Abstract
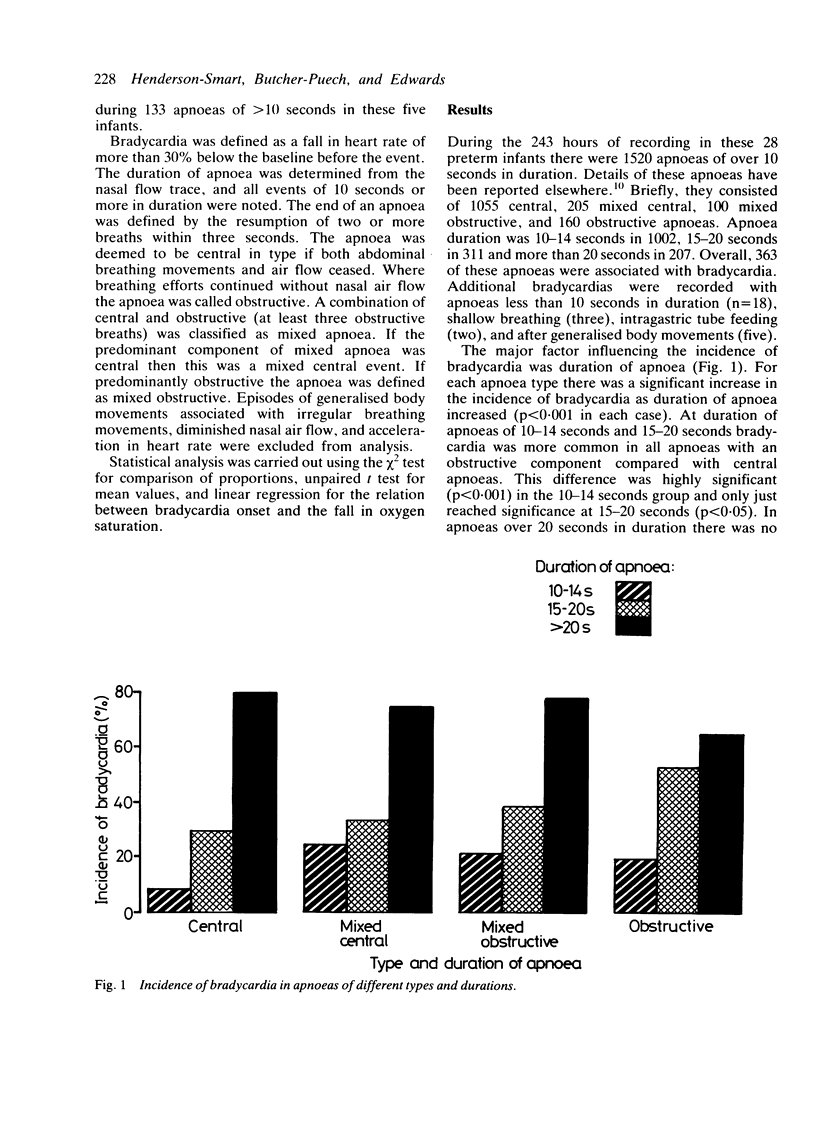
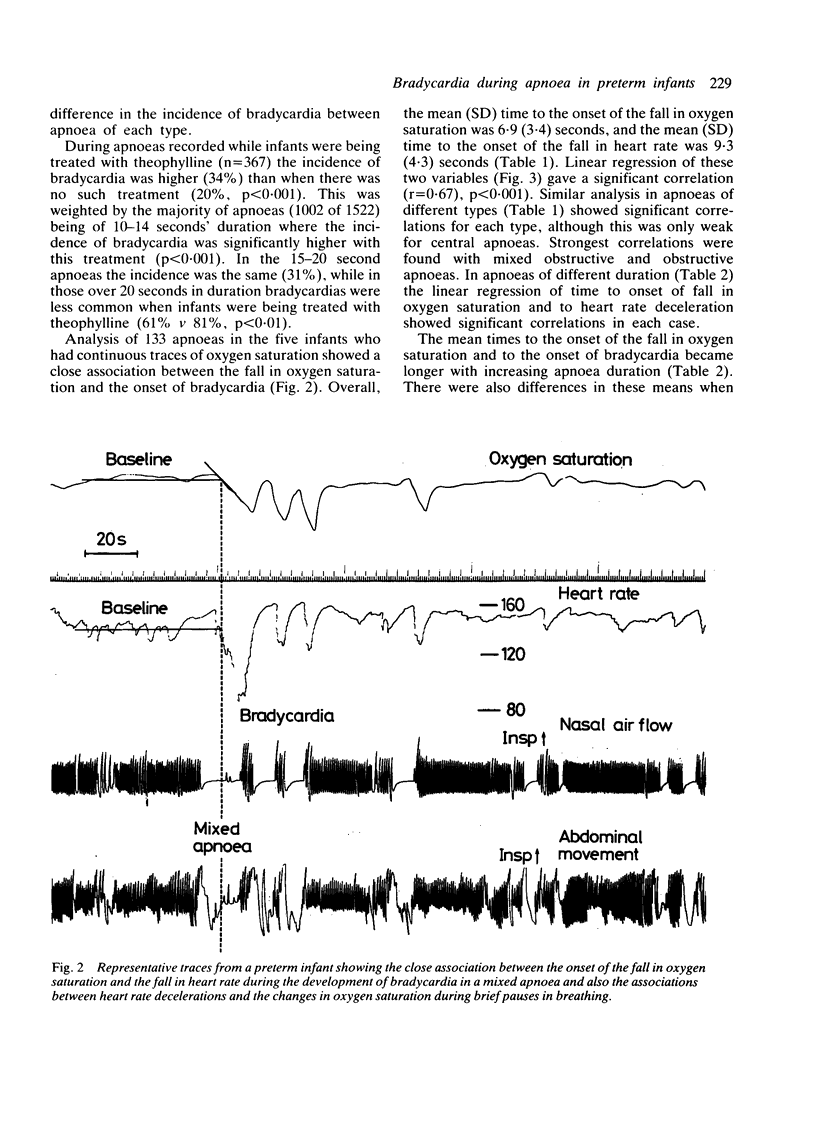
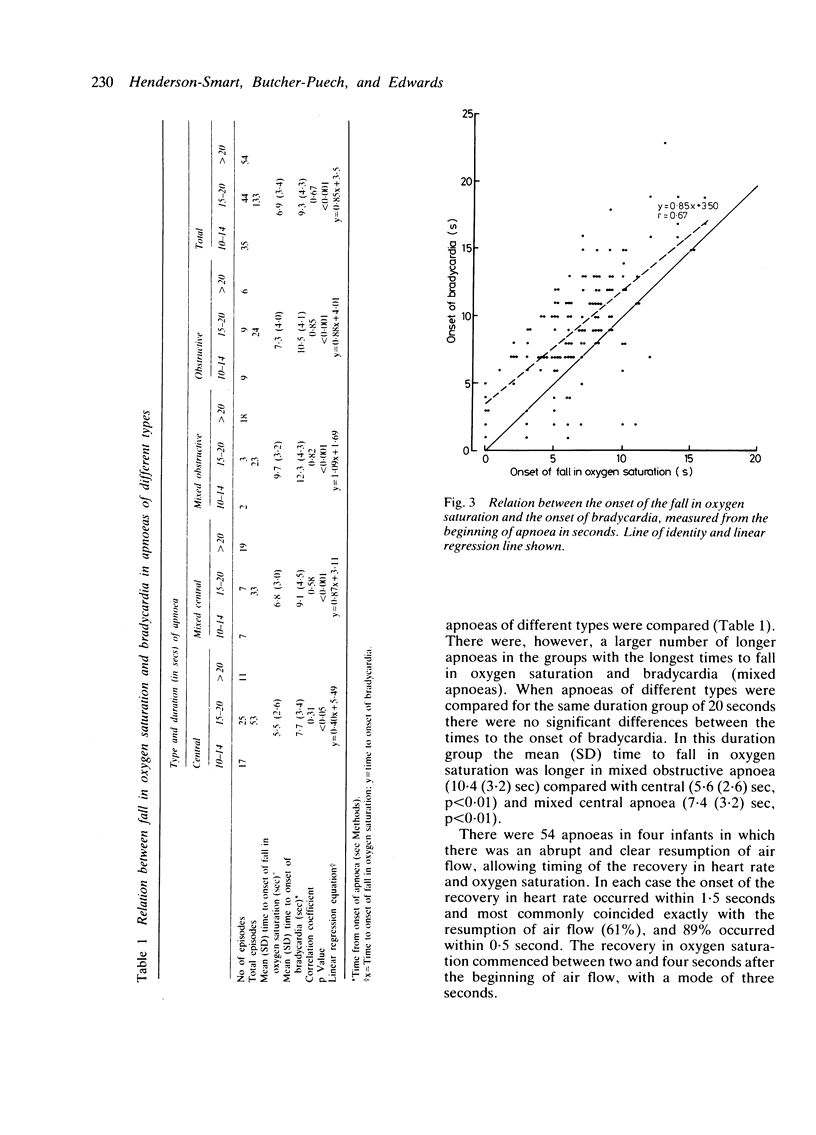
Bradycardia occurred during 363 of 1520 apnoeas of 10 seconds' duration recorded in 28 preterm infants. The incidence increased with increasing duration of apnoea (10% of 10-14 seconds, 34% of 15-20 seconds, and 75% of greater than 20 seconds, p less than 0.001). This was similar for each type of apnoea--central, mixed, and obstructive. During 133 apnoeas in five infants the time from the start of the apnoea to the onset in the fall in oxygen saturation (mean 6.9 seconds) was significantly related to the onset of the fall in heart rate (mean 9.3 seconds) (r = 0.67, p less than 0.001). Recovery in heart rate coincided with resumption of air flow rather than breathing efforts and preceded the recovery in oxygen saturation. These results suggest that bradycardia occurs during apnoea as a response to falling oxygen saturation, probably through a peripheral chemoreceptor reflex that is manifest when breathing efforts are absent or ineffective.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butcher-Puech M. C., Henderson-Smart D. J., Holley D., Lacey J. L., Edwards D. A. Relation between apnoea duration and type and neurological status of preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Oct;60(10):953–958. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.10.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK C. D., CHERRY R. B., O'BRIEN D., KARLBERG P., SMITH C. A. Studies of respiratory physiology in the newborn infant. I. Observations on normal premature and full-term infants. