Abstract
1 The effects on tryptophan distribution and metabolism of drugs altering plasma unesterified fatty acid (UFA) concentration were investigated in the rat.
2 UFA and plasma free (i.e. ultrafilterable) tryptophan altered in the same direction.
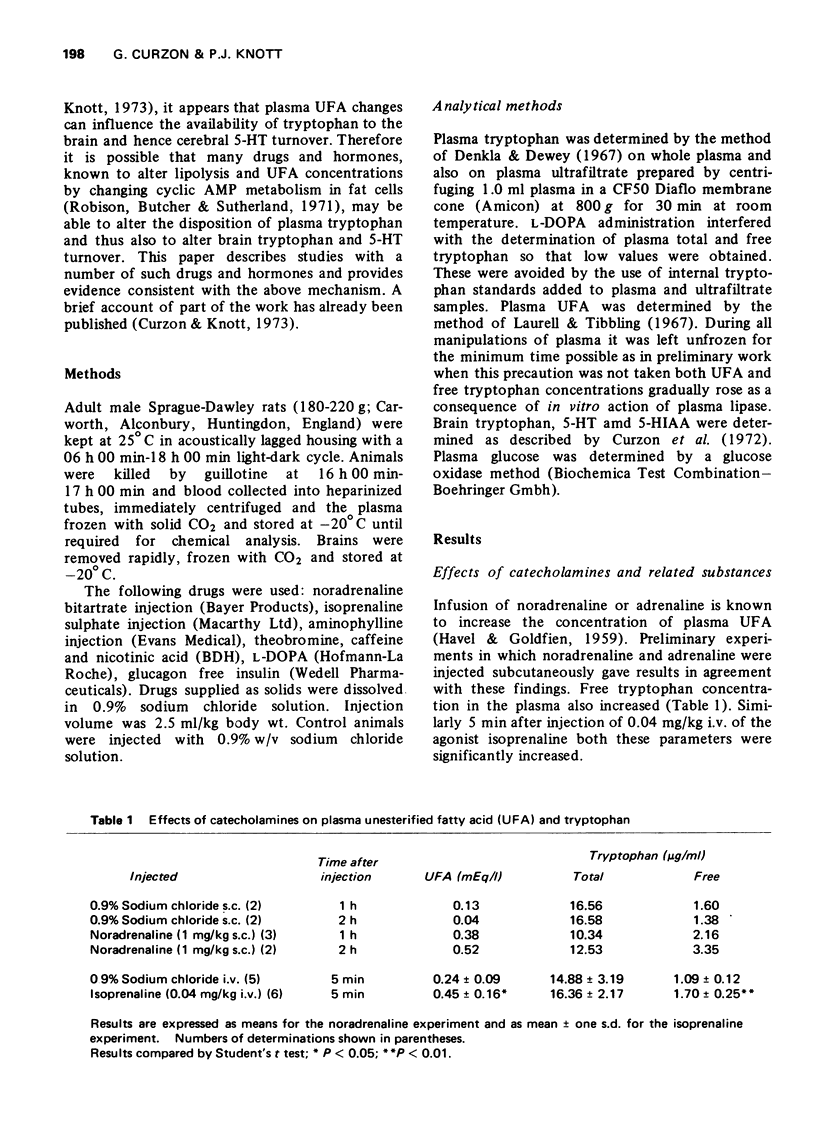
3 Catecholamines and L-DOPA increased both plasma UFA and free tryptophan. L-DOPA also increased brain tryptophan and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) but decreased brain 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT).
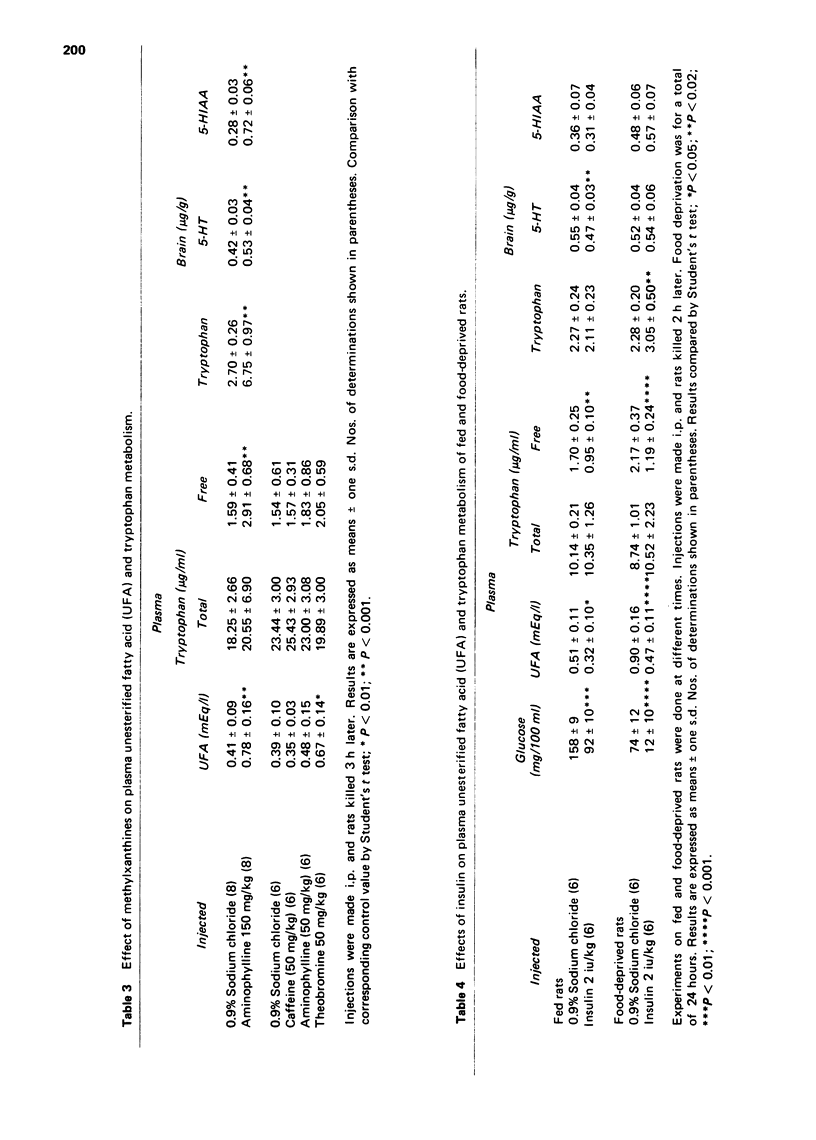
