Abstract
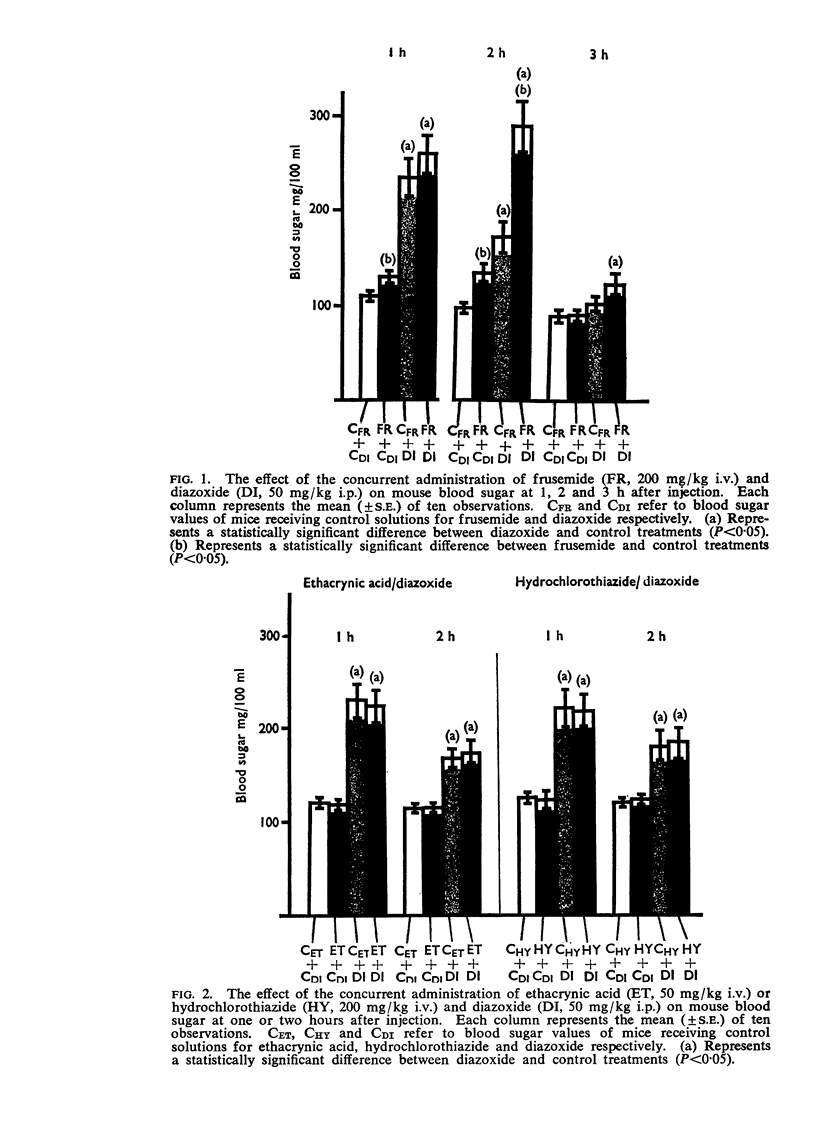
1. Frusemide produced hyperglycaemia in mice when administered together with diazoxide. The interaction between the drugs in elevating the blood sugar was shown to be additive.
