Abstract
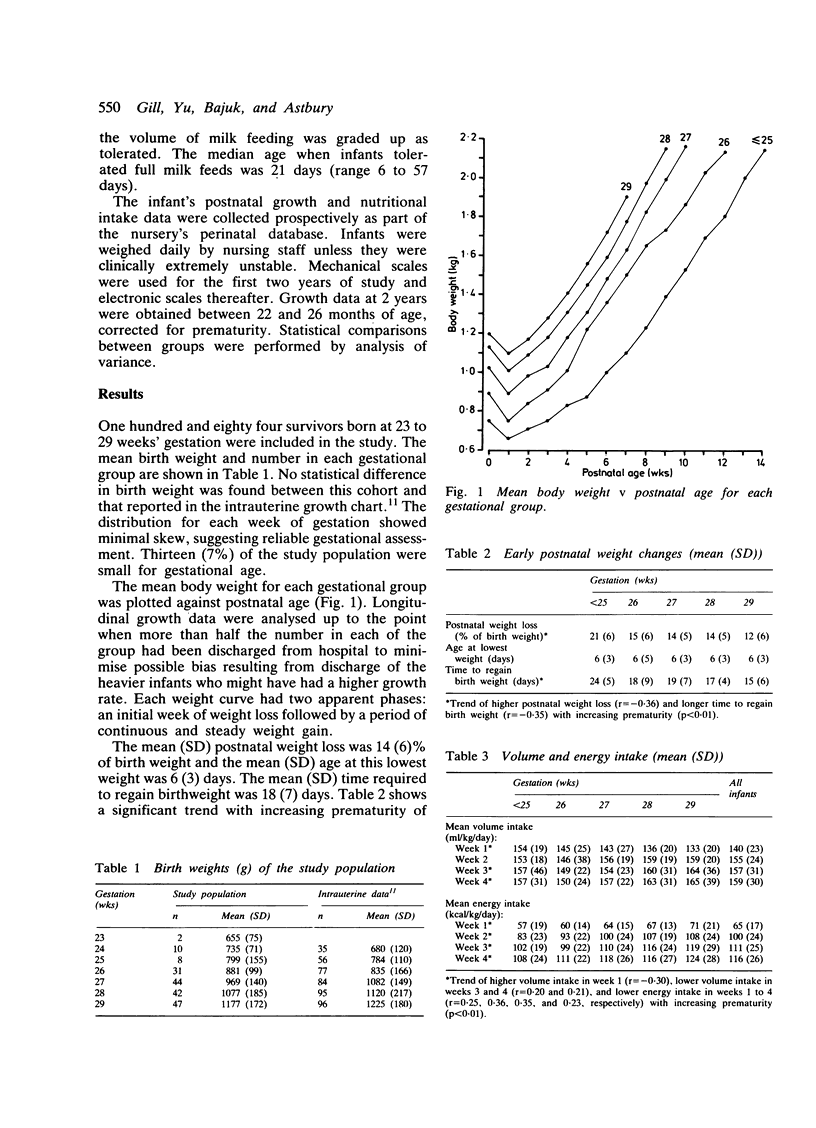
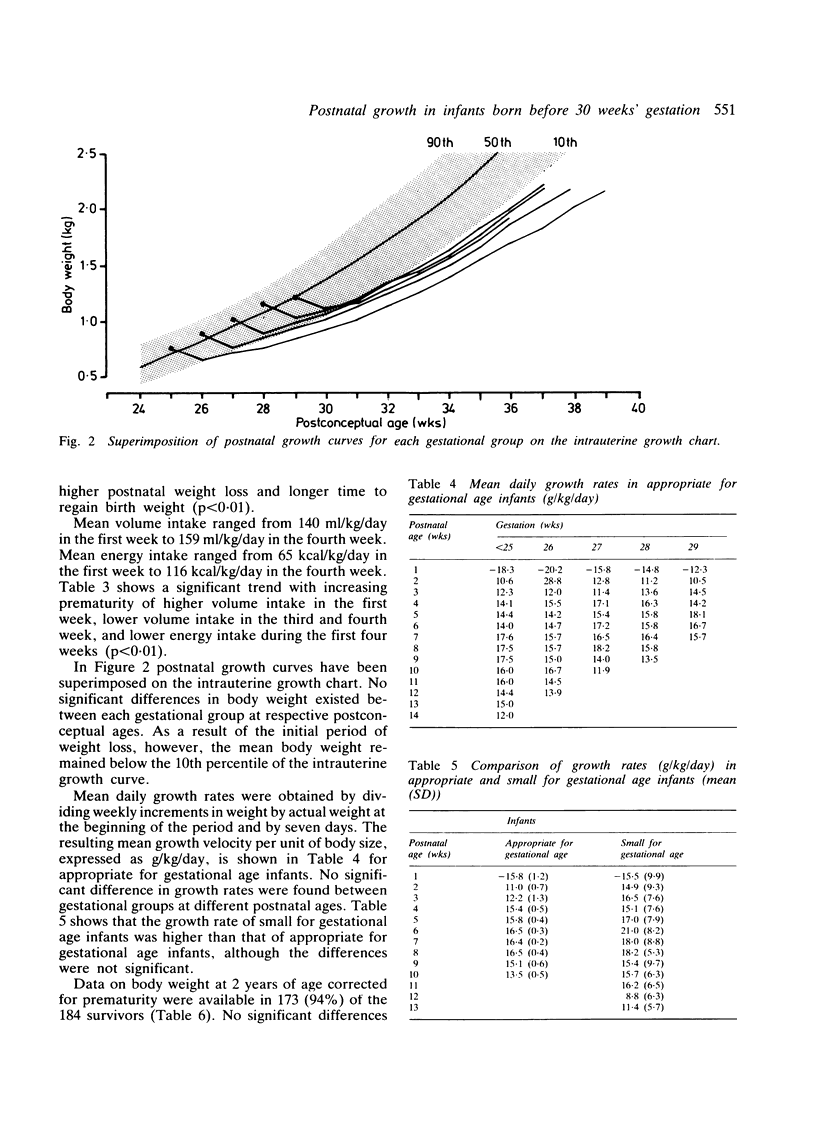
The postnatal weight pattern up to 14 weeks after birth was determined in 184 singleton survivors born at 23 to 29 weeks' gestation in whom routine parenteral nutrition was used before milk feeding was established. A mean postnatal weight loss of 14% of birth weight occurred at a mean of 6 days. The more immature infants had significantly higher postnatal weight loss and longer time to regain birth weight despite a higher volume intake in the first week. From the fourth postnatal week all gestational subgroups had a mean weight gain at above intrauterine growth rate. As a result of the initial period of weight loss, however, the mean body weight remained below the 10th percentile of the intrauterine growth curve. The early growth rate in infants small for gestational age was higher than those who were appropriate weight for gestation, although the mean body weight of the former group remained significantly lower at 2 years.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babson S. G. Growth of low-birth-weight infants. J Pediatr. 1970 Jul;77(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(70)80039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke O. G., Wood C., Barley J. Energy balance, nitrogen balance, and growth in preterm infants fed expressed breast milk, a premature infant formula, and two low-solute adapted formulae. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Dec;57(12):898–904. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.12.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius K. K., Ritter D. A., Kenny J. D. Postnatal growth curve of the infant with extremely low birth weight who was fed enterally. Pediatrics. 1984 Nov;74(5):778–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruise M. O. A longitudinal study of the growth of low birth weight infants. I. Velocity and distance growth, birth to 3 years. Pediatrics. 1973 Apr;51(4):620–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. W., Vale J., Sims D. G., Chiswick M. L. Feeding, growth, and biochemical studies in very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Mar;60(3):215–218. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.3.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzhardinge P. M., Steven E. M. The small-for-date infant. I. Later growth patterns. Pediatrics. 1972 May;49(5):671–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. A., Shaw J. C., Barber A., Golden M. H. Nitrogen metabolism in preterm infants fed human donor breast milk: the possible essentiality of glycine. Pediatr Res. 1981 Nov;15(11):1454–1461. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198111000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaworski A. A. New premature weight chart for hospital use. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1974 Jun;13(6):513–516. doi: 10.1177/000992287401300608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagan B. M., Stanincova V., Felix N. S., Hodgman J., Kalman D. Body composition of premature infants: relation to nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Nov;25(11):1153–1164. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.11.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen D. V., Pearse R. G. Birthweight between 14 and 42 weeks' gestation. Arch Dis Child. 1985 May;60(5):440–446. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.5.