Abstract
1. The effects of various phenylethylamine analogues on the inhibition of 3H-noradrenaline and 3H-dopamine uptake into homogenates of rat hypothalamus and corpus striatum respectively, were examined.
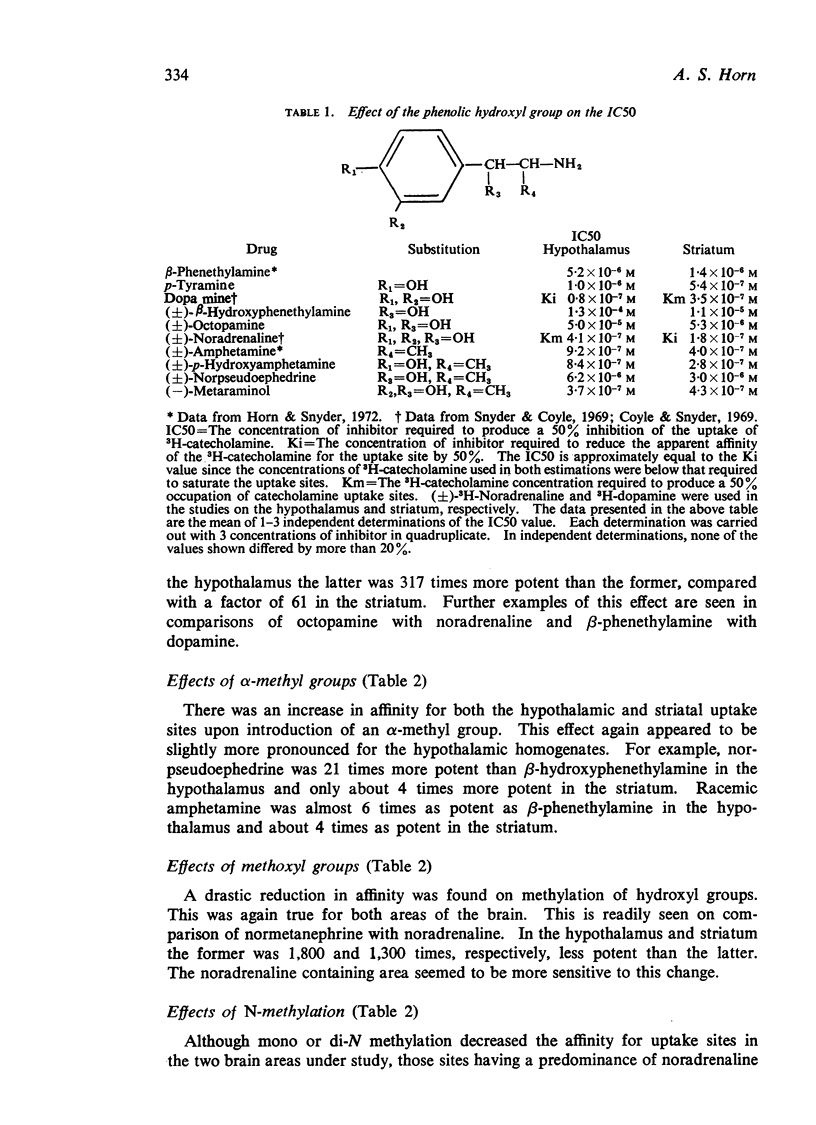
2. Phenolic hydroxyl groups and α-methylation of the side chain were both found to enhance the affinity for the neuronal uptake sites.
3. Methoxylation, β-hydroxylation and N-methylation were all found to reduce the ability of a compound to inhibit catecholamine transport.
4. The noradrenaline and dopamine transport systems responded in a quantitatively different manner to the various phenylethylamine analogues. It was found that, in general, the noradrenaline uptake process was more sensitive to structural changes, both positive and negative, than the dopamine system.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlström D., Bergin R. The structure of the catecholamines. I. The crystal structure of noradrenaline hydrochloride. Acta Crystallogr. 1967 Aug 10;23(2):313–319. doi: 10.1107/s0365110x67002646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Snyder S. H. Catecholamine uptake by synaptosomes in homogenates of rat brain: stereospecificity in different areas. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Dec;170(2):221–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillarp N. A., Fuxe K., Dahlström A. Demonstration and mapping of central neurons containing dopamine, noradrenaline, and 5-hydroxytryptamine and their reactions to psychopharmaca. Pharmacol Rev. 1966 Mar;18(1):727–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn A. S., Coyle J. T., Snyder S. H. Catecholamine uptake by synaptosomes from rat brain. Structure-activity relationships of drugs with differential effects on dopamine and norepinephrine neurons. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;7(1):66–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn A. S., Snyder S. H. Steric requirements for catecholamine uptake by rat brain synaptosomes: studies with rigid analogs of amphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Mar;180(3):523–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L., Jarrott B., Simmonds M. A. Differences in the uptake, storage and metabolism of (+)- and (-)-noradrenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;43(4):845–855. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen L. L. Role of transmitter uptake mechanisms in synaptic neurotransmission. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Apr;41(4):571–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville G. A., Deslauriers R., Blackburn B. J., Smith I. C. Conformational studies of amphetamine and medicinally important derivatives by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Med Chem. 1971 Aug;14(8):717–721. doi: 10.1021/jm00290a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen L., Hoskins R. E., Cable H. The preferred conformation of noradrenaline. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1971 Mar;23(3):216–218. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1971.tb08646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman B., Coubeils J. L., Courrière P., Gervois J. P. Quantum mechanical study of the conformational properties of phenethylamines of biochemical and medicinal interest. J Med Chem. 1972 Jan;15(1):17–23. doi: 10.1021/jm00271a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Coyle J. T. Regional differences in H3-norepinephrine and H3-dopamine uptake into rat brain homogenates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1969 Jan;165(1):78–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



