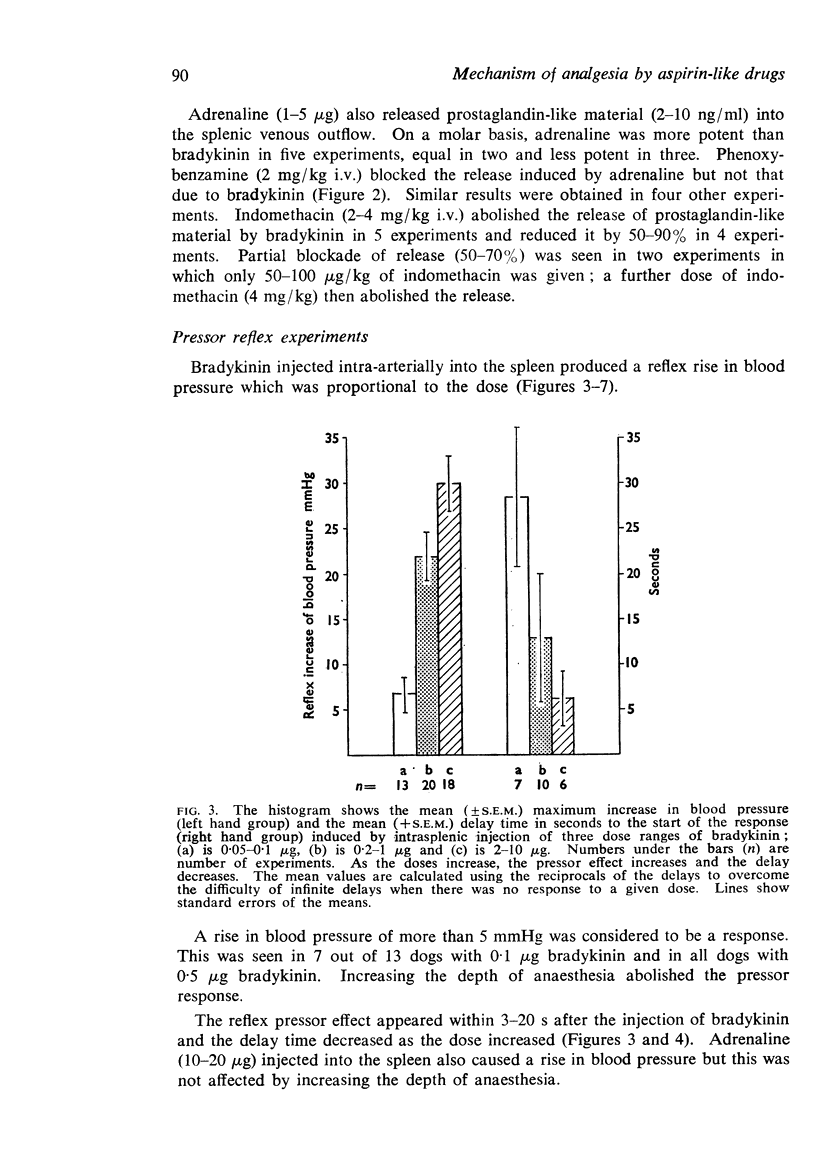
1. Resting splenic venous outflow from anaesthetized dogs contains prostaglandin-like material: the concentration increases after intra-arterial injections of bradykinin into the spleen, and is abolished by treatment with indomethacin.