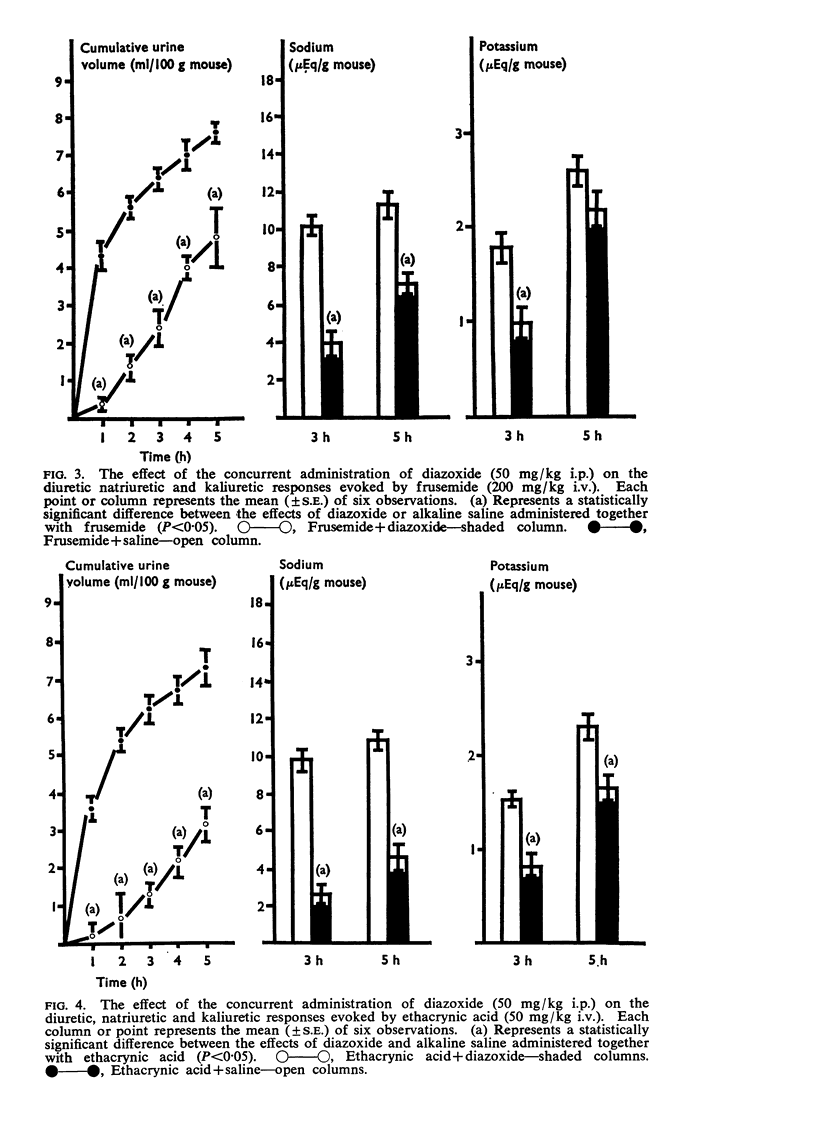
2. The diuretic, natriuretic and kaliuretic effects of frusemide were very markedly attenuated by diazoxide.
3. Neither ethacrynic acid nor hydrochlorothiazide exerted any effect upon blood sugar when administered together with diazoxide.
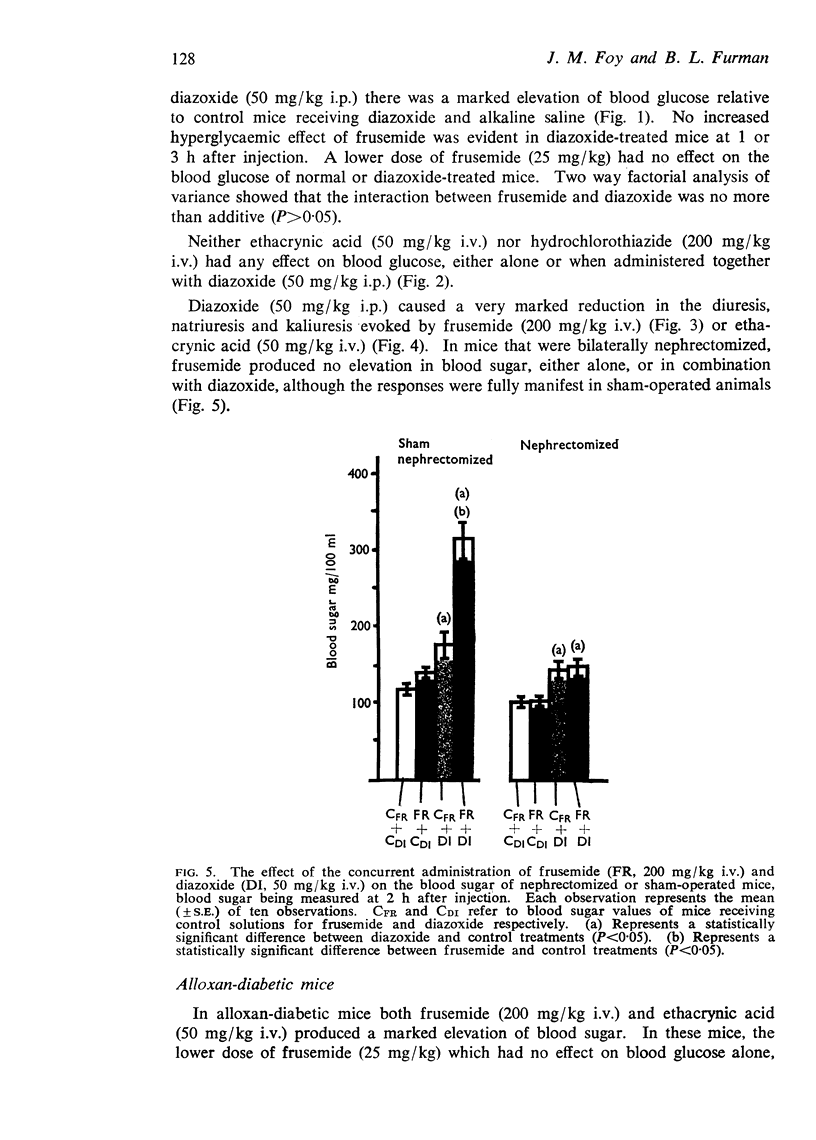
4. Bilateral nephrectomy completely prevented the hyperglycaemic effect of frusemide in normal mice and in mice treated with diazoxide. Diazoxide itself still produced hyperglycaemia in nephrectomized mice.
