Abstract
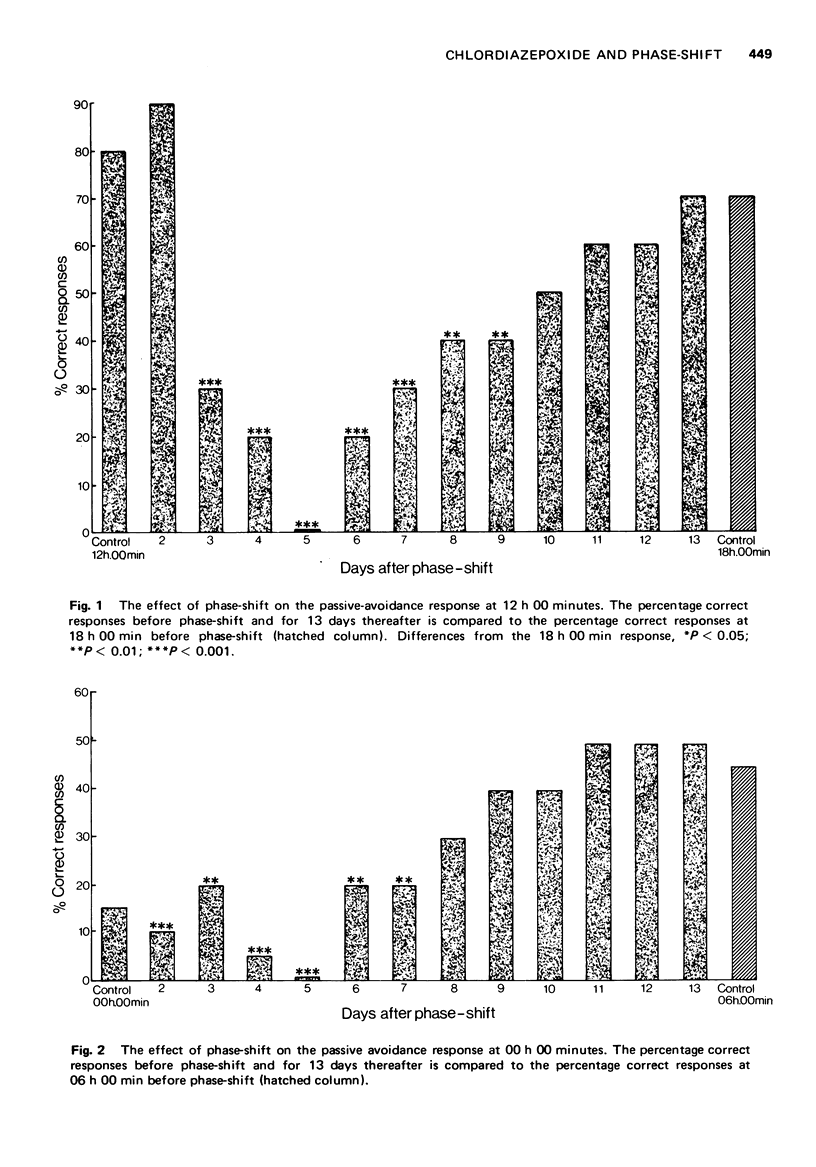
1 In rats trained to a 12 h light-12 h dark cycle, advancing the phase by 6 h produced a resynchronization of the 24 h variation in passive avoidance response (PAR) which was completed after 10 days.
2 The attainment of the new steady state was preceded by a period of disruption which was greatest 5 days after phase-shift.
