Abstract
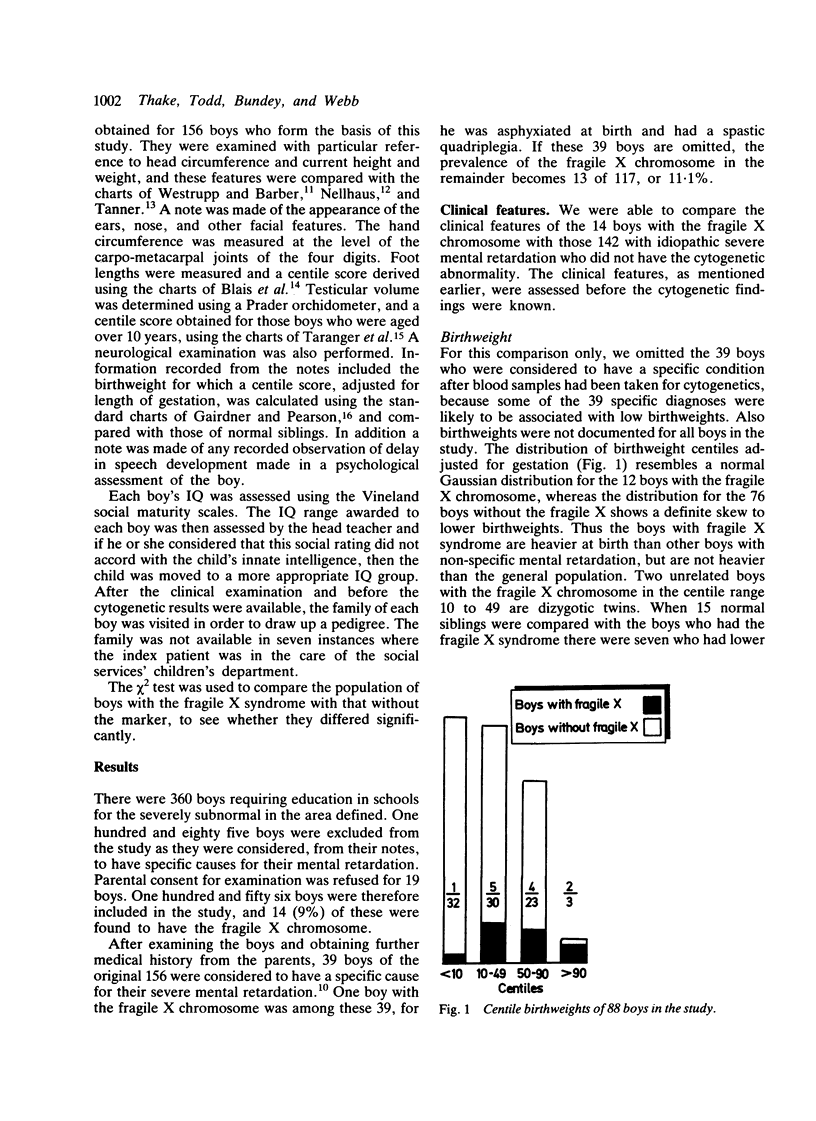
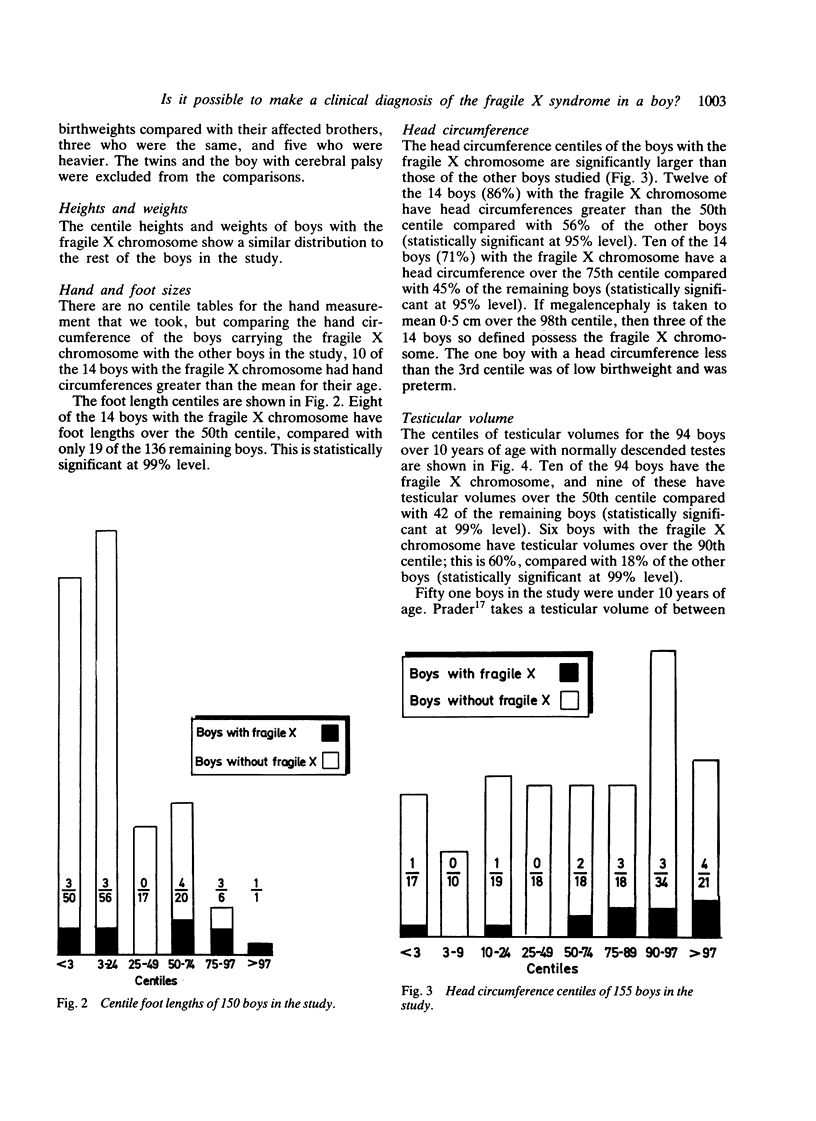
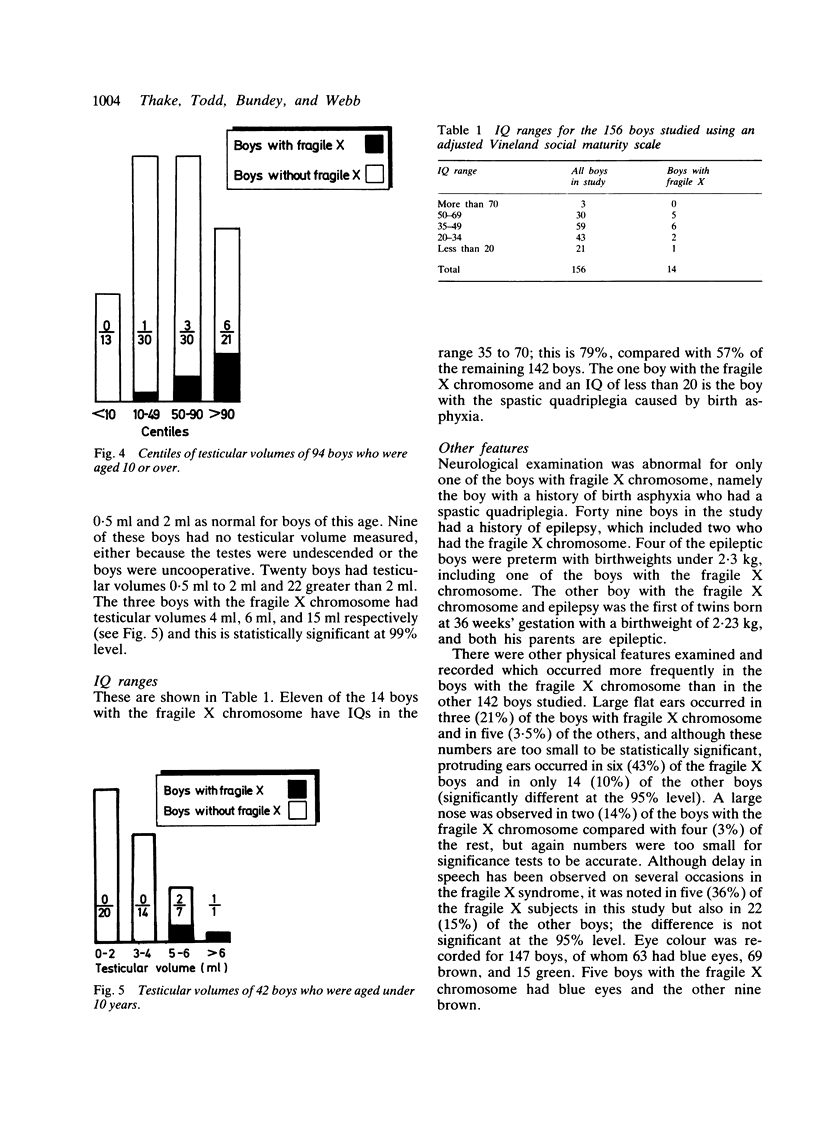
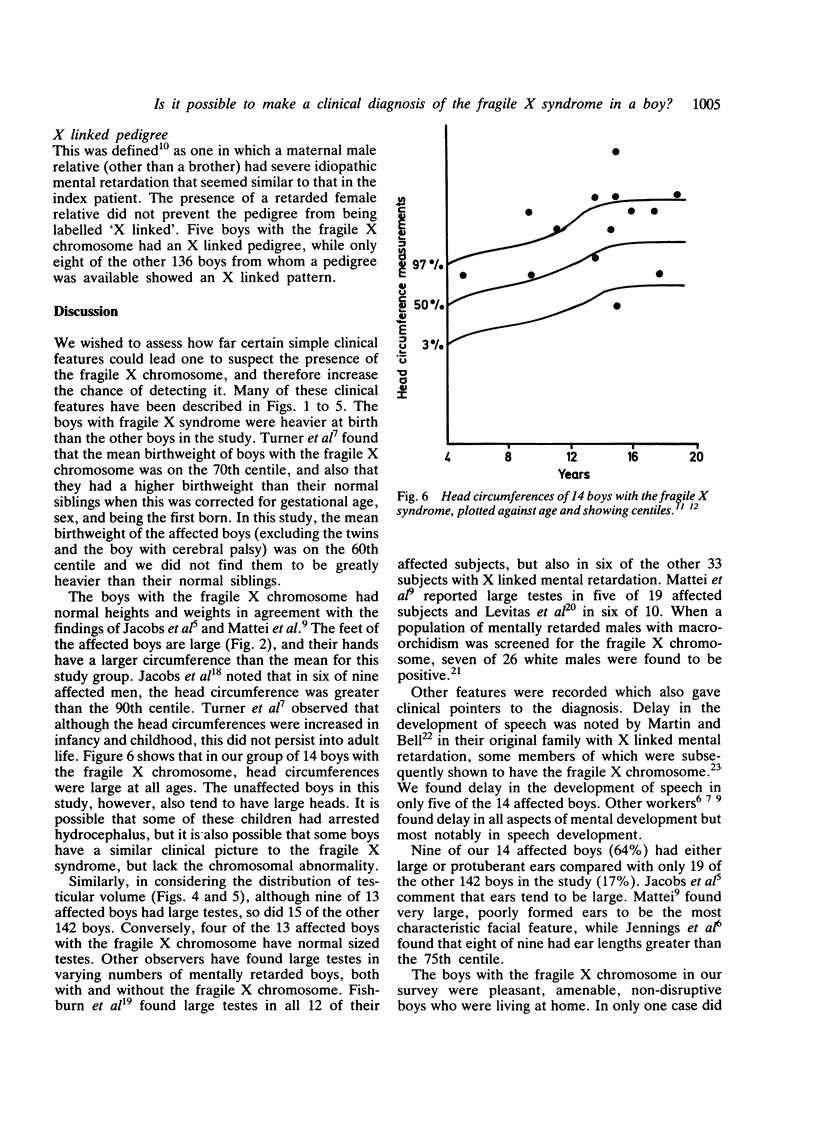
Clinical observations were made on a series of 156 boys with severe mental retardation, before cytogenetic results were known. The clinical features that helped to distinguish the 14 boys with the fragile X chromosome from those without were: head circumference over the 50th centile, postpubertal testicular volume over the 50th centile, and an IQ between 35 and 70. If the above clinical features were all present, then the chance of finding the fragile X chromosome was 1 in 3.6, whereas the chance of finding this abnormality in any boy with severe idiopathic mental retardation, regardless of his clinical features, was 1 in 9. Two boys with fragile X syndrome did not, however, possess any of the above clinical features. Moreover, some of the other retarded boys had clinical features of the syndrome, or an X linked pedigree, but lacked the chromosome abnormality.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON M., BLAIS M. M., GREEN W. T. Lengths of the growing foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1956 Oct;38-A(5):998–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundey S., Webb T. P., Thake A., Todd J. A community study of severe mental retardation in the West Midlands and the importance of the fragile X chromosome in its aetiology. J Med Genet. 1985 Aug;22(4):258–266. doi: 10.1136/jmg.22.4.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishburn J., Turner G., Daniel A., Brookwell R. The diagnosis and frequency of X-linked conditions in a cohort of moderately retarded males with affected brothers. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Apr;14(4):713–724. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P. The fragile X syndrome. A study of 83 families. Clin Genet. 1984 Dec;26(6):497–528. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gairdner D., Pearson J. A growth chart for premature and other infants. Arch Dis Child. 1971 Dec;46(250):783–787. doi: 10.1136/adc.46.250.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavson K. H., Holmgren G., Blomquist H. K., Mikkelsen M., Nordenson I., Poulsen H., Tommerup N. Familial X-linked mental retardation and fragile X chromosomes in two Swedish families. Clin Genet. 1981 Feb;19(2):101–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1981.tb00678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey J., Judge C., Wiener S. Familial X-linked mental retardation with an X chromosome abnormality. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):46–50. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Peebles P. N., Finley W. H. Screening of mentally retarded males for macro-orchidism and the fragile X chromosome. Am J Med Genet. 1983 Aug;15(4):631–635. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320150414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard-Peebles P. N., Stoddard G. R. X-linked mental retardation with macro-orchidism and marker X chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1979 Sep;50(3):247–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00399389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Mayer M., Matsuura J., Rhoads F., Yee S. C. A cytogenetic study of a population of mentally retarded males with special reference to the marker (X) syndrome. Hum Genet. 1983;63(2):139–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00291533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M., Hall J. G., Hoehn H. Significance of phenotypic and chromosomal abnormalities in X-linked mental retardation (Martin-Bell or Renpenning syndrome). Am J Med Genet. 1980;7(4):417–432. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320070404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitas A., Hagerman R. J., Braden M., Rimland B., McBogg P., Matus I. Autism and the fragile X syndrome. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1983 Sep;4(3):151–158. doi: 10.1097/00004703-198309000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A. A marker X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 May;21(3):231–244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei J. F., Mattei M. G., Aumeras C., Auger M., Giraud F. X-linked mental retardation with the fragile X. A study of 15 families. Hum Genet. 1981;59(4):281–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00295459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellhaus G. Head circumference from birth to eighteen years. Practical composite international and interracial graphs. Pediatrics. 1968 Jan;41(1):106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K. B., Tommerup N., Poulsen H., Mikkelsen M. X-linked mental retardation with fragile X. A pedigree showing transmission by apparently unaffected males and partial expression in female carriers. Hum Genet. 1981;59(1):23–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00278849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prader A. Testicular size: assessment and clinical importance. Triangle. 1966;7(6):240–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards B. W., Sylvester P. E., Brooker C. Fragile X-linked mental retardation: the Martin-Bell syndrome. J Ment Defic Res. 1981 Dec;25(Pt 4):253–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1981.tb00115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. Fragile sites on human chromosomes: demonstration of their dependence on the type of tissue culture medium. Science. 1977 Jul 15;197(4300):265–266. doi: 10.1126/science.877551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TANNER J. M. The assessment of growth and development in children. Arch Dis Child. 1952 Feb;27(131):10–33. doi: 10.1136/adc.27.131.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taranger J., Engström I., Lichtenstein H., Svennberg- Redegren I. VI. Somatic pubertal development. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1976;(258):121–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Daniel A., Frost M. X-linked mental retardation, macro-orchidism, and the Xq27 fragile site. J Pediatr. 1980 May;96(5):837–841. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80552-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Turner B. X-linked mental retardation. J Med Genet. 1974 Jun;11(2):109–113. doi: 10.1136/jmg.11.2.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTROPP C. K., BARBER C. R. Growth of the skull in young children. I. Standards of head circumference. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 Feb;19(1):52–54. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


