Abstract
1. The acute effects of a purified toxin from Australian Tiger snake (Notechis scutatus scutatus) venom have been investigated at the mammalian neuromuscular junction.
2. The toxin was injected into the tail vein of mice. Death was due to respiratory paralysis.
3. The resting membrane potential, and action potential of muscle fibres in muscles from in vivo intoxicated animals were normal.
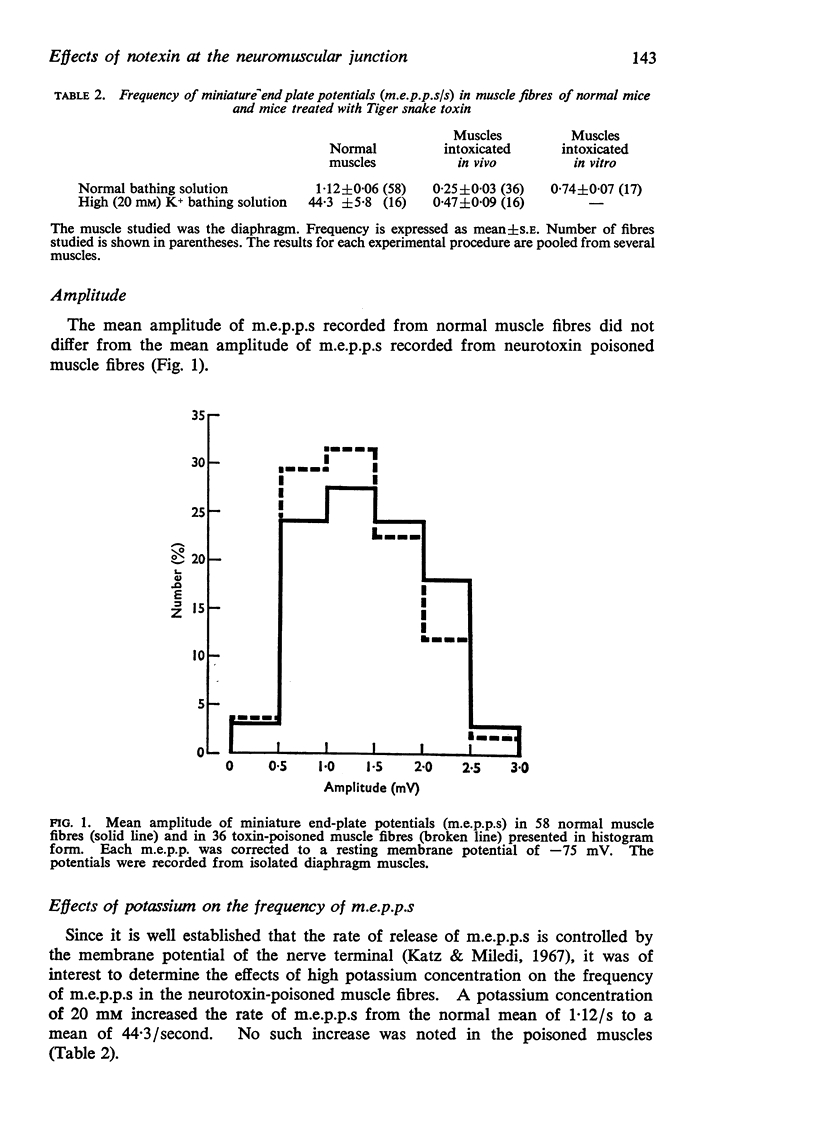
4. The frequency of miniature end plate potentials (m.e.p.p.s) from intoxicated nerve-muscle preparations was reduced, although m.e.p.p. amplitude was unaltered.
