Abstract
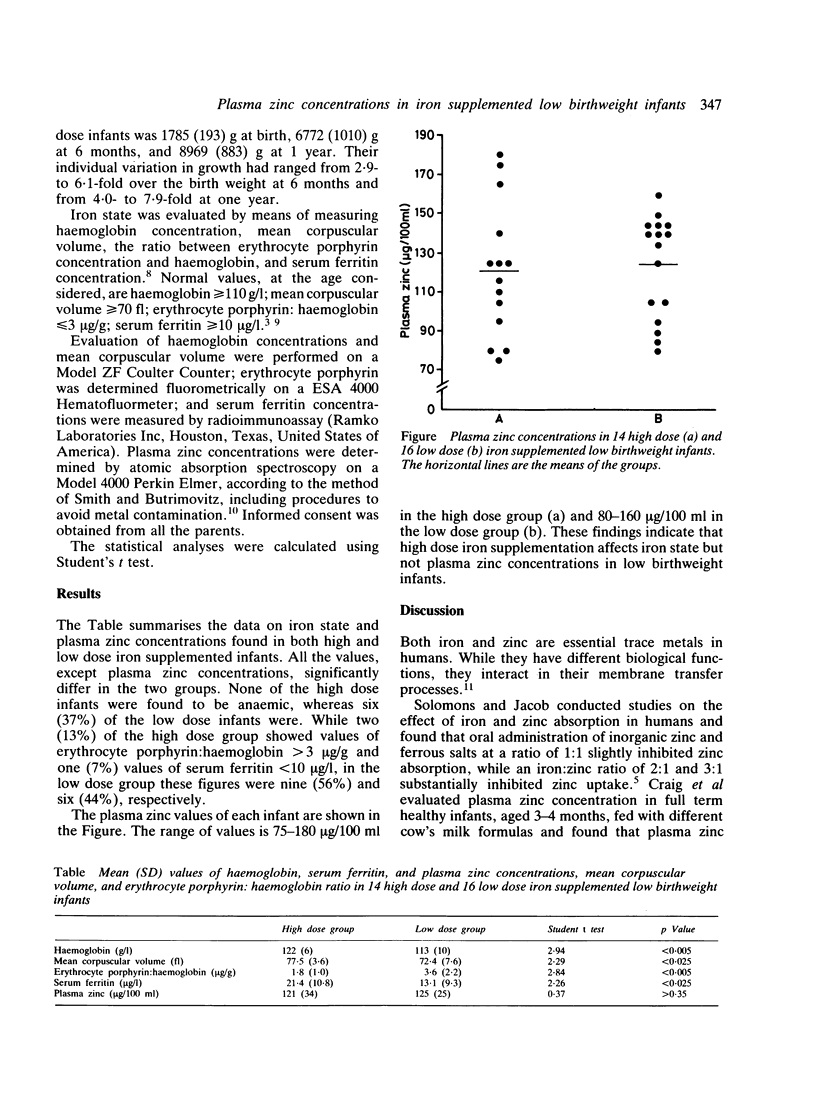
We investigated the effect of prolonged iron supplementation of low birthweight infants on plasma zinc concentrations. Thirty infants (neonatal weight 820-2000 g) were examined at 6 or 12 months of life to assess their iron state and plasma zinc concentration. All of them were feeding on iron fortified formulas, which supply about 1 mg/kg/day of iron. In addition, 14 of them had been receiving 2 mg/kg/day of medicinal ferrous salts for at least five months. The other 16 were not given medicinal iron supplementation. Whereas iron state significantly differed in the two groups, plasma zinc concentrations were similar. Moreover, no zinc values below 75 micrograms/100 ml were found in any case. The results suggest that long term iron supplementation of low birthweight infants, at the recommended doses, does not influence zinc plasma concentrations unfavourably.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Craig W. J., Balbach L., Harris S., Vyhmeister N. Plasma zinc and copper levels of infants fed different milk formulas. J Am Coll Nutr. 1984;3(2):183–186. doi: 10.1080/07315724.1984.10720051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman P. R. New approaches to screening for iron deficiency. J Pediatr. 1977 Apr;90(4):678–681. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80427-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faldella G., Alessandroni R., Salvioli G. P., Capelli M., Paolini M., Minak G., Jr, Tiraferri S. Lack of correlation between free erythrocyte porphyrin and serum ferritin values at birth and at 2 months of life in low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Mar;58(3):216–219. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.3.216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson L., Holmberg L., Ekman R. Medicinal iron to low birth weight infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Sep;68(5):705–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb18442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundström U., Siimes M. A., Dallman P. R. At what age does iron supplementation become necessary in low-birth-weight infants? J Pediatr. 1977 Dec;91(6):878–883. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundström U., Siimes M. A. Red blood cell values in low-birth-weight infants: ages at which values become equivalent to those of term infants. J Pediatr. 1980 Jun;96(6):1040–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80636-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siimes M. A., Järvenpä A. L. Prevention of anemia and iron deficiency in very low-birth-weight infants. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):277–280. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Jr, Butrimovitz G. P., Purdy W. C. Direct measurement of zinc in plasma by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Clin Chem. 1979 Aug;25(8):1487–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomons N. W., Jacob R. A. Studies on the bioavailability of zinc in humans: effects of heme and nonheme iron on the absorption of zinc. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Apr;34(4):475–482. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.4.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyer M., Davakis M., Antener I., Valleur D. Zinc balances in preterm infants. Biol Neonate. 1982;42(1-2):87–92. doi: 10.1159/000241580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip R., Reeves J. D., Lönnerdal B., Keen C. L., Dallman P. R. Does iron supplementation compromise zinc nutrition in healthy infants? Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Oct;42(4):683–687. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.4.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