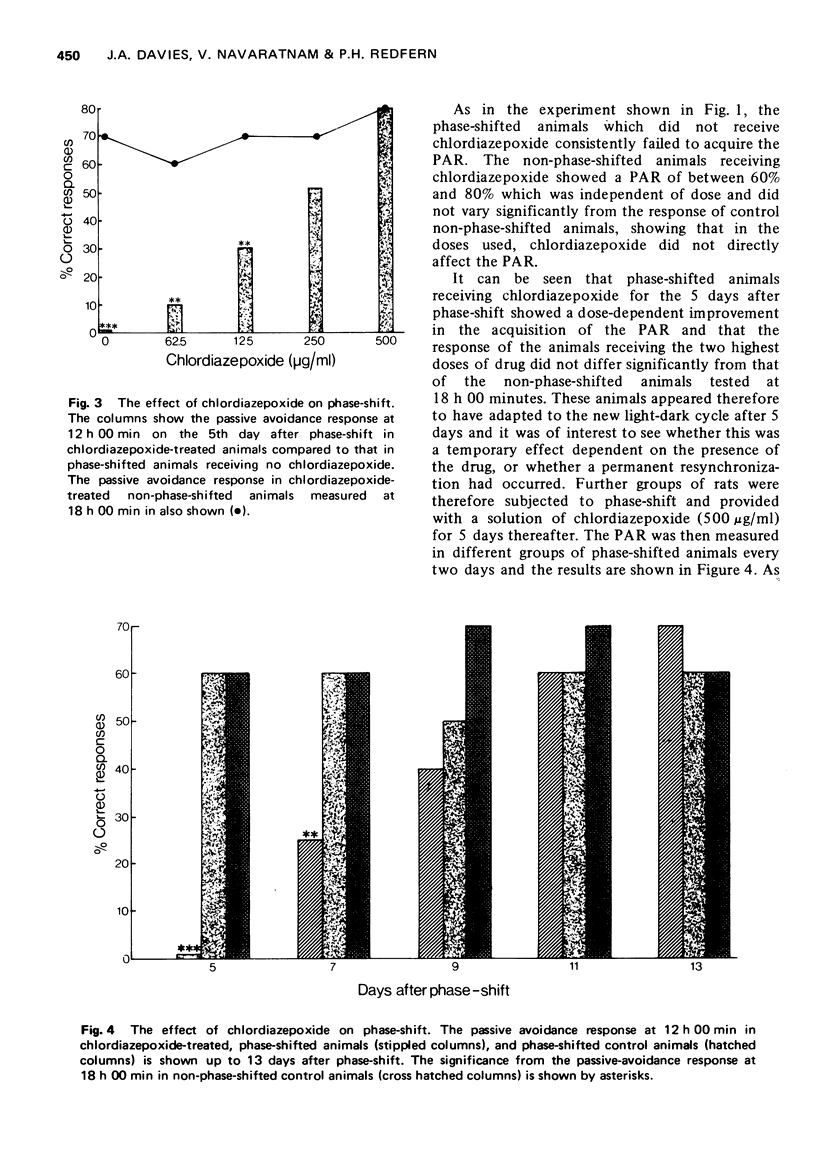
3 The presence of chlordiazepoxide (62.5-500 μg/ml) in the drinking water during the days after phase-shift produced a dose-dependent lessening of the disruptive effect of phase-shift, and a more rapid adaptation to the new light-dark cycle.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURESOVA O., BURES J., BOHDANECKY Z., WEISS T. EFFECT OF ATROPINE ON LEARNING, EXTINCTION, RETENTION AND RETRIEVAL IN RATS. Psychopharmacologia. 1964 Mar 11;5:255–263. doi: 10.1007/BF02341258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy R. T. Time zone transitions and business executives. Trans Soc Occup Med. 1971 Jul;21(3):69–72. doi: 10.1093/occmed/21.3.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein W., Schaffler K., Müller-Limmroth W. Die Wirkung von Oxazepam auf den gestörten Tagschlaf nach Nachtschichtarbeit. Arzneimittelforschung. 1972 Feb;22(2):421–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale H. B., Hartman B. O., Harris D. A., Williams E. W., Miranda R. E., Hosenfeld J. M. Time zone entrainment and flight stressors as interactants. Aerosp Med. 1972 Oct;43(10):1089–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauty G. T., Adams T. Phase shifts of the human circadian system and performance deficit during the periods of transition. II. West-East flight. Aerosp Med. 1966 Oct;37(10):1027–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauty G. T., Adams T. Phase shifts of the human circadian system and performance deficit during the periods of transition: I. East-west flight. Aerosp Med. 1966 Jul;37(7):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway F. A., Wansley R. Multiphasic retention deficits at periodic intervals after passive-avoidance learning. Science. 1973 Apr 15;180(4082):208–210. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4082.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein K. E., Brüner H., Holtmann H., Rehme H., Stolze J., Steinhoff W. D., Wegmann H. M. Circadian rhythm of pilots' efficiency and effects of multiple time zone travel. Aerosp Med. 1970 Feb;41(2):125–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein K. E., Wegmann H. M., Hunt B. I. Desynchronization of body temperature and performance circadian rhythm as a result of outgoing and homegoing transmeridian flights. Aerosp Med. 1972 Feb;43(2):119–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITTENDRIGH C. S. Circadian rhythms and the circadian organization of living systems. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1960;25:159–184. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1960.025.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman E. D., Kripke D. F., Goldmacher D., McGregor P., Nogeire C. Acute reversal of the sleep-waking cycle in man. Effect on sleep stage patterns. Arch Neurol. 1970 Jun;22(6):483–489. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480240003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


