Abstract
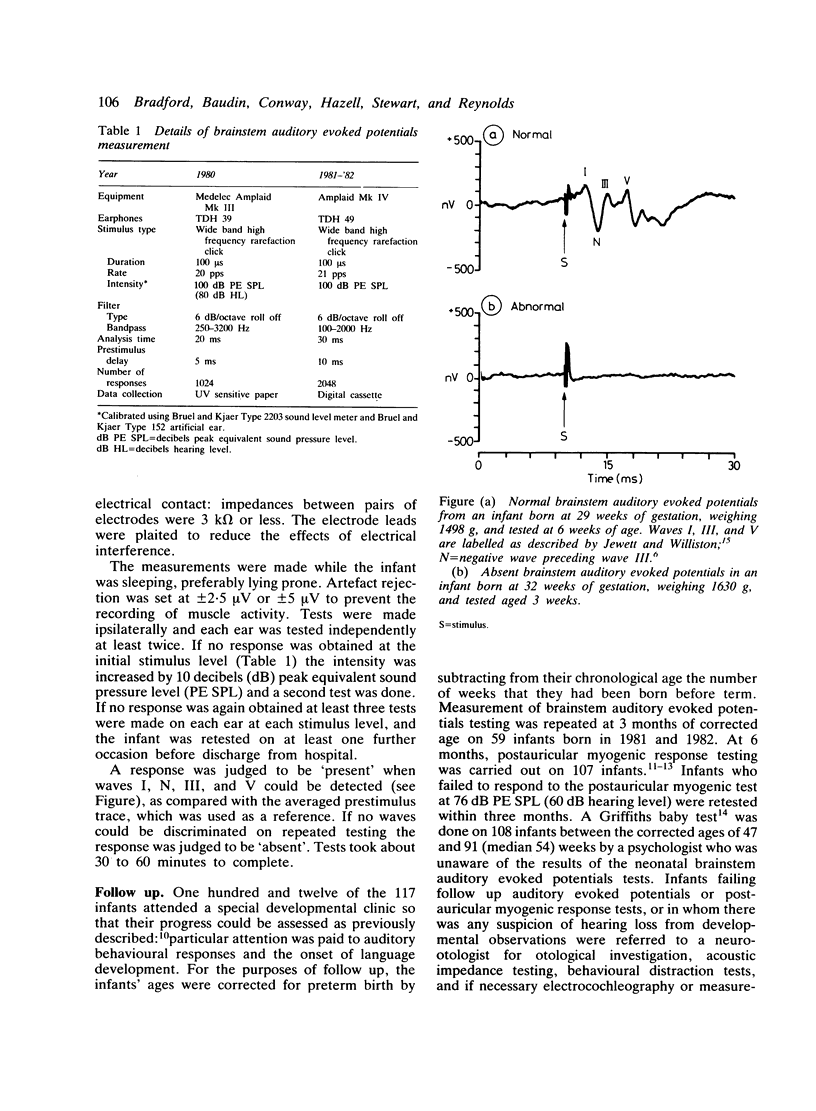
Brainstem auditory evoked potentials were recorded in 117 newborn infants of less than 33 weeks of gestation. The potentials were absent in 10 infants (bilaterally in eight and unilaterally in two) and present in 107. By 1 year of age nine of the 10 infants with absent brainstem auditory evoked potentials were shown to have sensory neural hearing loss and required hearing aids: the remaining infant had secretory otitis media. None of the 107 infants whose auditory evoked potentials were present were found to have sensory neural hearing loss but 13 had secretory otitis media. Measurement of brainstem auditory evoked potentials is an accurate method of identifying sensory neural hearing loss in very preterm infants.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramovich S. J., Gregory S., Slemick M., Stewart A. Hearing loss in very low birthweight infants treated with neonatal intensive care. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Jun;54(6):421–426. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.6.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achor L. J., Starr A. Auditory brain stem responses in the cat. I. Intracranial and extracranial recordings. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;48(2):154–173. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90301-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achor L. J., Starr A. Auditory brain stem responses in the cat. II. Effects of lesions. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980 Feb;48(2):174–190. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(80)90302-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberti P. W., Hyde M. L., Riko K., Corbin H., Abramovich S. An evaluation of BERA for hearing screening in high-risk neonates. Laryngoscope. 1983 Sep;93(9):1115–1121. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198309000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amadeo M., Shagass C. Brief latency click-evoked potentials during waking and sleep in man. Psychophysiology. 1973 May;10(3):244–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1973.tb00523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkany T. J., Berman S. A., Simmons M. A., Jafek B. W. Middle ear effusions in neonates. Laryngoscope. 1978 Mar;88(3):398–405. doi: 10.1288/00005537-197803000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchwald J. S., Huang C. Far-field acoustic response: origins in the cat. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):382–384. doi: 10.1126/science.1145206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox L. C., Hack M., Metz D. A. Longitudinal ABR in the NICU infant. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 1982 Aug;4(3):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0165-5876(82)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despland P. A., Galambos R. The auditory brainstem response (ABR) is a useful diagnostic tool in the intensive care nursery. Pediatr Res. 1980 Feb;14(2):154–158. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198002000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawer C. L., Dubowitz L. M. Auditory brain stem response in neurologically normal preterm and full-term newborn infants. Neuropediatrics. 1982 Nov;13(4):200–206. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flood L. M., Fraser J. G., Conway M. J., Stewart A. The assessment of hearing in infancy using the post-auricular myogenic response. Evaluation of an instrument which simplifies its detection. Br J Audiol. 1982 Nov;16(4):211–214. doi: 10.3109/03005368209081464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser J. G., Conway M. J., Keene M. H., Hazell J. W. The post-auricular myogenic response: a new instrument which simplifies its detection by machine scoring. J Laryngol Otol. 1978 Apr;92(4):293–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein P. J., Krumholz A., Feflix J. K., Shannon D., Carr R. F. Brain stem-evoked response in neonates. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979 Nov 1;135(5):622–628. