Abstract
1. The role of ejecting and retaining currents in determining the kinetics of the release of [14C]-noradrenaline (NA) from micropipettes of the type used in microelectrophoresis experiments has been investigated by the liquid scintillation counting technique.
2. In the absence of any electrophoretic current a constant rate of release of NA was established.
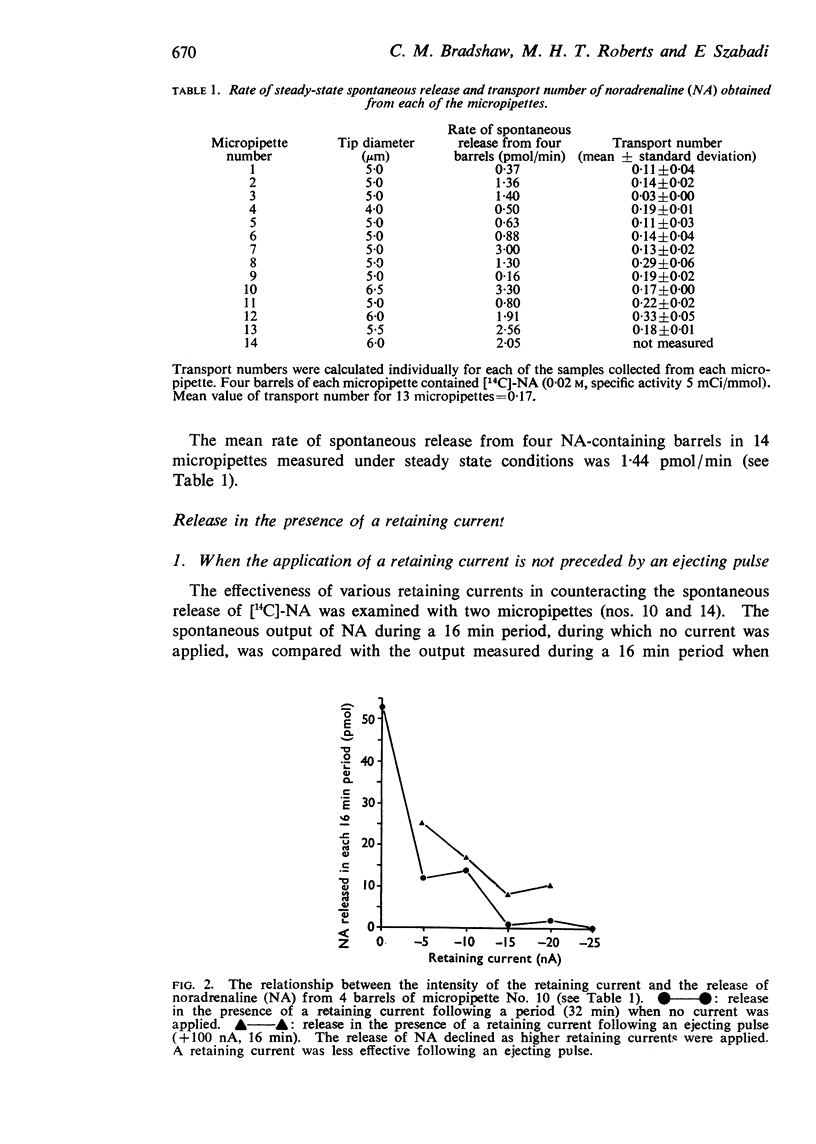
3. All retaining currents examined gradually reduced the spontaneous release to zero. Higher retaining currents abolished spontaneous release more quickly.
