Abstract
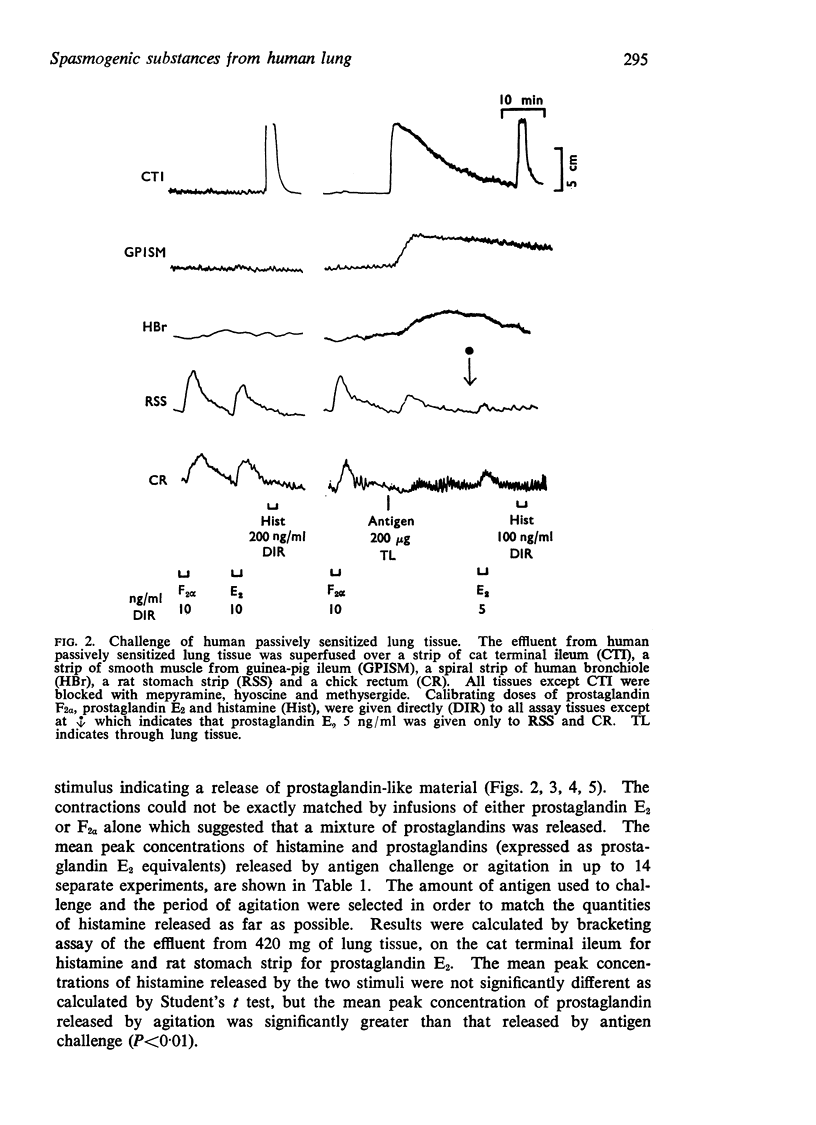
1. Human lung tissue, passively sensitized with reaginic antibodies, released prostaglandins E1, E2 and F2α in addition to histamine and slow reacting substance (SRS-A), when exposed to the appropriate antigen. No rabbit aorta contracting substance (RCS) was detected.
2. Experiments with rats and guinea-pigs showed that the release of RCS is not confined to anaphylactic reactions mediated by non-reaginic antibodies but may be a feature of anaphylaxis in guinea-pigs alone.