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)32987-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecox K., Galambos R. Brain stem auditory evoked responses in human infants and adults. Arch Otolaryngol. 1974 Jan;99(1):30–33. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1974.00780030034006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes N., Conway M. J., Flood L., Fraser J. G., Stewart A. Language development in a group of very low-birth-weight children whose postauricular myogenic response was tested in infancy. Pediatrics. 1983 Feb;71(2):257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerger J., Mauldin L. Prediction of sensorineural hearing level from the brain stem evoked response. Arch Otolaryngol. 1978 Aug;104(8):456–461. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1978.00790080038010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewett D. L., Williston J. S. Auditory-evoked far fields averaged from the scalp of humans. Brain. 1971;94(4):681–696. doi: 10.1093/brain/94.4.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev A., Sohmer H. Sources of averaged neural responses recorded in animal and human subjects during cochlear audiometry (electro-cochleogram). Arch Klin Exp Ohren Nasen Kehlkopfheilkd. 1972;201(2):79–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00341066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. E., Reichert T. J., Kerley S. M., Davis H. Auditory function in newborn intensive care unit patients revealed by auditory brain-stem potentials. J Pediatr. 1980 Apr;96(4):731–735. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80755-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson T., Salamy A., Lenoir M., McKean C. Brain stem evoked potential findings in children with otitis media. Arch Otolaryngol. 1979 Jan;105(1):17–20. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1979.00790130021005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mokotoff B., Schulmann-Galambos C., Galambos R. Brain stem auditory evoked responses in children. Arch Otolaryngol. 1977 Jan;103(1):38–43. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1977.00780180076010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. L., Davis H., Phon G. L., Reichert T. J., Sturtevant E. M., Marshall R. E. Auditory brainstem responses in preterm neonates: maturation and follow-up. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):257–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salamy A., McKean C. M. Postnatal development of human brainstem potentials during the first year of life. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1976 Apr;40(4):418–426. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(76)90193-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman-Galambos C., Galambos R. Brain stem auditory-evoked responses in premature infants. J Speech Hear Res. 1975 Sep;18(3):456–465. doi: 10.1044/jshr.1803.456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman-Galambos C., Galambos R. Brain stem evoked response audiometry in newborn hearing screening. Arch Otolaryngol. 1979 Feb;105(2):86–90. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1979.00790140032006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohmer H., Feinmesser M. Cochlear action potentials recorded from the external ear in man. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1967 Jun;76(2):427–435. doi: 10.1177/000348946707600211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr A., Amlie R. N., Martin W. H., Sanders S. Development of auditory function in newborn infants revealed by auditory brainstem potentials. Pediatrics. 1977 Dec;60(6):831–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. L., Thorburn R. J., Hope P. L., Goldsmith M., Lipscomb A. P., Reynolds E. O. Ultrasound appearance of the brain in very preterm infants and neurodevelopmental outcome at 18 months of age. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Aug;58(8):598–604. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.8.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods J. R., Jr, Plessinger M. A., Mack C. E. Fetal auditory brainstem evoked response (ABR). Pediatr Res. 1984 Jan;18(1):83–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


