Abstract
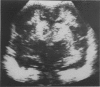
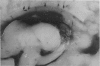
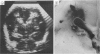
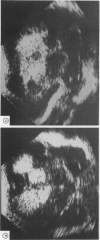
Sixty seven of 216 infants weighing less than 2 kg at birth had cerebral lesions on ultrasonic scanning. Eight of 17 who had periventricular leukomalacia, with or without subependymal or intraventricular haemorrhage, or both, died. These and one larger baby were the subject of a combined ultrasound, and where appropriate, necropsy study. There was excellent correlation between the ultrasound and necropsy findings, only some of the earlier lesions of periventricular leukomalacia being missed by ultrasound. The data suggest it is now possible to distinguish periventricular leukomalacia and subependymal/intraventricular haemorrhage by ultrasound, that both lesions may be present in the same brain, that apparent parenchymal extension of an intraventricular haemorrhage is more probably the result of haemorrhage into ischaemic periventricular tissue, and that the term 'periventricular haemorrhage' should be abandoned since it confuses two lesions of differing aetiology and differing clinical importance. Future advances in neonatal brain ultrasound depend on accurate assessment of both the nature and site of lesions within the cerebral hemispheres and ventricular system since the interpretation of these parameters is of critical importance.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Norman M. G. Periventricular leucomalacia in neonates. Complications and sequelae. Arch Dis Child. 1974 May;49(5):367–375. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.5.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANKER B. Q., LARROCHE J. C. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy. A form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1962 Nov;7:386–410. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210050022004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeReuck J., Chattha A. S., Richardson E. P., Jr Pathogenesis and evolution of periventricular leukomalacia in infancy. Arch Neurol. 1972 Sep;27(3):229–236. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490150037007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfin T., Skidmore M. B., Fong K. W., Hoskins E. M., Shennan A. T., Hill A. Diagnosis and evolution of periventricular leukomalacia: a study with real-time ultrasound. Early Hum Dev. 1984 Feb;9(2):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(84)90090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flodmark O., Becker L. E., Harwood-Nash D. C., Fitzhardinge P. M., Fitz C. R., Chuang S. H. Correlation between computed tomography and autopsy in premature and full-term neonates that have suffered perinatal asphyxia. Radiology. 1980 Oct;137(1 Pt 1):93–103. doi: 10.1148/radiology.137.1.7422867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton G., Wigglesworth J. S. Origin of intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm infant. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Sep;51(9):651–659. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.9.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill A., Melson G. L., Clark H. B., Volpe J. J. Hemorrhagic periventricular leukomalacia: diagnosis by real time ultrasound and correlation with autopsy findings. Pediatrics. 1982 Mar;69(3):282–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene M. I., Wigglesworth J. S., Dubowitz V. Hemorrhagic periventricular leukomalacia in the neonate: a real-time ultrasound study. Pediatrics. 1983 May;71(5):794–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwaesei C. G., Pape K. E., Martin D. J., Becker L. E., Fitz C. R. Periventricular infarction diagnosed by ultrasound: a postmortem correlation. J Pediatr. 1984 Jul;105(1):106–110. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80372-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston P. R., Rushton D. I., Durbin G. M. Ultrasound periventricular echo densities in neonatal brains. Lancet. 1983 Aug 20;2(8347):459–459. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90427-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymonowicz W., Schafler K., Cussen L. J., Yu V. Y. Ultrasound and necropsy study of periventricular haemorrhage in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jul;59(7):637–642. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.7.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J., Herscovitch P., Perlman J. M., Raichle M. E. Positron emission tomography in the newborn: extensive impairment of regional cerebral blood flow with intraventricular hemorrhage and hemorrhagic intracerebral involvement. Pediatrics. 1983 Nov;72(5):589–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]