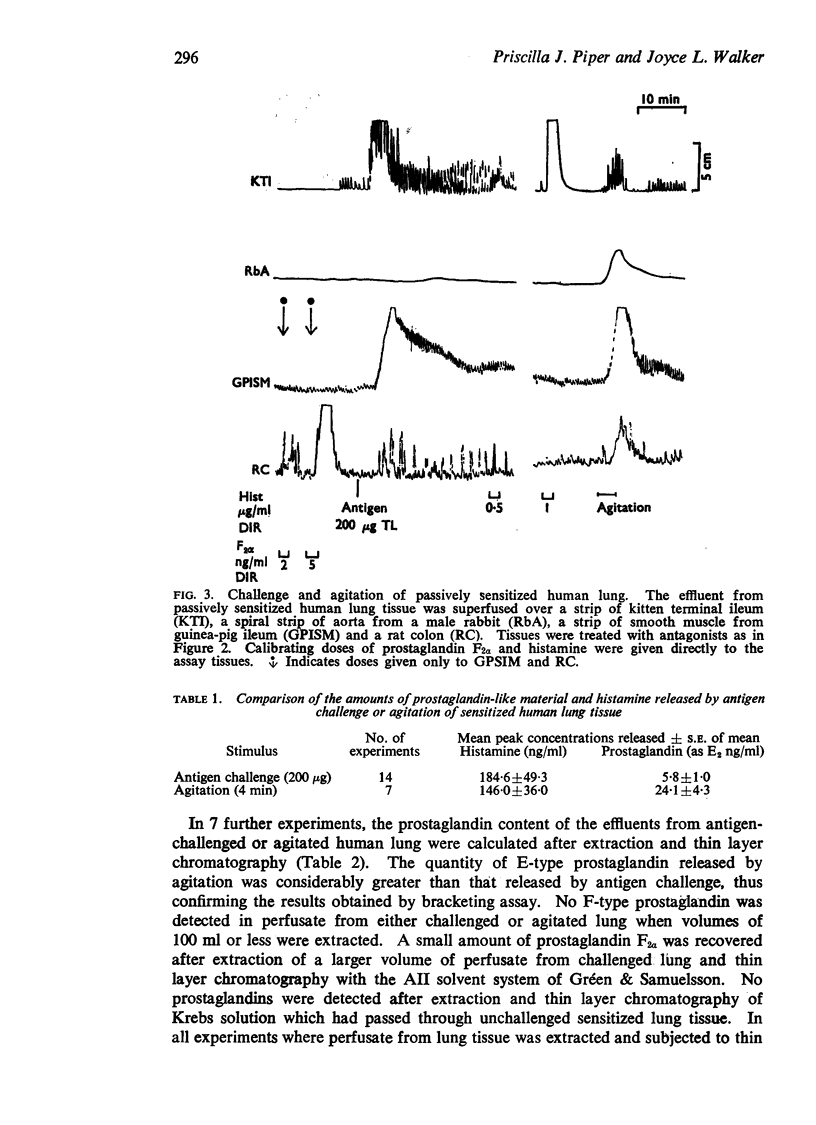
3. Human lung tissue gently agitated with a blunt nylon rod liberated an E-type prostaglandin and RCS in addition to histamine and SRS-A.
4. Human isolated bronchial muscle was contracted by RCS.
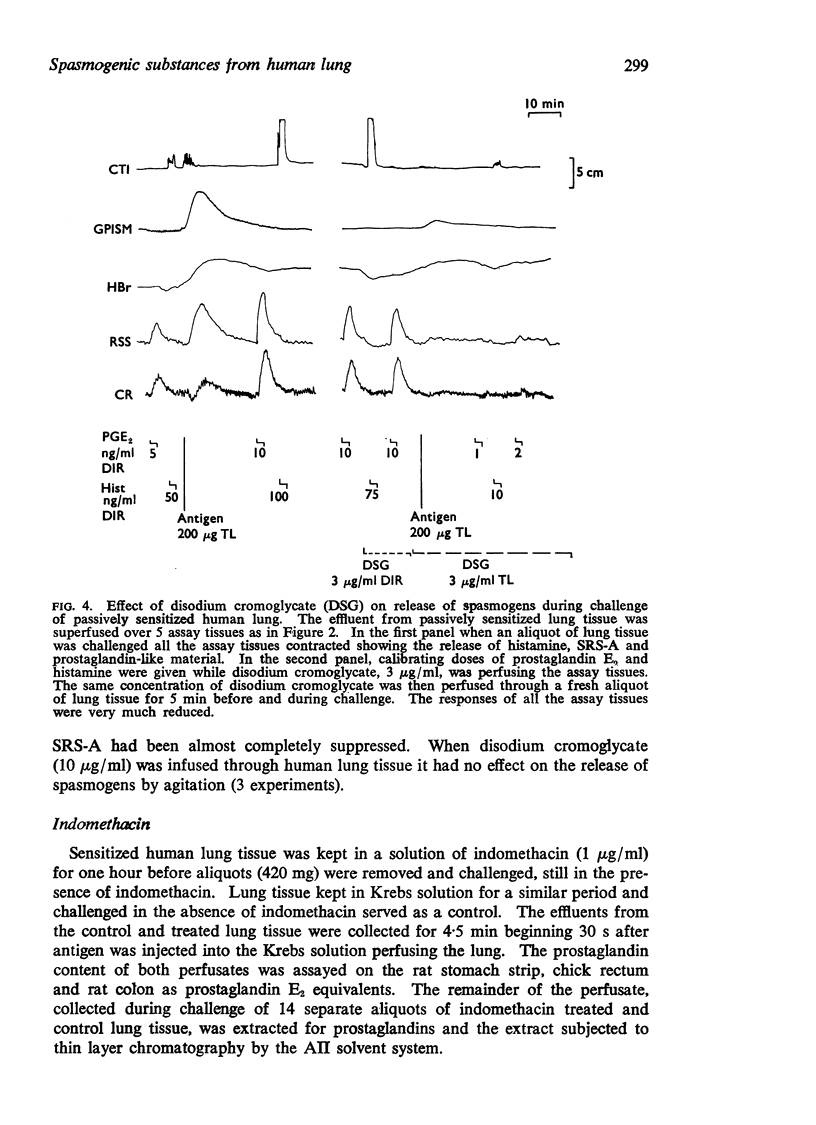
5. Disodium cromoglycate antagonized the release of prostaglandins during anaphylaxis but not during agitation of human lung tissue, whereas indomethacin blocked the release of prostaglandins during agitation and anaphylaxis.
6. The release of an E-type prostaglandin during anaphylaxis in human lung tissue, which inhibits the further release of histamine could be another example of the regulatory role of prostaglandins in body functions.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cuthbert M. F. Effect on airways resistance of prostaglandin E1 given by aerosol to healthy and asthmatic volunteers. Br Med J. 1969 Dec 20;4(5685):723–726. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5685.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS: XIX. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROSTAGLANDINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R., Vane J. R. Rabbit-aorta contracting substance (RCS) may be a prostaglandin precursor. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;43(2):420P–421P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. W. Hypotheses on physiological roles of prostaglandins. Physiol Rev. 1969 Jan;49(1):122–161. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1969.49.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman W. J., Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Prostaglandin inhibition of the immunologic release of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):64–67. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTA I. THE MECHANISM OF ANAPHYLAXIS. I. PRODUCTION AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF 'MAST CELL SENSITIZING' ANTIBODY. Immunology. 1964 Nov;7:681–699. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGILVIE B. M. REAGIN-LIKE ANTIBODIES IN ANIMALS IMMUNE TO HELMINTH PARASITES. Nature. 