Abstract
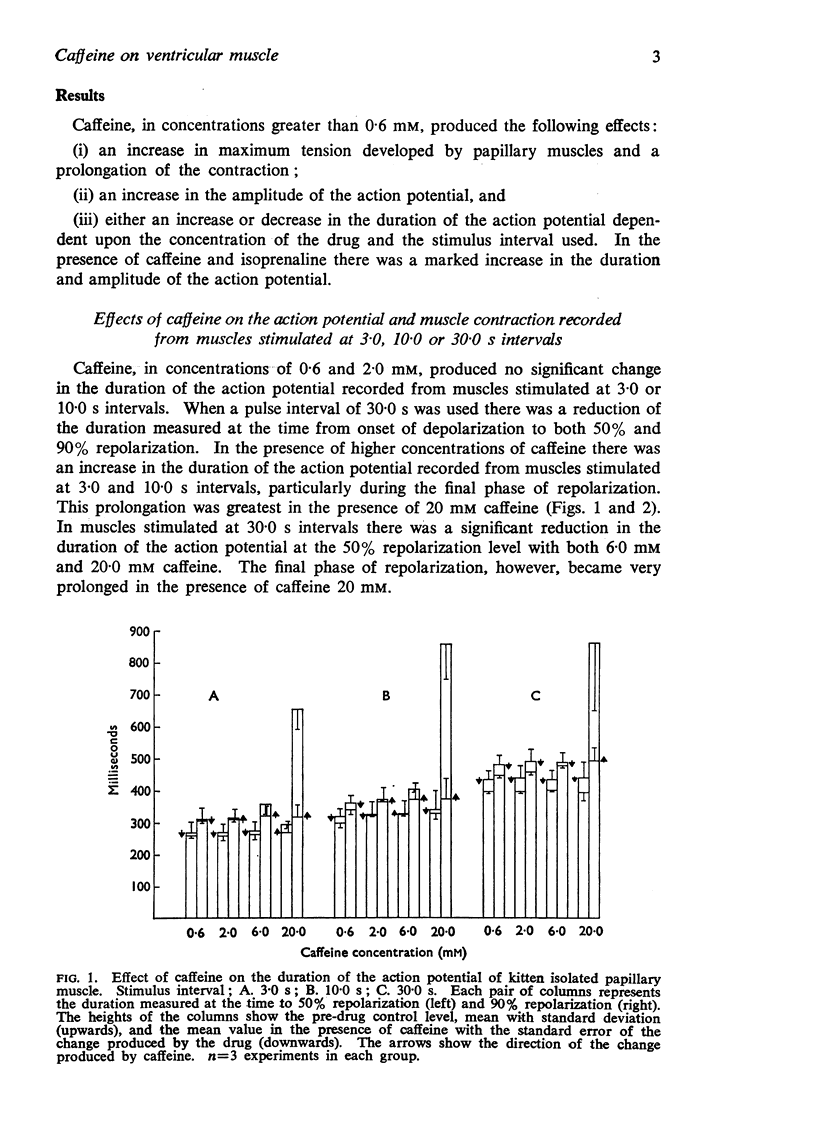
1. Caffeine, 0·6-20·0 mM, altered the duration of the action potential recorded from kitten papillary muscles; low concentrations shortened and high concentrations prolonged the action potential.