4 Aminophylline increased plasma UFA and free tryptophan and also brain tryptophan, 5-HT and 5-HIAA. Food deprivation had qualitatively similar effects.
5 Insulin decreased plasma UFA and free tryptophan in both fed and food-deprived rats. However, while in fed rats these changes were associated with small decreases of brain indoles, in food-deprived animals small increases occurred.
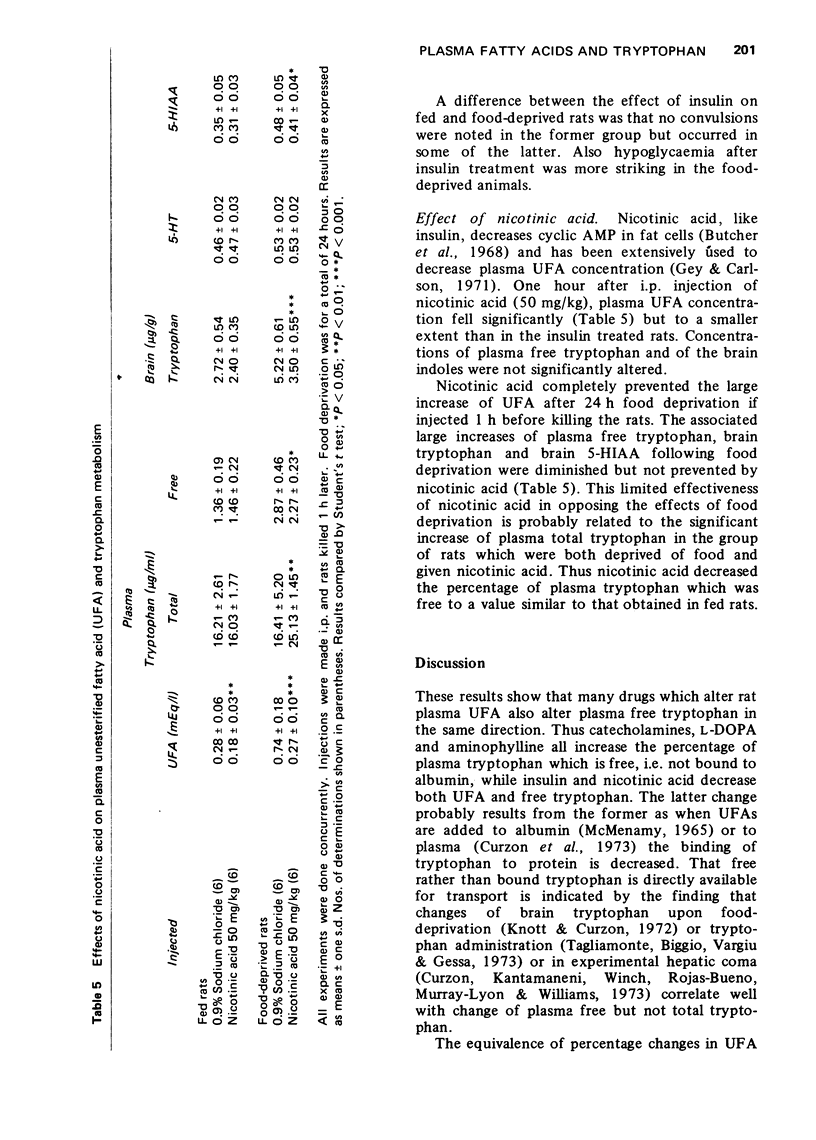
6 Nicotinic acid had only small effects in fed rats but it opposed both the UFA and indole changes in food-deprived animals. Total plasma tryptophan increased in nicotinic acid treated, food-deprived rats.