1964 Oct 3;204:91–92. doi: 10.1038/204091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., BENACERRAF B., BLOCH K. J. Properties of guinea pig 7S antibodies. II. Identification of antibodies involved in passive cutaneous and systemic anaphylaxis. J Exp Med. 1963 Jun 1;117:951–964. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.6.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer M. A., Piper P. J., Vane J. R. The release of rabbit aorta contracting substance (RCS) from chopped lung and its antagonism by anti-inflammatory drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;40(3):581P–582P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P. J., Vane J. R. Release of additional factors in anaphylaxis and its antagonism by anti-inflammatory drugs. Nature. 1969 Jul 5;223(5201):29–35. doi: 10.1038/223029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P., Vane J. The release of prostaglandins from lung and other tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Apr 30;180:363–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb53205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANG H. P. STIMULANT ACTIONS OF VOLATILE ANAESTHETICS ON SMOOTH MUSCLE. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Apr;22:356–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard P., Blair A. M. Disodium cromoglycate. Activity in three in vitro models of the immediate hypersensitivity reaction in lung. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(2):217–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard P., Killingback P. G., Blair A. M. Antigen induced release of histamine and SRS-A from human lung passively sensitized with reaginic serum. Nature. 1967 Oct 21;216(5112):283–284. doi: 10.1038/216283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P., Cuthbert M. F. Antagonistic Action of Aerosols of Prostaglandins F(2)alpha and E(2) on Bronchial Muscle Tone in Man. Br Med J. 1972 Jul 22;3(5820):212–213. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5820.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweatman W. J., Collier H. O. Effects of prostaglandins on human bronchial muscle. Nature. 1968 Jan 6;217(5123):69–69. doi: 10.1038/217069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):232–235. doi: 10.1038/newbio231232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