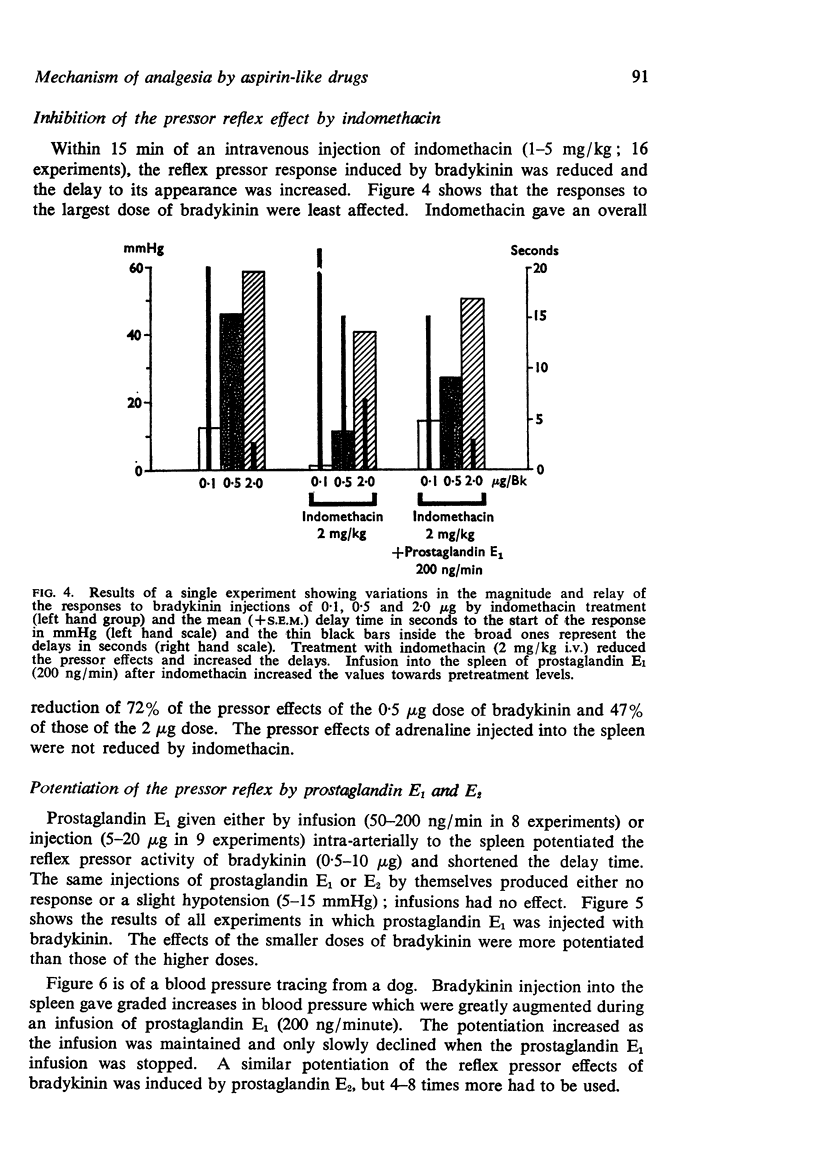
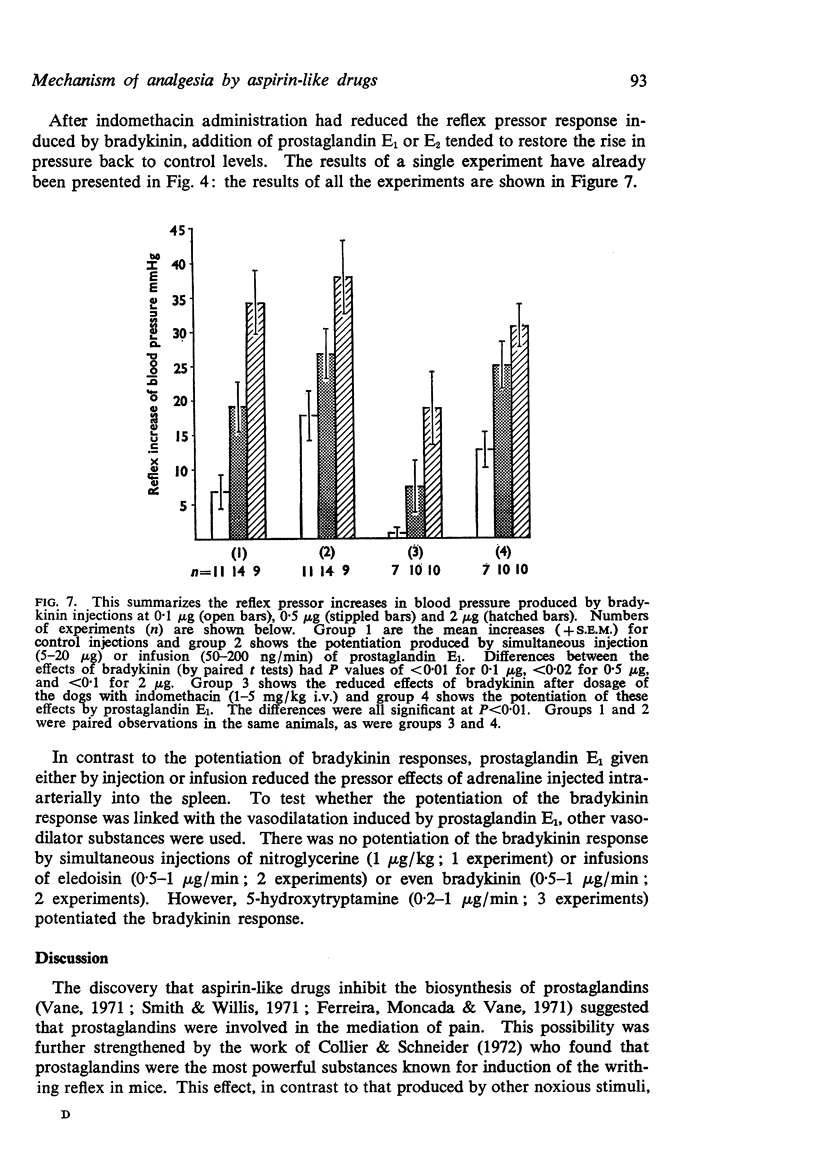
2. Intra-arterial injections of bradykinin into the spleen of lightly anaesthetized dogs elicit a dose-dependent reflex increase in the blood pressure, which is reduced but not abolished by treatment with indomethacin.