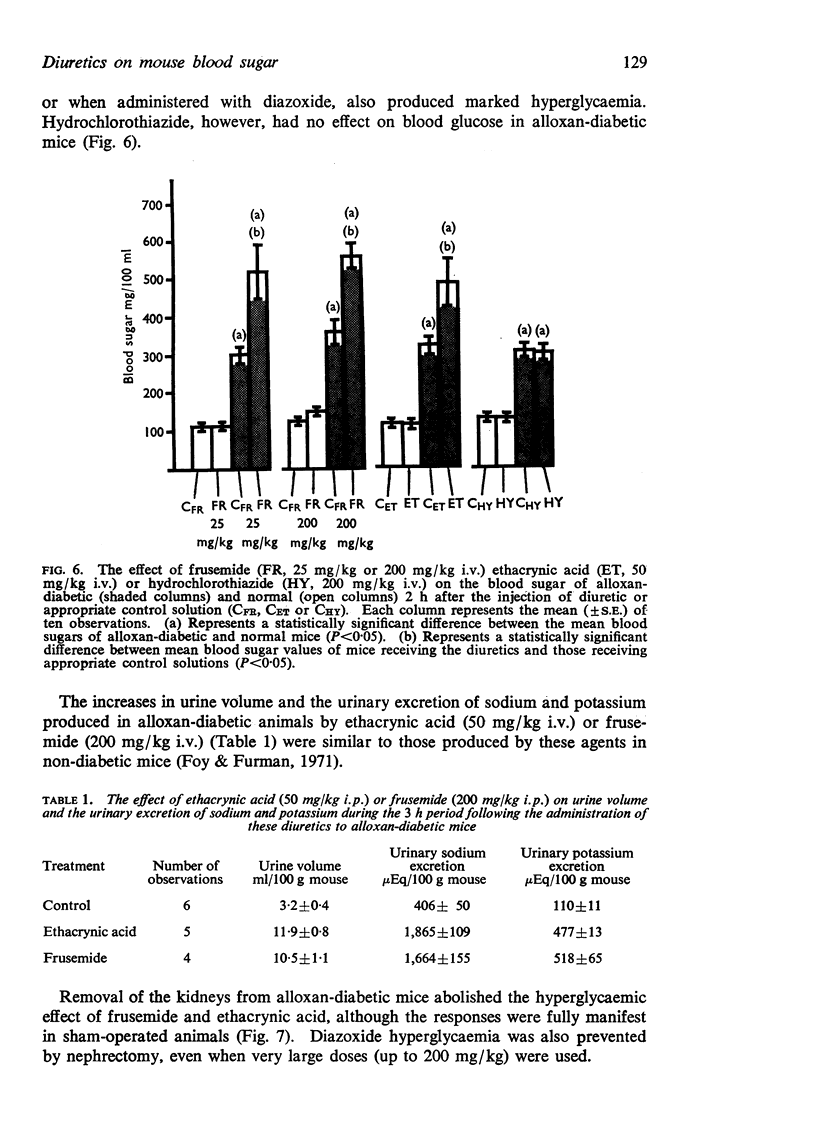
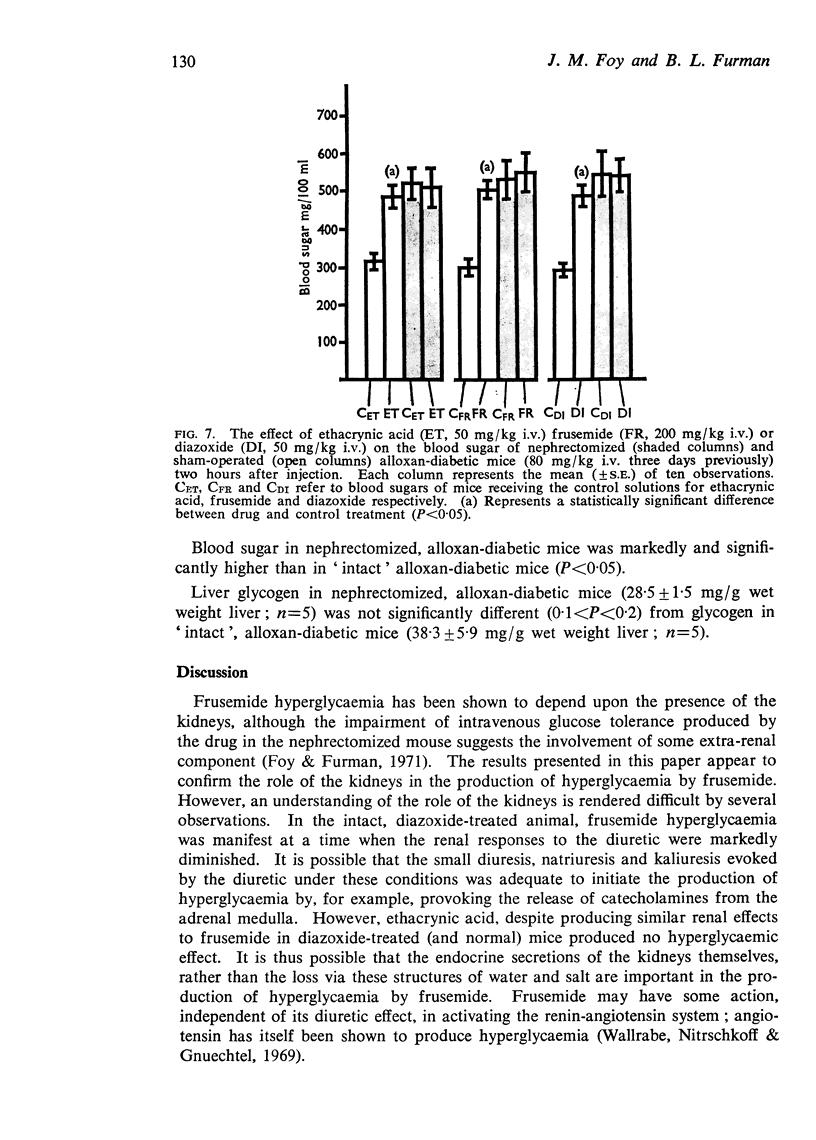
5. Frusemide, ethacrynic acid and diazoxide, but not hydrochlorothiazide, each produced hyperglycaemia in alloxan-diabetic mice, this being prevented by bilateral nephrectomy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DOLLERY C. T., PENTECOST B. L., SAMAAN N. A. Drug-induced diabetes. Lancet. 1962 Oct 13;2(7259):735–737. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy J. M., Furman B. L. Effect of diuretics on mouse blood sugar following single dose administration. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Jun;42(2):287–297. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy J. M., Furman B. L. The effect of fourteen day treatment with diuretics on mouse blood sugar and glucose tolerance. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 May;24(5):390–395. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb09013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslewood G. A., Strookman T. A. A method for the estimation of "true" sugar in 0.05 ml. of blood. Biochem J. 1939 Jun;33(6):920–923. doi: 10.1042/bj0330920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTGOMERY R. Determination glycogen. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Apr;67(2):378–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl J. E., Thurston H. Use of diazoxide in hypertension with renal failure. Br Med J. 1971 Oct 16;4(5780):142–145. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5780.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF F. W., PARMLEY W. W. Actiological factors in benzothiadiazine hyperglycemia. Lancet. 1963 Jul 13;2(7298):69–69. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallrabe D., Nitschkoff S., Gnüchtel U. Untersuchungen über Glukosekonzentrationen im Plasma nach experimentellen Eingriffen in die Blutdruckhomöstase beim Kaninchen. I. Die Wirkung von synthetischem Angiotensin II auf den Blutzuckerspiegel des normotonen und nephrogenen hypertonen Versuchstieres. Dtsch Gesundheitsw. 1969 Nov 20;24(47):2209–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