2. Caffeine, 20 mM, prolonged the action potential by delaying the final phase of repolarization.
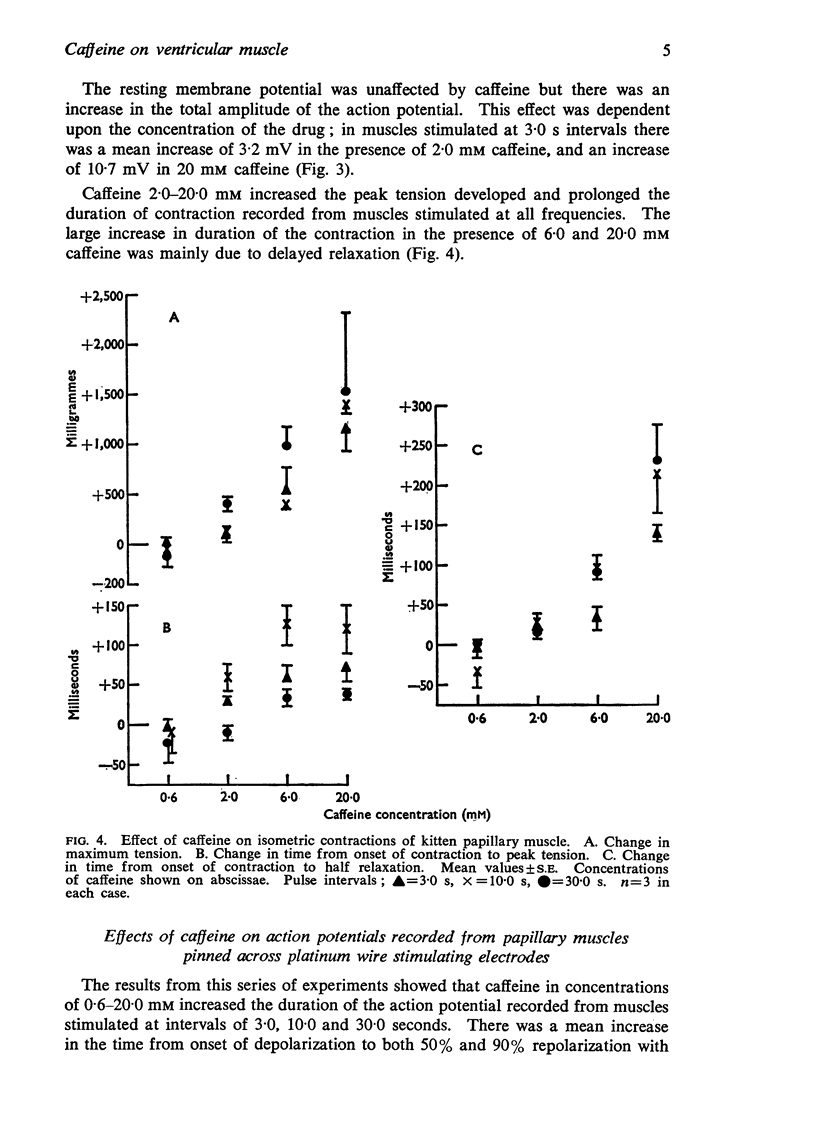
3. Caffeine, 2·0-20·0 mM increased the tension developed and the duration of the isometric contraction.
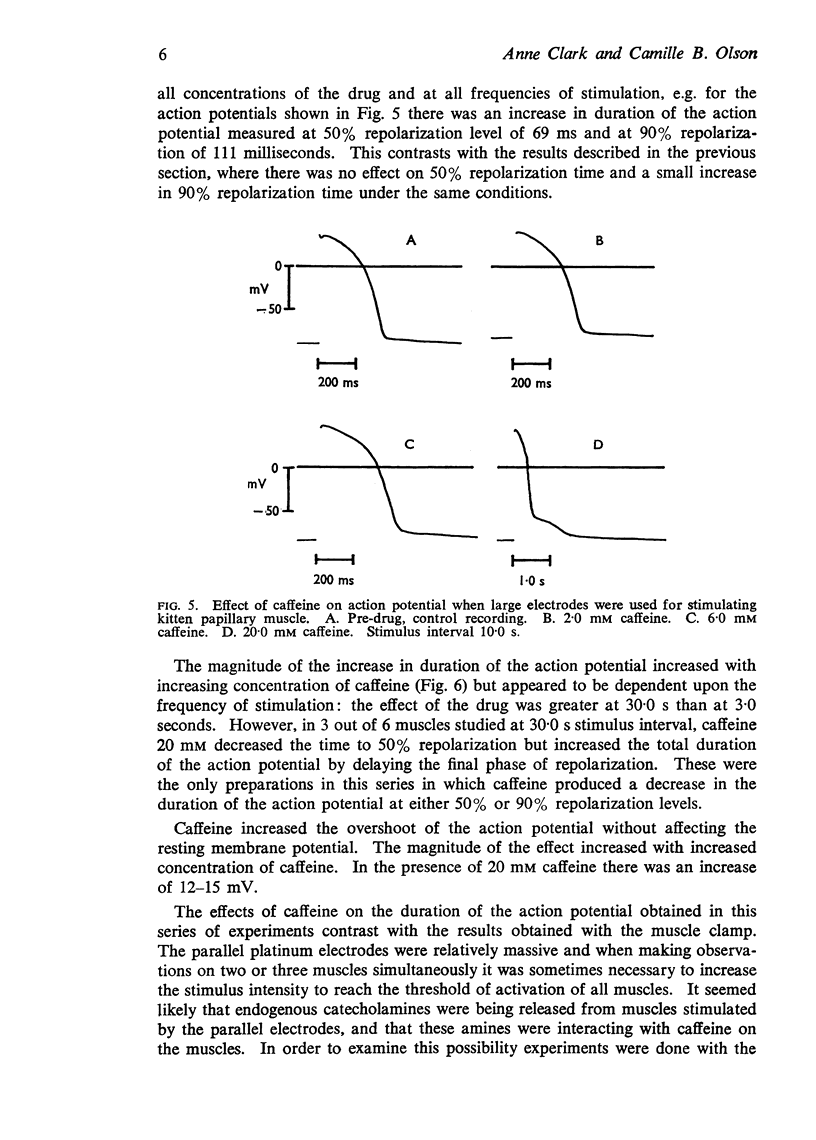
