Abstract
1 The effects of α- and β-adrenoceptor stimulants on the histamine-forming capacity (HFC) of human isolated leucocytes have been studied, in vitro.
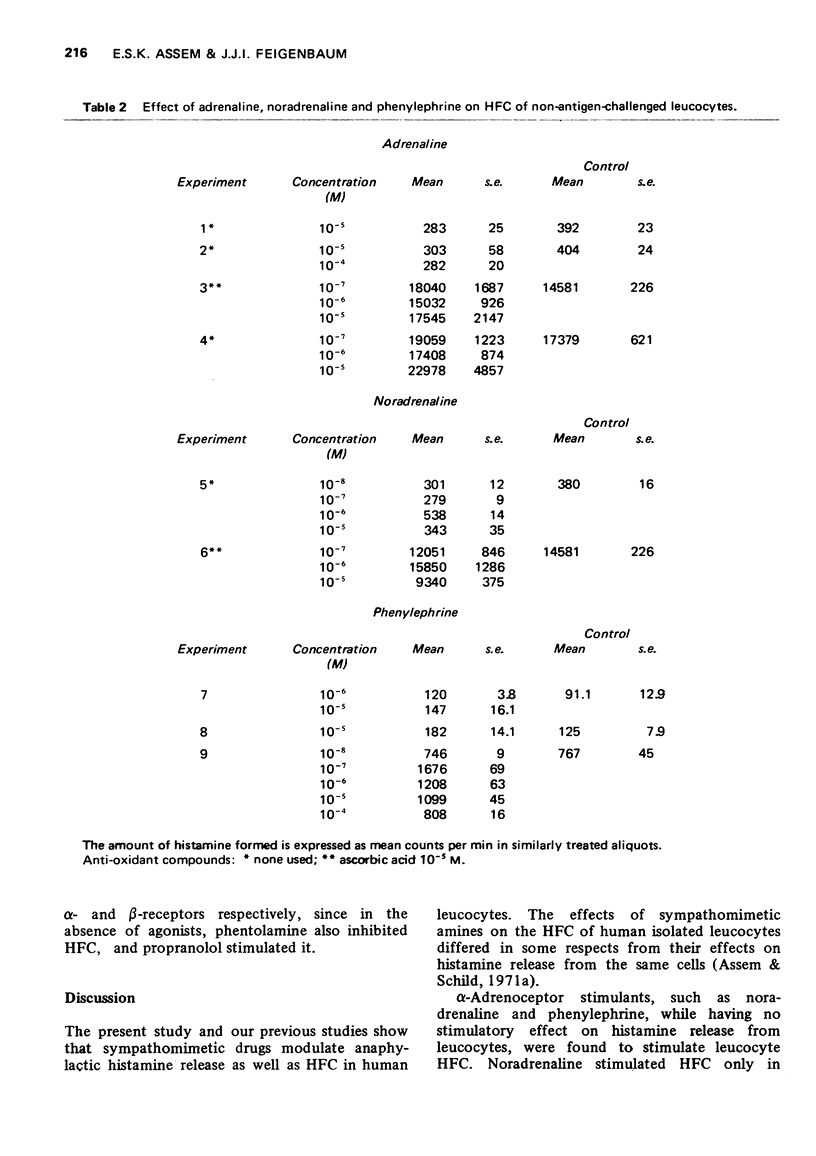
2 It was confirmed that antigen significantly stimulates the HFC of human leucocytes.
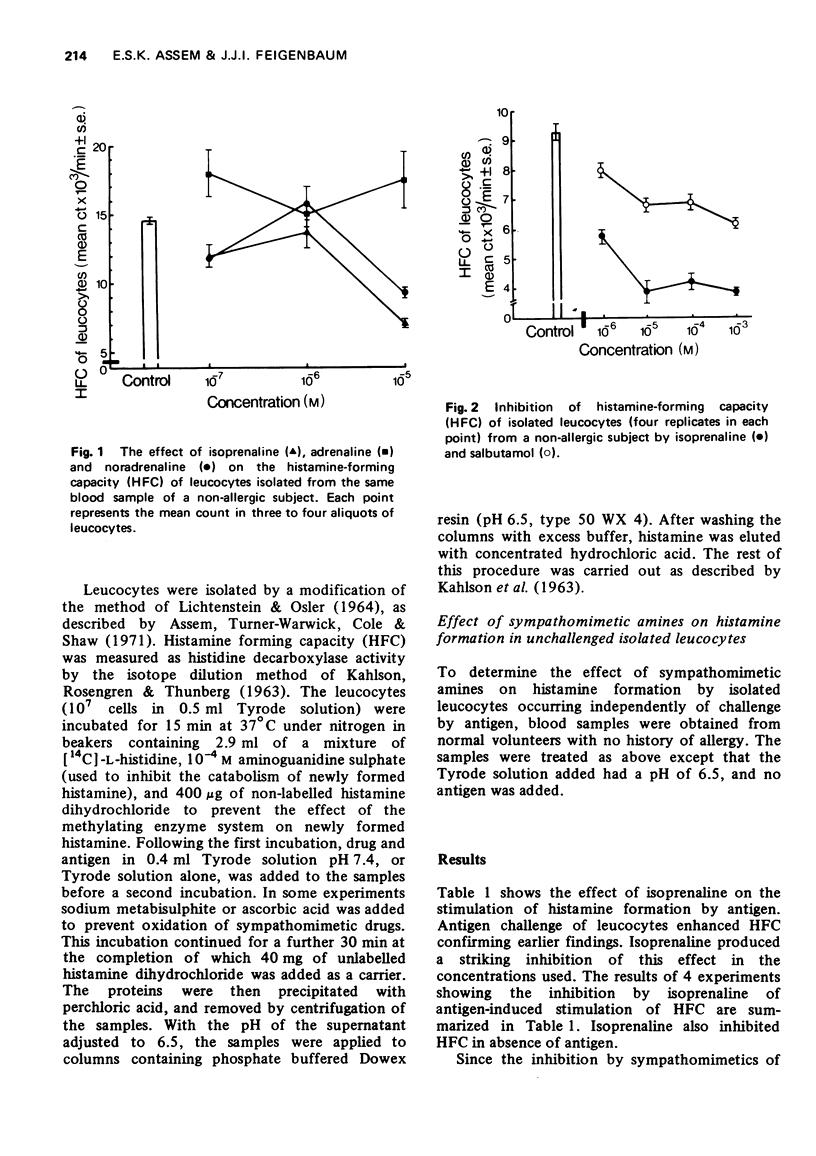
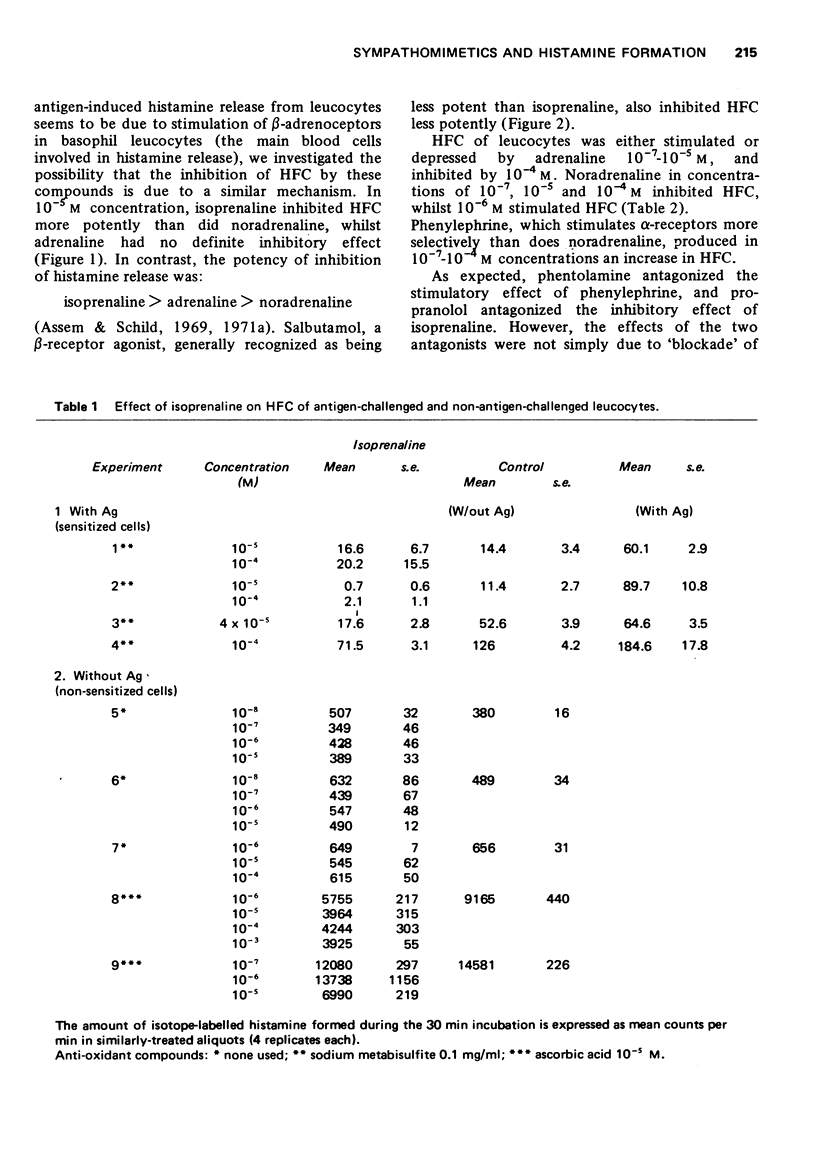
3 β-Adrenoceptor stimulants, such as isoprenaline and salbutamol (10-6-10-3 M) significantly inhibited the HFC of human leucocytes in the presence and absence of antigen. At concentrations lower than 10-6 M, this effect was not observed. In general the degree of inhibition of HFC by β-adrenoceptor stimulants followed their potency as β-adrenoceptor stimulants.
4 α-Adrenoceptor stimulants significantly stimulated leucocyte HFC; noradrenaline within a limited concentration of 10-6 M, while stimulation was seen consistently with phenylephrine at concentrations of 10-7-10-4 M. Adrenaline, which stimulates both α- and β-adrenoceptors, produced small inhibition, no effect, or a degree of stimulation.
5 Phentolamine, an α-adrenoceptor blocking agent, produced an effect opposite to that of the α-adrenoceptor stimulants, i.e. a significant inhibition of the HFC of human isolated leucocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alston W. C., Patel K. R., Kerr J. W. Response of leucocyte adenyl cyclase to isoprenaline and effect of alpha-blocking drugs in extrinsic bronchial asthma. Br Med J. 1974 Jan 19;1(5898):90–93. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5898.