Abstract
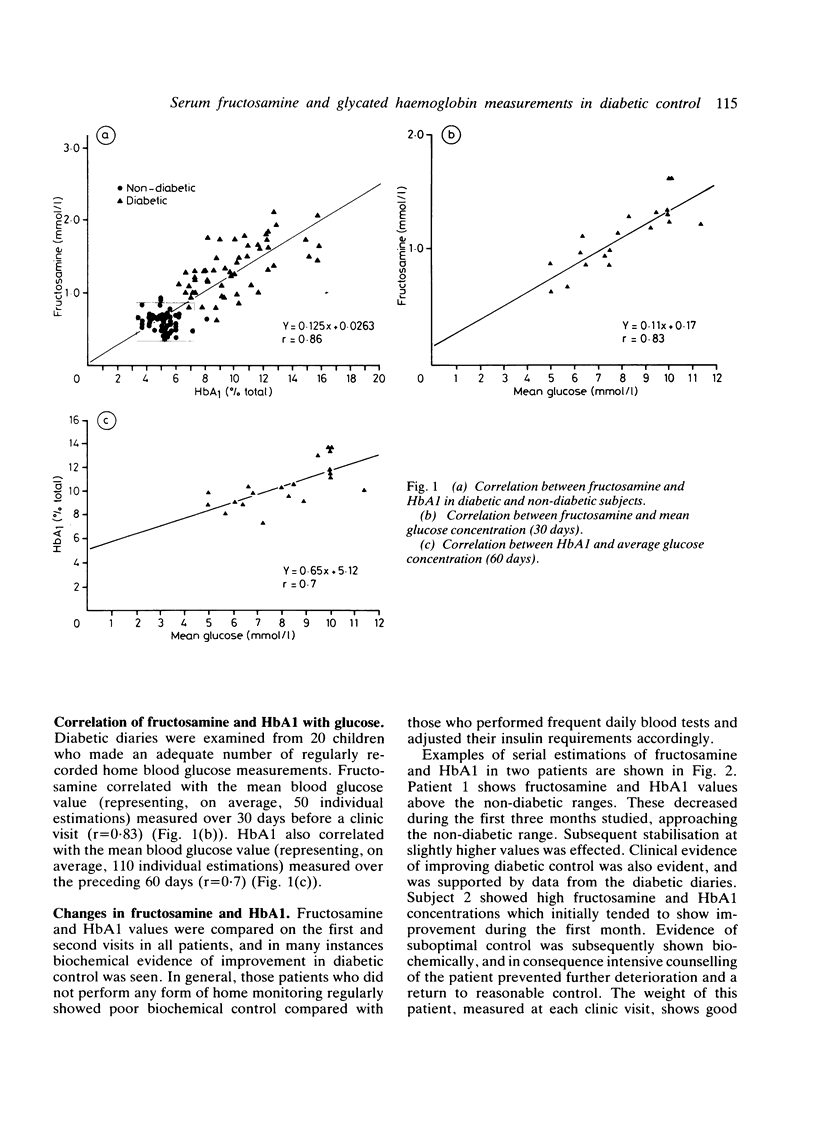
Serum fructosamine and glycated haemoglobin (HbA1) were measured in capillary samples from diabetic children and compared with samples from non-diabetic children. Glycaemic control was assessed clinically and by average daily glucose values recorded by home monitoring. Fructosamine correlated with HbA1 and with average glucose values measured over 30 days. HbA1 also correlated with average glucose values measured over 60 days. Changes in fructosamine with time tended to parallel those of HbA1, and advance indication of deteriorating or improving glycaemic control was possible by observing changes in these. Fructosamine has many advantages over HbA1 measurement such as speed, technical ease, and low cost, and is a reliable alternative to HbA1 estimation as an indication of glycaemic control.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambler J., Janik B., Walker G. Measurement of glycosylated hemoglobin on cellulose acetate membranes by mobile affinity electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1983 Feb;29(2):340–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. R., Johnson R. N., Scott D. J. Serum fructosamine concentrations in patients with type II (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus during changes in management. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 May 19;288(6429):1484–1486. doi: 10.1136/bmj.288.6429.1484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. R., Metcalf P. A., Holdaway I. M., Johnson R. N. Serum fructosamine concentration as measure of blood glucose control in type I (insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Feb 2;290(6465):352–355. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6465.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodansky H. J., Wolf E., Cudworth A. G., Dean B. M., Nineham L. J., Bottazzo G. F., Matthews J. A., Kurtz A. B., Kohner E. M. Genetic and immunologic factors in microvascular disease in type I insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Jan;31(1):70–74. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. E. Is glycosylated hemoglobin clinically useful? N Engl J Med. 1984 Feb 9;310(6):384–385. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198402093100609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. E., Peth S. B., England J. D., Hess R. L., Da Costa J. Effects of acute changes in blood glucose on HbA1c. Diabetes. 1980 Aug;29(8):623–628. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.8.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. E., Walker B., Rawlings S. S., Hess R. L., England J. D., Peth S. B., Hewett J. E. Hemoglobin A1c levels in children and adolescents with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1980 Jul-Aug;3(4):503–507. doi: 10.2337/diacare.3.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindle E. J., Rostron G. M., Gatt J. A. The estimation of serum fructosamine: an alternative measurement to glycated haemoglobin. Ann Clin Biochem. 1985 Jan;22(Pt 1):84–89. doi: 10.1177/000456328502200109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. N., Metcalf P. A., Baker J. R. Fructosamine: a new approach to the estimation of serum glycosylprotein. An index of diabetic control. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jan 7;127(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miedema K., Casparie T. Glycosylated haemoglobins: biochemical evaluation and clinical utility. Ann Clin Biochem. 1984 Jan;21(Pt 1):2–15. doi: 10.1177/000456328402100102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen H. B., Vestermark S., Kastrup K. W. Metabolic control in children with insulin dependent diabetes mellitus assessed by hemoglobin A1c. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1982 Mar;71(2):217–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1982.tb09402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. M., Avezzano E., Palmer J. L. Rapid method for eliminating labile glycosylated hemoglobin from the assay for hemoglobin A1. Clin Chem. 1982 Mar;28(3):512–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. M. Labile glycosylated hemoglobin contributes to hemoglobin A1 as measured by liquid chromatography or electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1981 Jul;27(7):1261–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Baker J. R., Court D. J., James A. G., Henley P., Ronayne I. D. Fructosamine in diabetic pregnancy. Lancet. 1983 Oct 29;2(8357):998–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90982-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