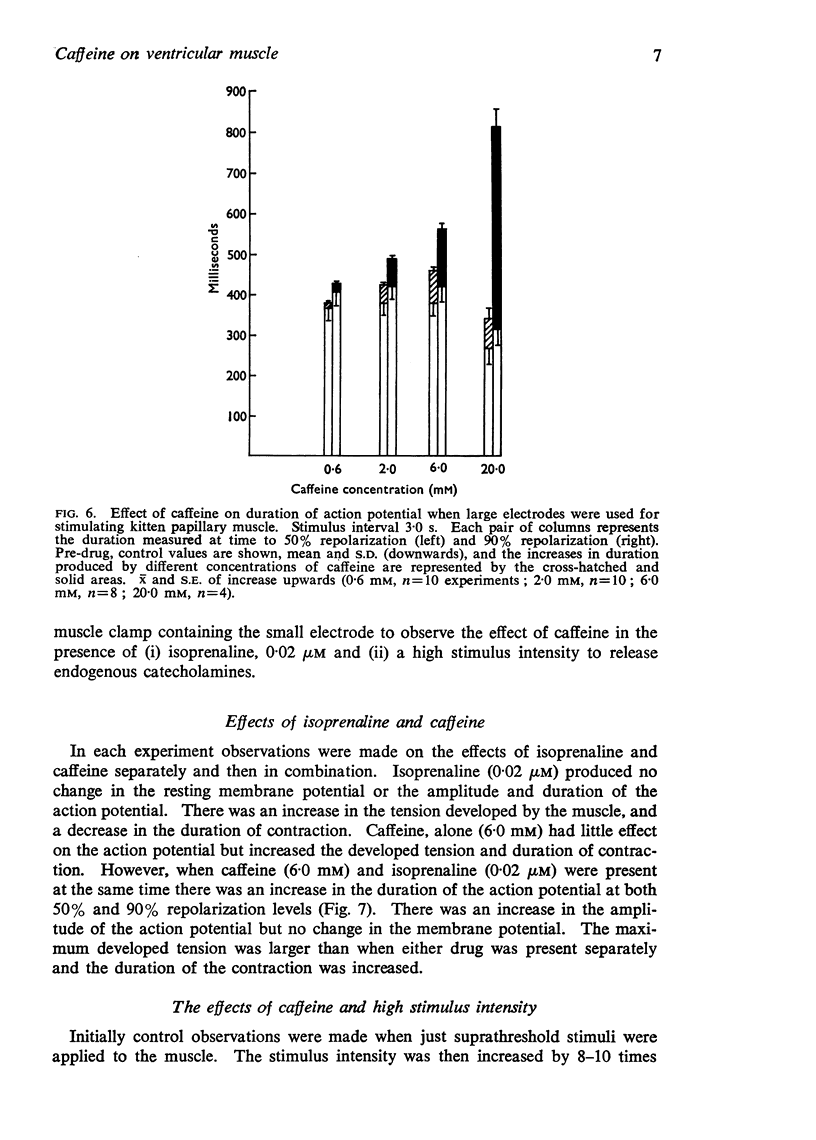
4. When large stimulating electrodes were used, all concentrations of caffeine increased the duration of the action potential; this effect was probably due to the interactions of caffeine and released endogenous catecholamines.