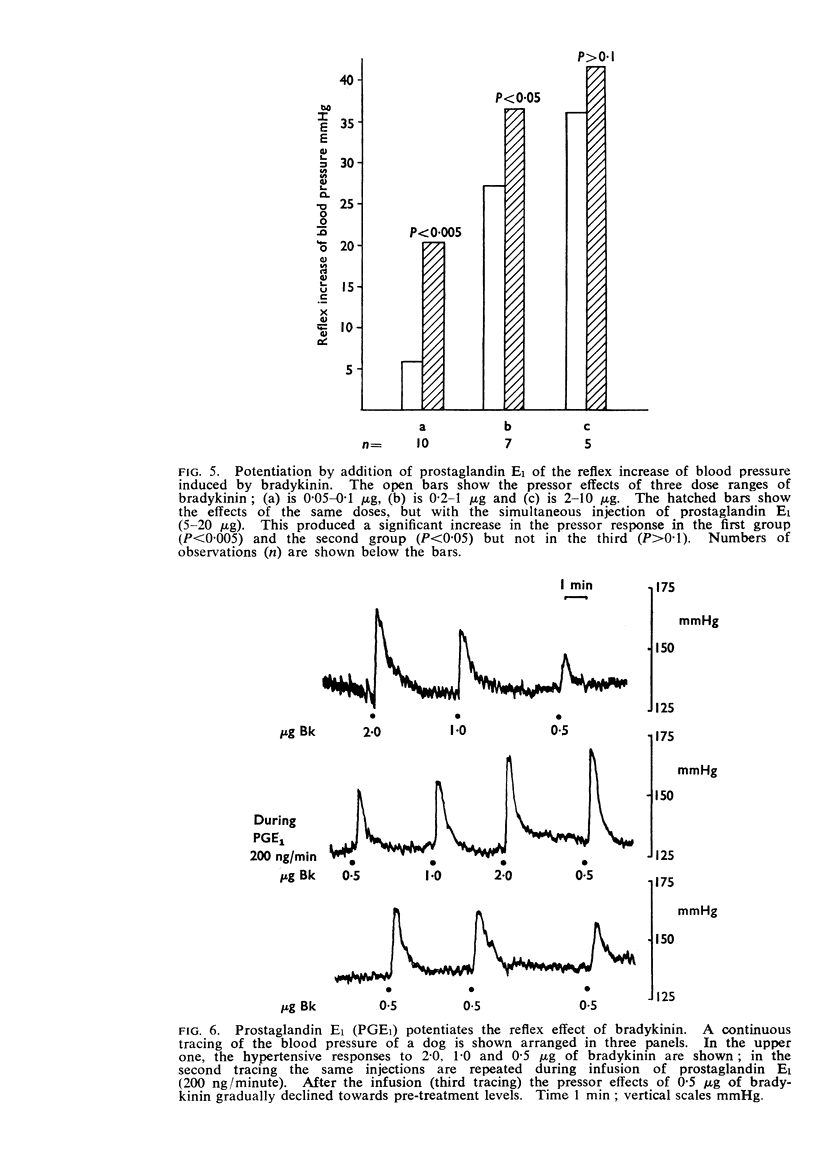
3. Addition of prostaglandin E1 or E2 either by injections or by infusions restores the reflex increase in the blood pressure due to bradykinin injections after indomethacin treatment.
