Abstract
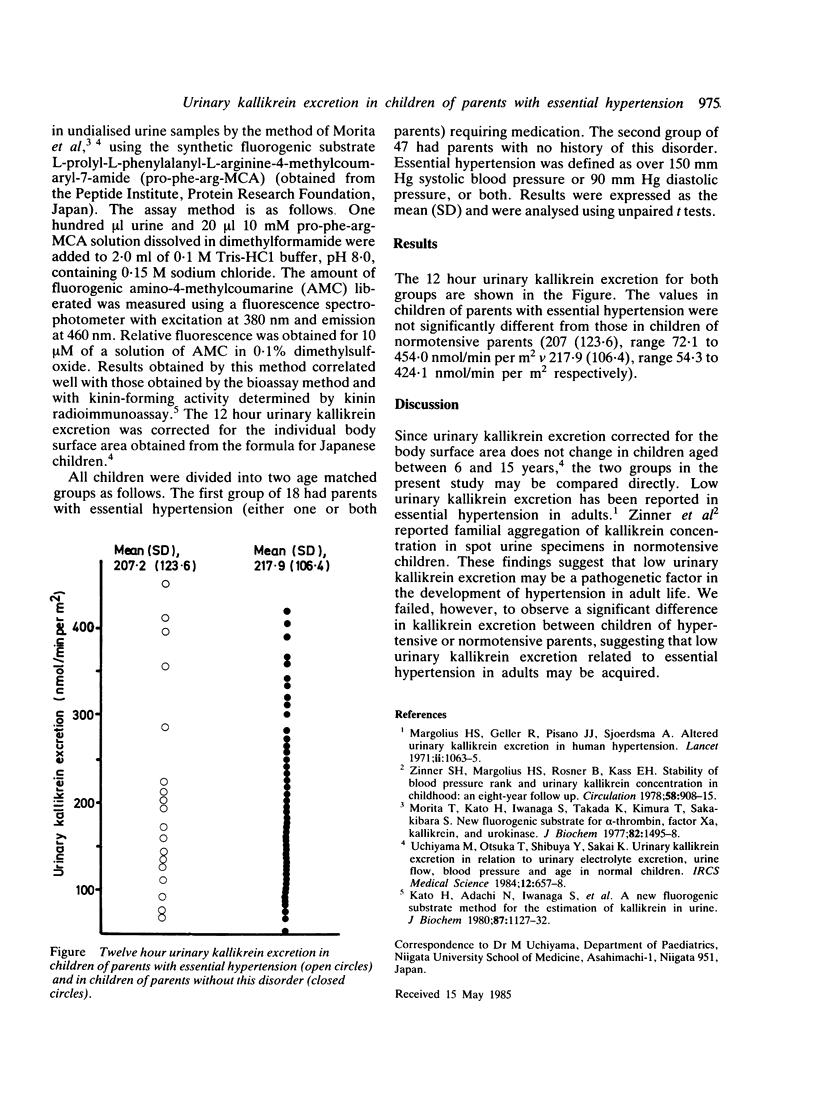
Twelve hour urinary kallikrein excretion was measured in 18 healthy children of parents with essential hypertension and in 47 healthy children of parents without this disorder. No statistically significant difference was observed between the two groups of children.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kato H., Adachi N., Iwanaga S., Abe K., Takada K., Kimura T., Sakakibara S. A new fluorogenic substrate method for the estimation of kallikrein in urine. J Biochem. 1980 Apr;87(4):1127–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis H. S., Geller R., Pisano J. J., Sjoerdsma A. Altered urinary kallikrein excretion in human hypertension. Lancet. 1971 Nov 13;2(7733):1063–1065. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90382-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Kato H., Iwanaga S., Takada K., Kimura T. New fluorogenic substrates for alpha-thrombin, factor Xa, kallikreins, and urokinase. J Biochem. 1977 Nov;82(5):1495–1498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinner S. H., Margolius H. S., Rosner B., Kass E. H. Stability of blood pressure rank and urinary kallikrein concentration in childhood: an eight-year follow-up. Circulation. 1978 Nov;58(5):908–915. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.5.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