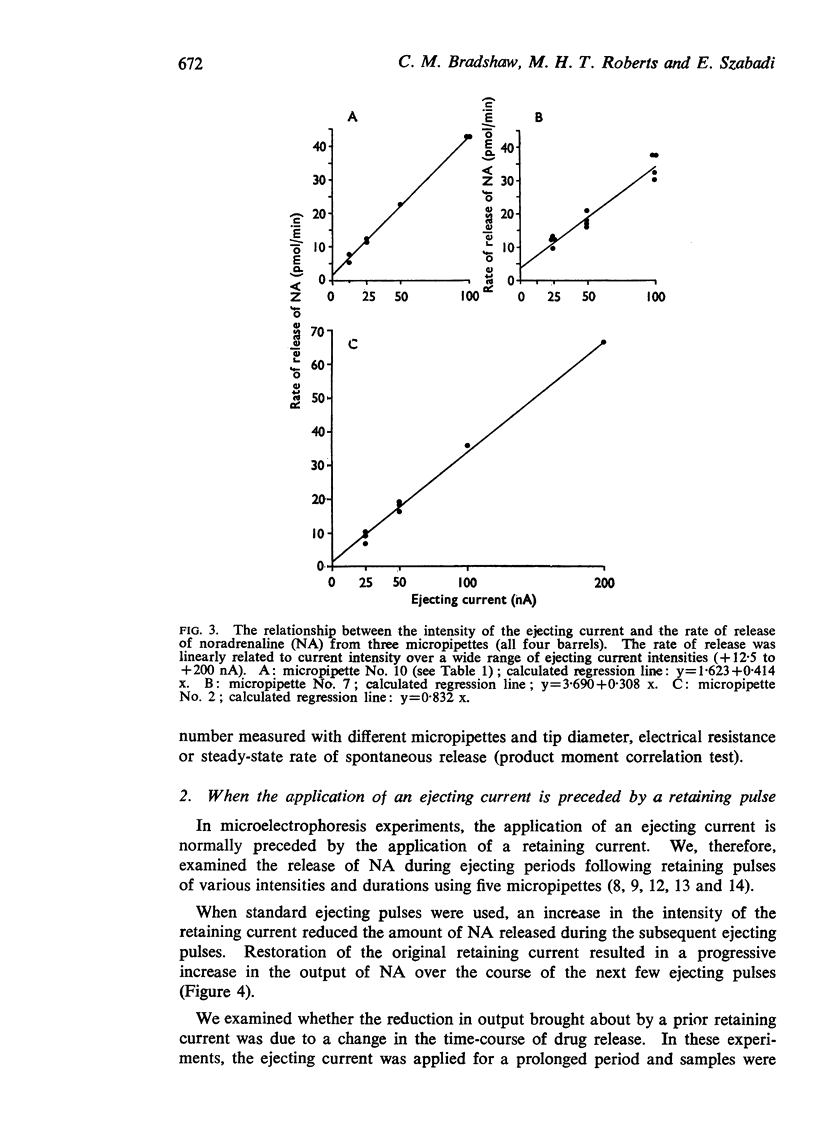
4. A linear relationship was identified between the rate of electrophoretic release of NA and the intensity of the ejecting current. The mean transport number of NA was found to be 0·17.
5. All retaining currents studied reduced the amount of NA released during a subsequent application of an ejecting current. This was due to a prolongation of the time necessary to establish a steady-state rate of release. The magnitude of this effect was related to both the intensity and the duration of application of the retaining current.
6. The results are discussed in terms of a theoretical model of ion movements within the tip of the micropipette.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley P. B., Candy J. M. Iontophoretic release of acetylcholine, noradrenaline, 5-hydroxytryptamine and D-lysergic acid diethylamide from micropipettes. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;40(2):194–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw C. M., Szabadi E., Roberts M. H. The reflection of ejecting and retaining currents in the time-course of neuronal responses to microelectrophoretically applied drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;25(7):513–520. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb09150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PERRIN D. D., WATKINS J. C. The excitation of spinal neurones by the ionophoretic application of agents which chelate calcium. J Neurochem. 1960 Aug;6:1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1960.tb13443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis D. R., Duggan A. W., Johnston G. A. The specificity of strychnine as a glycine antagonist in the mammalian spinal cord. Exp Brain Res. 1971 Jun 29;12(5):547–565. doi: 10.1007/BF00234248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO L., KATZ B. A study of curare action with an electrical micromethod. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):339–356. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H., Werman R. The effects of strychnine on the inhibition of interneurons by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Mar;8(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERZ A., WICKELMAIER M., NACIMIENTO A. UBER DIE HERSTELLUNG VON MEHRFACHELEKTRODEN FUER DIE MIKROELEKTROPHORESE. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 May 10;284:95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffer B. J., Neff N. H., Siggins G. R. Microiontophoretic release of norepinephrine from micropipettes. Neuropharmacology. 1971 Mar;10(21):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(71)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. Amino-acid induced depression of cortical neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;38(4):659–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb09875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., LAVERTY R., SHARMAN D. F. Iontophoretic release of adrenaline, noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine from micropipettes. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Jun;20:491–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offerman J. L., Merrills R. J. The purification of tritiated noradrenaline. Experientia. 1968 Nov 15;24(11):1182–1183. doi: 10.1007/BF02147841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. Excitation and depression of cortical neurones by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):269–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


