Abstract
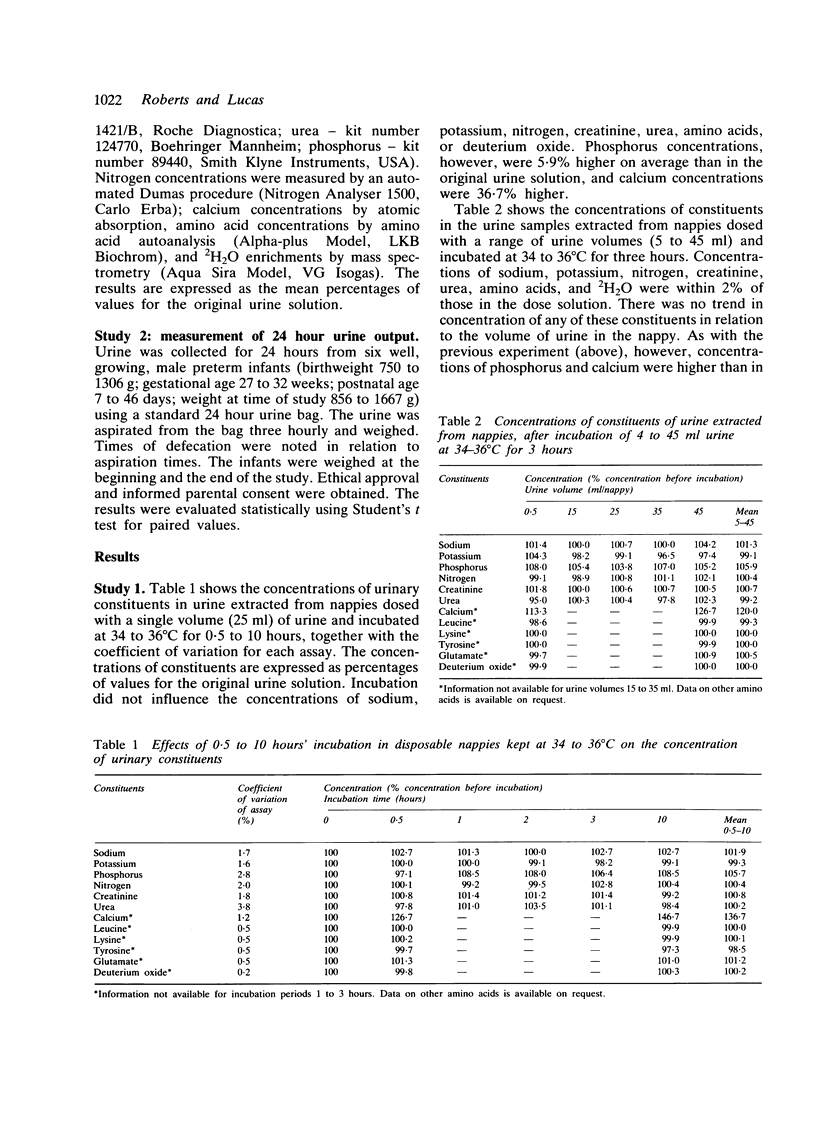
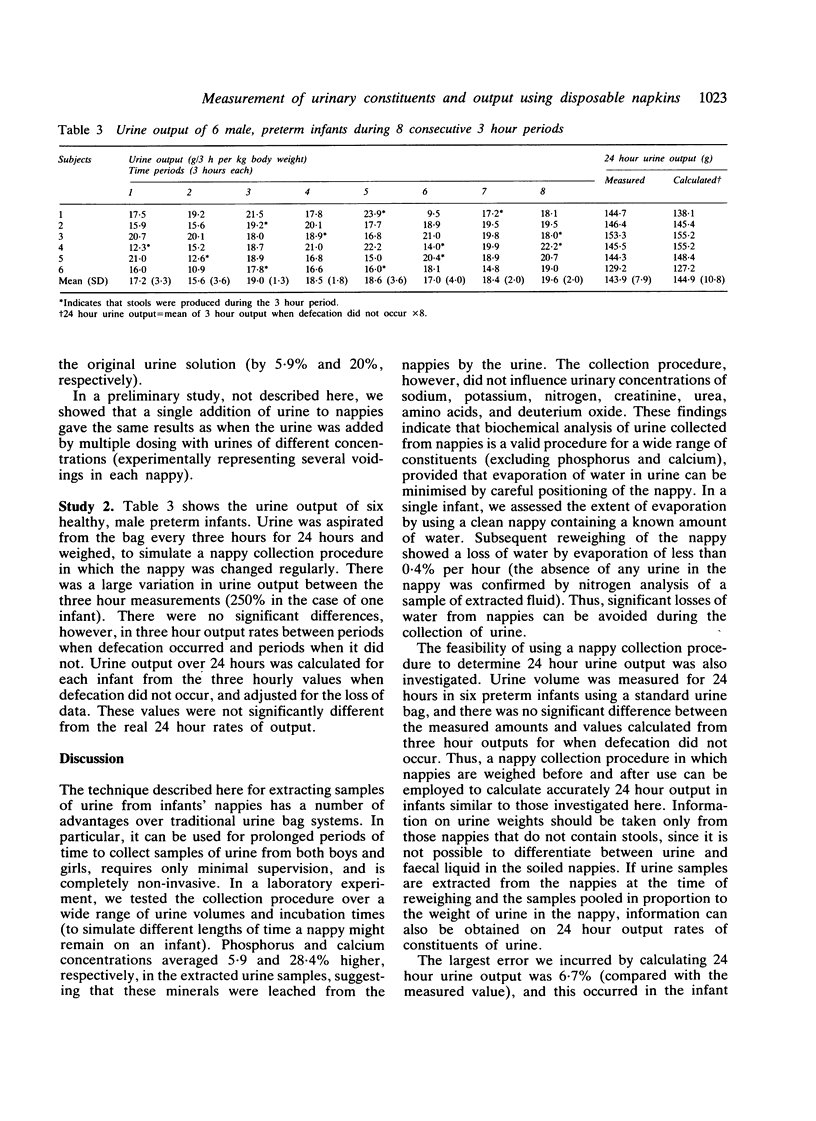
A procedure for estimating 24 hour urine output in infants using disposable nappies has been validated. In addition, it has been shown experimentally that the urinary concentrations, and hence 24 hour outputs of a range of constituents (sodium, potassium, nitrogen, creatinine, urea, amino acids, and deuterium oxide), may be measured accurately using samples of urine obtained from nappies. It is concluded that the urine collection procedure described has several major advantages over traditional urine bag methods, and has a wide application in clinical practice and research.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jackson A. A., Shaw J. C., Barber A., Golden M. H. Nitrogen metabolism in preterm infants fed human donor breast milk: the possible essentiality of glycine. Pediatr Res. 1981 Nov;15(11):1454–1461. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198111000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemoh J. N., Brooke O. G. Frequency and weight of normal stools in infancy. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Sep;54(9):719–720. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.9.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver L. T., Steiner H. The bowel habit of young children. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jul;59(7):649–652. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.7.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