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jul;34(7 Pt 1):975–982. doi: 10.1172/JCI103165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordero L., Jr, Hon E. H. Neonatal bradycardia following nasopharyngeal stimulation. J Pediatr. 1971 Mar;78(3):441–447. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80224-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daily W. J., Klaus M., Meyer H. B. Apnea in premature infants: monitoring, incidence, heart rate changes, and an effect of environmental temperature. Pediatrics. 1969 Apr;43(4):510–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz L. M., Dubowitz V., Goldberg C. Clinical assessment of gestational age in the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1970 Jul;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80038-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling D. J. Changes in heart rate, blood pressure, and pulse pressure during apnoeic attacks in newborn babies. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Jun;47(253):405–410. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.253.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiatt I. M., Hegyi T., Indyk L., Dangman B. C., James L. S. Continuous monitoring of PO2 during apnea of prematurity. J Pediatr. 1981 Feb;98(2):288–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80663-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER H. C., BEHRLE F. C., SMULL N. W. Severe apnea and irregular respiratory rhythms among premature infants; a clinical and laboratory study. Pediatrics. 1959 Apr;23(4):676–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. M., Volpe J. J. Episodes of apnea and bradycardia in the preterm newborn: impact on cerebral circulation. Pediatrics. 1985 Sep;76(3):333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID D. H., TUNSTALL M. E. RECURRENT NEONATAL APNOEA. Lancet. 1965 Jul 24;2(7404):155–156. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigatto H., Brady J. P. Periodic breathing and apnea in preterm infants. II. Hypoxia as a primary event. Pediatrics. 1972 Aug;50(2):219–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigatto H., Brady J. P., de la Torre Verduzco R. Chemoreceptor reflexes in preterm infants: I. The effect of gestational and postnatal age on the ventilatory response to inhalation of 100% and 15% oxygen. Pediatrics. 1975 May;55(5):604–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte F. J. Apnea. Clin Perinatol. 1977 Mar;4(1):65–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southall D. P., Levitt G. A., Richards J. M., Jones R. A., Kong C., Farndon P. A., Alexander J. R., Wilson A. J. Undetected episodes of prolonged apnea and severe bradycardia in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 1983 Oct;72(4):541–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrs C. N. Cardiovascular effects of apnoea in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Jul;52(7):534–540. doi: 10.1136/adc.52.7.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