7 There was a tendency towards inverse relations between changes of plasma free and total tryptophan.
8 The results suggest that drugs which influence plasma UFA through actions on cyclic AMP thereby alter the binding of tryptophan to plasma protein and that this leads to altered distribution and metabolism of tryptophan.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aghajanian G. K. Influence of drugs on the firing of serotonin-containing neurons in brain. Fed Proc. 1972 Jan-Feb;31(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellet S., Kershbaum A., Finck E. M. Response of free fatty acids to coffee and caffeine. Metabolism. 1968 Aug;17(8):702–707. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(68)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz B. A., Spector S. The effect of caffeine and theophylline on the disposition of brain serotonin in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Nov-Dec;16(3):322–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher R. W., Baird C. E., Sutherland E. W. Effects of lipolytic and antilipolytic substances on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in isolated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1705–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher R. W., Ho R. J., Meng H. C., Sutherland E. W. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in biological materials. II. The measurement of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in tissues and the role of the cyclic nucleotide in the lipolytic response of fat to epinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4515–4523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrodi H., Fuxe K., Jonsson G. Effects of caffeine on central monoamine neurons. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Feb;24(2):155–158. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08952.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Friedel J., Knott P. J. The effect of fatty acids on the binding of tryptophan to plasma protein. Nature. 1973 Mar 16;242(5394):198–200. doi: 10.1038/242198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Green A. R. Regional and subcellular changes in the concentration of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in the rat brain caused by hydrocortisone, DL- -methyl-tryptophan l-kynurenine and immobilization. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Sep;43(1):39–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Joseph M. H., Knott P. J. Effects of immobilization and food deprivation on rat brain tryptophan metabolism. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1967–1974. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Kantamaneni B. D., Winch J., Rojas-Bueno A., Murray-Lyon I. M., Williams R. Plasma and brain tryptophan changes in experimental acute hepatic failure. J Neurochem. 1973 Jul;21(1):137–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb04233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Knott P. J. Drugs influencing plasma and brain tryptophan. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Jun;48(2):352P–353P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denckla W. D., Dewey H. K. The determination of tryptophan in plasma, liver, and urine. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):160–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston D., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B. 5-hydroxyindole metabolism in rat brain. A study of intermediate metabolism using the technique of tryptophan loading. II. Applications and drug studies. J Neurochem. 1965 Jun;12(6):493–503. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1965.tb06776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Brain serotonin content: increase following ingestion of carbohydrate diet. Science. 1971 Dec 3;174(4013):1023–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4013.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom J. D., Wurtman R. J. Brain serotonin content: physiological regulation by plasma neutral amino acids. Science. 1972 Oct 27;178(4059):414–416. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4059.414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom J. D., Wurtmen R. J. Elevation of plasma tryptophan by insulin in rat. Metabolism. 1972 Apr;21(4):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Kappelman A. H., Kaufman S. Partial purification and characterization of tryptophan hydroxylase from rabbit hindbrain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4165–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame-Smith D. G. Studies in vivo on the relationship between brain tryptophan, brain 5-HT synthesis and hyperactivity in rats treated with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor and L-tryptophan. J Neurochem. 1971 Jun;18(6):1053–1066. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott P. J., Joseph M. H., Curzon G. Effects of food deprivation and immobilization on tryptophan and other amino acids in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):249–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell S., Tibbling G. Colorimetric micro-determination of free fatty acids in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1967 Apr;16(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(67)90269-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsett D., Madras B. K., Wurtman R. J., Munro H. N. Serum tryptophan level after carbohydrate ingestion: selective decline in non-albumin-bound tryptophan coincident with reduction in serum free fatty acids. Life Sci II. 1973 Jan 22;12(2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. Y., Chase T. N., Colburn R. W., Kopin I. J. L-Dopa-induced release of cerebral monoamines. Science. 1970 Oct 2;170(3953):76–77. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3953.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1629–1639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Calimlim L., Bianchine J. R. Effect of L-dopa on plasma free fatty acids and plasma glucose. Metabolism. 1972 Jul;21(7):611–617. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90085-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliamonte A., Biggio G., Vargiu L., Gessa G. L. Free tryptophan in serum controls brain tryptophan level and serotonin synthesis. Life Sci II. 1973 Mar 22;12(6):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90361-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliamonte A., Tagliamonte P., Forn J., Perez-Cruet J., Krishna G., Gessa G. L. Stimulation of brain serotonin synthesis by dibutyryl-cyclic AMP in rats. J Neurochem. 1971 Jul;18(7):1191–1196. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B. F., Munro H. N., Wurtman R. J. L-dopa: disaggregation of brain polysomes and elevation of brain tryptophan. Science. 1971 Aug 27;173(3999):833–835. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3999.833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. Y., Rosenthal H. L. Induction of tryptophan pyrrolase activity in starving rabbits of different ages. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jun;122(2):414–417. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