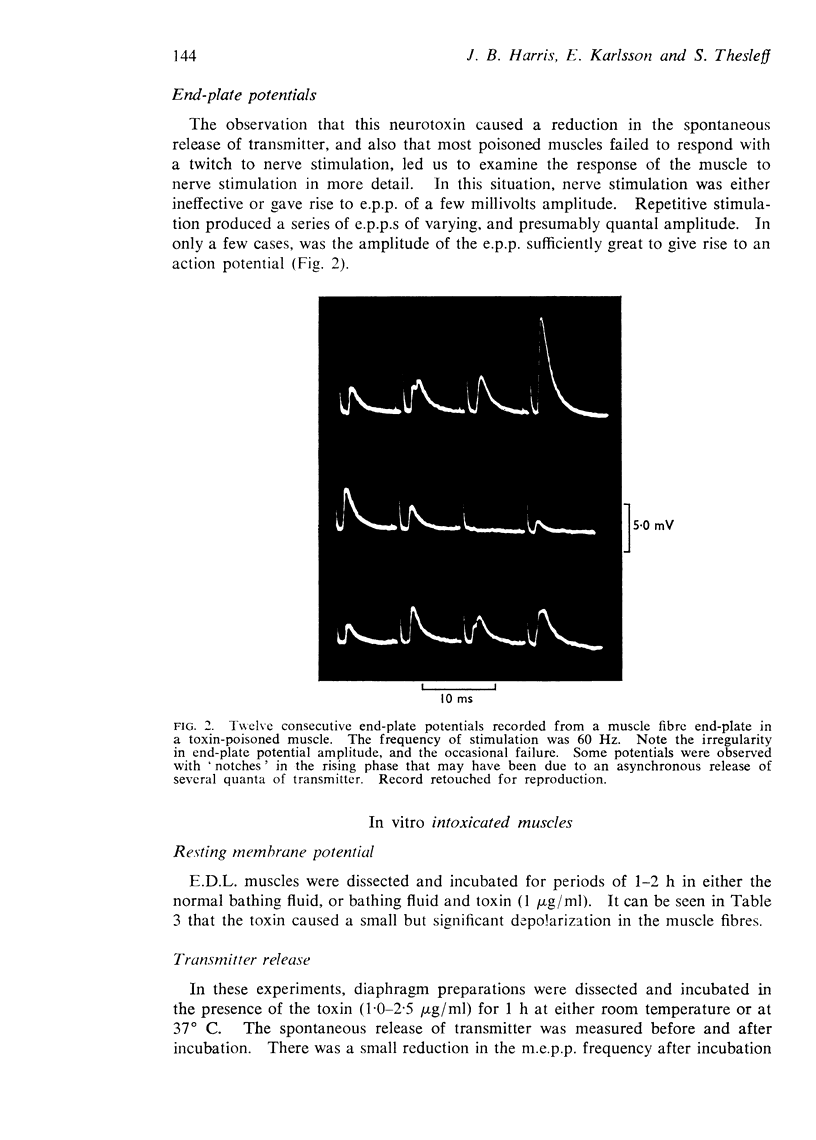
5. Nerve stimulation resulted in end plate potentials (e.p.p.s) of quantal amplitude; only rarely was the e.p.p. large enough to give rise to an action potential.
6. High (20 mM) K+ did not increase m.e.p.p. frequency in intoxicated preparations.
7. The toxin was largely ineffective in vitro.
8. The similarities and differences between this toxin, β-bungarotoxin and botulinum toxin are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROOKS V. B. An intracellular study of the action of repetitive nerve volleys and of botulinum toxin on miniature end-plate potentials. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):264–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGEN A. S. V., DICKENS F., ZATMAN L. J. The action of botulinum toxin on the neuro-muscular junction. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):10–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG C. C., LEE C. Y. ISOLATION OF NEUROTOXINS FROM THE VENOM OF BUNGARUS MULTICINCTUS AND THEIR MODES OF NEUROMUSCULAR BLOCKING ACTION. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963 Jul 1;144:241–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaker D., Harris J. B., Thesleff S. Action of a cobra neurotoxin on denervated rat skeletal muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Jul;15(2):254–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES R., WHALER B. C. Influence of nerve-ending activity and of drugs on the rate of paralysis of rat diaphragm preparations by Cl. botulinum type A toxin. J Physiol. 1962 Feb;160:221–233. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. On the factors which determine the amplitude of the miniature end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):267–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang C. C. Modes of actions of purified toxins from elapid venoms on neuromuscular transmission. Mem Inst Butantan. 1966;33(2):555–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A. Postsynaptic action of cobra toxin at the myoneural junction. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):727–728. doi: 10.1038/227727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. I. Quantitative aspects. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Apr;81(4):557–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. L. Ionic requirements for the neuromuscular blocking action of botulinum toxin: implications with regard to synaptic transmission. Neuropharmacology. 1971 Nov;10(6):673–684. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(71)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THESLEFF S. Supersensitivity of skeletal muscle produced by botulinum toxin. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:598–607. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