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchen W. H., Bajuk B., Lissenden J. V., Yu V. Y. Intrauterine growth charts from 24 to 29 weeks' gestation. Aust Paediatr J. 1981 Dec;17(4):269–272. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1981.tb01956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchen W. H., Robinson H. P., Dickinson A. J. Revised intrauterine growth curves for an Australian hospital population. Aust Paediatr J. 1983 Sep;19(3):157–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1983.tb02082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBCHENCO L. O., HANSMAN C., DRESSLER M., BOYD E. INTRAUTERINE GROWTH AS ESTIMATED FROM LIVEBORN BIRTH-WEIGHT DATA AT 24 TO 42 WEEKS OF GESTATION. Pediatrics. 1963 Nov;32:793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Gore S. M., Cole T. J., Bamford M. F., Dossetor J. F., Barr I., Dicarlo L., Cork S., Lucas P. J. Multicentre trial on feeding low birthweight infants: effects of diet on early growth. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Aug;59(8):722–730. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.8.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunyong V. E., Friedman Z. Myofibrillar protein degradation in premature infants with respiratory distress as assessed by 3-methylhistidine and creatinine excretions. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982 Sep;36(3):485–491. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/36.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martell M., Falkner F., Bertolini L. B., Díaz J. L., Nieto F., Tenzer S. M., Belitzky R. Early postnatal growth evaluation in full-term, preterm and small-for-dates infants. Early Hum Dev. 1978 Feb;1(4):313–323. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(78)90039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orgill A. A., Astbury J., Bajuk B., Yu V. Y. Early development of infants 1000 g or less at birth. Arch Dis Child. 1982 Nov;57(11):823–827. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.11.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson F. E., Yu V. Y., Hawgood S., Adamson T. M., Wilkinson M. H. Computerised nutritional data management in neonatal intensive care. Arch Dis Child. 1983 Sep;58(9):732–736. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.9.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. Y., James B. E., Hendry P. G., MacMahon R. A. Glucose tolerance in very low birthweight infants. Aust Paediatr J. 1979 Sep;15(3):147–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1979.tb01213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. Y., James B., Hendry P., MacMahon R. A. Total parenteral nutrition in very low birthweight infants: a controlled trial. Arch Dis Child. 1979 Sep;54(9):653–661. doi: 10.1136/adc.54.9.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. Y., Jamieson J., Bajuk B. Breast milk feeding in very low birthweight infants. Aust Paediatr J. 1981 Sep;17(3):186–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1981.tb01936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. Y., Orgill A. A., Bajuk B., Astbury J. Survival and 2-year outcome of extremely preterm infants. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1984 Jul;91(7):640–646. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1984.tb04823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. Y., Zhao S. M., Bajuk B. Results of intensive care for 375 very low birthweight infants. Aust Paediatr J. 1982 Sep;18(3):188–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1982.tb02025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