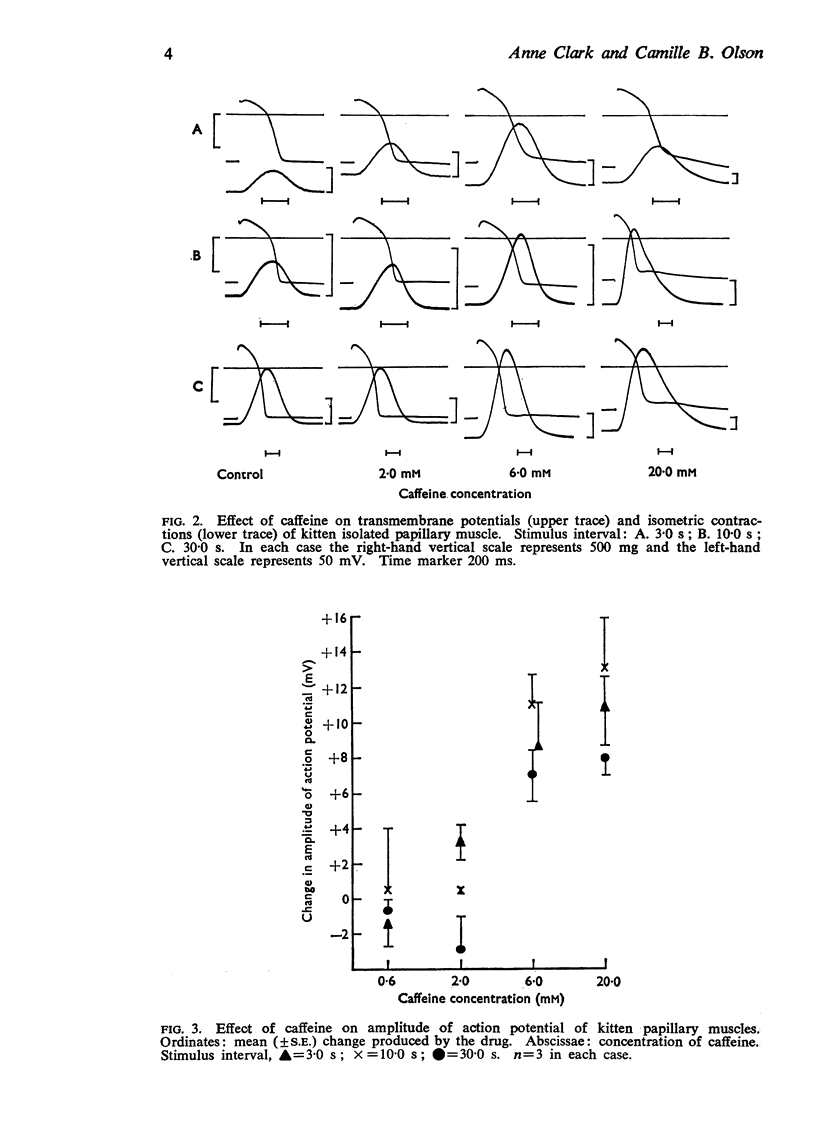
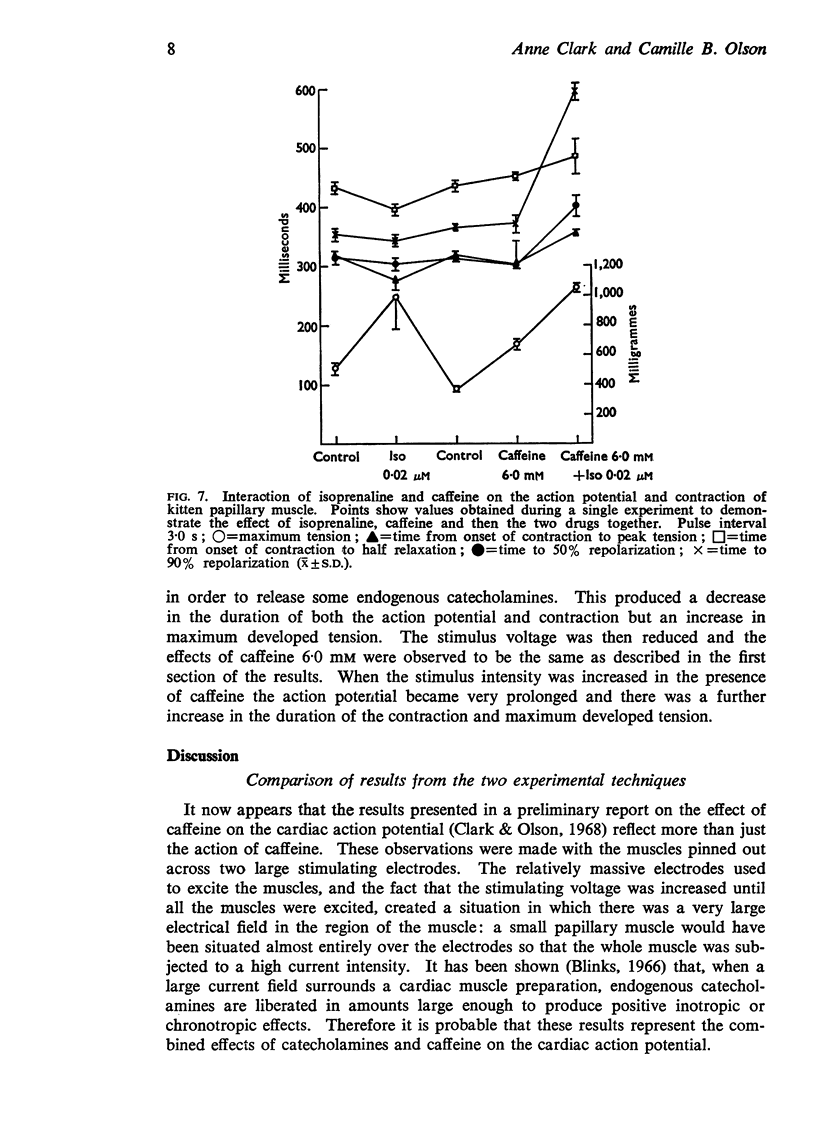
5. Concentrations of caffeine and isoprenaline, which separately caused little change in the duration of the action potential, greatly prolonged the action potential when used together.
6. The effects of caffeine may be due to an increase in membrane calcium current in addition to an action on intracellular calcium stores.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beeler G. W., Jr, Reuter H. Membrane calcium current in ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):191–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., Jr, Reuter H. The relation between membrane potential, membrane currents and activation of contraction in ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):211–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R. Field stimulation as a means of effecting the graded release of autonomic transmitters in isolated heart muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Feb;151(2):221–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Olson C. B., Jewell B. R., Bravený P. Influence of caffeine and other methylxanthines on mechanical properties of isolated mammalian heart muscle. Evidence for a dual mechanism of action. Circ Res. 1972 Apr;30(4):367–392. doi: 10.1161/01.res.30.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmeliet E., Vereecke J. Adrenaline and the plateau phase of the cardiac action potential. Importance of Ca++, Na+ and K+ conductance. Pflugers Arch. 1969;313(4):300–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00593955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEGUBAREFF T., SLEATOR W., Jr EFFECTS OF CAFFEINE ON MAMMALIAN ATRIAL MUSCLE, AND ITS INTERACTION WITH ADENOSINE AND CALCIUM. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 May;148:202–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGER G. A., BRADY A. J. Calcium flux in the mammalian ventricular myocardium. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Mar;46:703–719. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüttgau H. C., Oetliker H. The action of caffeine on the activation of the contractile mechanism in straited muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):51–74. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble D., Tsien R. W. Reconstruction of the repolarization process in cardiac Purkinje fibres based on voltage clamp measurements of membrane current. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):233–254. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RALL T. W., WEST T. C. The potentiation of cardiac inotropic responses to norepinephrine by theophylline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Mar;139:269–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. The dependence of slow inward current in Purkinje fibres on the extracellular calcium-concentration. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):479–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Vassort G., Garnier D., Gargouil Y. M., Coraboeuf E. Existence and role of a slow inward current during the frog atrial action potential. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):91–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00587018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Sep;17(3):265–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. R., Preiser H., Sandow A. Mechanical threshold as a factor in excitation-contraction coupling. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Sep;54(3):352–368. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.3.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassort G., Rougier O., Garnier D., Sauviat M. P., Coraboeuf E., Gargouïl Y. M. Effects of adrenaline on membrane inward currents during the cardiac action potential. Pflugers Arch. 1969;309(1):70–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00592283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber A., Herz R. The relationship between caffeine contracture of intact muscle and the effect of caffeine on reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Nov;52(5):750–759. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.5.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood E. H., Heppner R. L., Weidmann S. Inotropic effects of electric currents. I. Positive and negative effects of constant electric currents or current pulses applied during cardiac action potentials. II. Hypotheses: calcium movements, excitation-contraction coupling and inotropic effects. Circ Res. 1969 Mar;24(3):409–445. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.3.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