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assem E. S., Feigenbaum J. J. Effect of adrenergic drugs on histamine forming capacity of human leucocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;46(3):519P–520P. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb08152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assem E. S., Schild H. O. Antagonism by beta-adrenoceptor blocking agents of the antianaphylactic effect of isoprenaline. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Aug;42(4):620–630. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07146.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assem E. S., Schild H. O. Inhibition by sympathomimetic amines of histamine release by antigen in passively sensitized human lung. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):1028–1029. doi: 10.1038/2241028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assem E. S., Schild H. O. Inhibition of the anaphylactic mechanism by sympathomimetic amines. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(4-5):576–589. doi: 10.1159/000230439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assem E. S., Schild H. O., Vickers M. R. Stimulation of histamine-forming capacity by antigen in sensitized human leucocytes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1972;42(3):343–352. doi: 10.1159/000230617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assem E. S., Turner-Warwick M., Cole P., Shaw K. M. Reversed anaphylactic reaction of leucocytes in intrinsic asthma. Clin Allergy. 1971 Dec;1(4):353–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1971.tb00786.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHLSON G., ROSENGREN E., THUNBERG R. OBSERVATIONS ON THE INHIBITION OF HISTAMINE FORMATION. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:467–486. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooman W. J., Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Immunochemical and biologic properties of rat IgE. 3. Modulation of the IgE-mediated release of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis by agents influencing the level of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monoposphate. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1096–1102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN L. M., OSLER A. G. STUDIES ON THE MECHANISMS OF HYPERSENSITIVITY PHENOMENA. IX. HISTAMINE RELEASE FROM HUMAN LEUKOCYTES BY RAGWEED POLLEN ANTIGEN. J Exp Med. 1964 Oct 1;120:507–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.4.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Margolis S. Histamine release in vitro: inhibition by catecholamines and methylxanthines. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):902–903. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robison G. A., Butcher R. W., Sutherland E. W. Adenyl cyclase as an adrenergic receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Feb 10;139(3):703–723. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb41239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