4. The sensitizing action of endogenously released prostaglandins at or near the afferent nerve endings is discussed.
5. The analgesic activity of aspirin-like drugs is explained in terms of the removal of the sensitizing activity of prostaglandins.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLLIER H. O., HAMMOND A. R., HORWOOD-BARRETT S., SCHNEIDER C. RAPID INDUCTION BY ACETYLCHOLINE, BRADYKININ AND POTASSIUM OF A NOCICEPTIVE RESPONSE IN MICE AND ITS SELECTIVE ANTAGONISM BY ASPIRIN. Nature. 1964 Dec 26;204:1316–1318. doi: 10.1038/2041316b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O. A pharmacological analysis of aspirin. Adv Pharmacol Chemother. 1969;7:333–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Dinneen L. C., Johnson C. A., Schneider C. The abdominal constriction response and its suppression by analgesic drugs in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Feb;32(2):295–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Schneider C. Nociceptive response to prostaglandins and analgesic actions of aspirin and morphine. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):141–143. doi: 10.1038/newbio236141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. O., Schneider C. Profiles of activity in rodents of some narcotic and narcotic antagonists drugs. Nature. 1969 Nov 8;224(5219):610–612. doi: 10.1038/224610a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier J. G., Karim S. M., Robinson B., Somers K. Proceedings: Action of prostaglandins A2, B-1, E2 and F2 alpha on superficial hand veins of man. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;44(2):374P–375P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVISON C., GUY J. L., LEVITTM, SMITH P. K. The distribution of certain non-narcotic analgetic agents in the CNS of several species. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Nov;134:176–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies B. N., Horton E. W., Withrington P. G. The occurrence of prostaglandin E2 in splenic venous blood of the dog following splenic nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jan;32(1):127–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00436.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMELE J. F., SHANAMAN J. BRADYKININ WRITHING: A METHOD FOR MEASURING ANALGESIA. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Dec;114:680–682. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Indomethacin and aspirin abolish prostaglandin release from the spleen. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):237–239. doi: 10.1038/newbio231237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Moncada S., Vane J. R. Some effects of inhibiting endogenous prostaglandin formation on the responses of the cat spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jan;47(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H. Prostaglandins, aspirin-like drugs and analgesia. Nat New Biol. 1972 Dec 13;240(102):200–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio240200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. Prostaglandins: their disappearance from and release into the circulation. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):868–873. doi: 10.1038/216868a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUZMAN F., BRAUN C., LIM R. K., POTTER G. D., RODGERS D. W. NARCOTIC AND NON-NARCOTIC ANALGESICS WHICH BLOCK VISCERAL PAIN EVOKED BY INTRA-ARTERIAL INJECTION OF BRADYKININ AND OTHER ALGESIC AGENTS. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Jun 1;149:571–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUZMAN F., BRAUN C., LIM R. K. Visceral pain and the pseudaffective response to intra-arterial injection of bradykinin and other algesic agents. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1962 Apr 1;136:353–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie A. Prostaglandin-oxytocin enhancement and potentiation and their clinical applications. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 15;1(5793):150–152. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5793.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore N., Vane J. R., Wyllie J. H. Prostaglandins released by the spleen. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1135–1140. doi: 10.1038/2181135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. W., Sondergaard J., McDonald-Gibson W. Recovery of prostaglandins in human cutaneous inflammation. Br Med J. 1971 May 1;2(5756):258–260. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5756.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASHIMOTO K., KUMAKURA S., TAIRA N. VASCULAR REFLEX RESPONSES INDUCED BY AN INTRAARTERIAL INJECTION OF AZAAZEPINOPHENOTHIAZINE, ANDROMEDOTOXIN, VERATRIDINE, BRADYKININ AND KALLIKREIN AND BLOCKING ACTION OF SODIUM SALICYLATE. Jpn J Physiol. 1964 Jun 15;14:299–308. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.14.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON E. W. ACTION OF PROSTAGLANDIN E1 ON TISSUES WHICH RESPOND TO BRADYKININ. Nature. 1963 Nov 30;200:892–893. doi: 10.1038/200892b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEITH E. F. Evaluation of analgesic substances. Am J Pharm Sci Support Public Health. 1960 Jun;132:202–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim S. Action of prostaglandin in the pregnant woman. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Apr 30;180:483–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb53216.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIM R. K., GUZMAN F., RODGERS D. W., GOTO K., BRAUN C., DICKERSON G. D., ENGLE R. J. SITE OF ACTION OF NARCOTIC AND NON-NARCOTIC ANALGESICS DETERMINED BY BLOCKING BRADYKININ-EVOKED VISCERAL PAIN. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1964 Nov 1;152:25–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANN M., WEST G. B. The nature of hepatic and splenic sympathin. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1950 Jun;5(2):173–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1950.tb01004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL L. O., SELITTO J. J. A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1957 Sep 1;111(4):409–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL L. O., SELITTO J. J. Anti-inflammatory effects of romilar CF. J Am Pharm Assoc Am Pharm Assoc. 1958 May;47(5):313–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGOLI D., VANE J. R. A SENSITIVE METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF ANGIOTENSIN. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:351–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIVA SANSEVERINO E., URBANO A. [Action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on the dog spleen]. Arch Sci Biol (Bologna) 1962 Oct-Dec;46:419–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E., Jessup R. Spontaneous and evoked release of prostaglandins from frog spinal cord. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):998–1004. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramwell P. W., Shaw J. E. Spontaneous and evoked release of prostaglandins from cerebral cortex of anesthetized cats. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):125–134. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siggins G., Hoffer B., Bloom F. Prostaglandin-norepinephrine interactions in brain: microelectrophoretic and histochemical correlates. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Apr 30;180:302–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb53199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Willis A. L. Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):235–237. doi: 10.1038/newbio231235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANE J. R. A sensitive method for the assay of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Sep;12(3):344–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANE J. R. THE USE OF ISOLATED ORGANS FOR DETECTING ACTIVE SUBSTANCES IN THE CIRCULATING BLOOD. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Oct;23:360–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. The release and fate of vaso-active hormones in the circulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;35(2):209–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTER C. A., FLATAKER L. NOCICEPTIVE THRESHOLDS AS AFFECTED BY PARENTERAL ADMINISTRATION OF IRRITANTS AND OF VARIOUS ANTINOCICEPTIVE DRUGS. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Jun;148:373–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff H. G., Hardy J. D., Goodell H. MEASUREMENT OF THE EFFECT ON THE PAIN THRESHOLD OF ACETYLSALICYLIC ACID, ACETANILID, ACETOPHENETIDIN, AMINOPYRINE, ETHYL ALCOHOL, TRICHLORETHYLENE, A BARBITURATE, QUININE, ERGOTAMINE TARTRATE AND CAFFEINE: AN ANALYSIS OF THEIR RELATION TO THE PAIN EXPERIENCE. J Clin Invest. 1941 Jan;20(1):63–80. doi: 10.1172/JCI101196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


